Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
SQL Server 2016 (13.x) and later - Windows only
The article explains how to use PolyBase on a SQL Server instance to query external data in Azure Blob Storage.
Prerequisites
If you haven't installed PolyBase, see Install PolyBase on Windows. The installation article explains the prerequisites.
SQL Server 2022
In SQL Server 2022 (16.x), configure your external data sources to use new connectors when you connect to Azure Storage. The following table summarizes the change:
| External Data Source | From | To |
|---|---|---|
| Azure Blob Storage | wasb[s] | abs |
| ADLS Gen 2 | abfs[s] | adls |
Configure Azure Blob Storage connectivity
First, configure SQL Server PolyBase to use Azure Blob Storage.
Run sp_configure with
'hadoop connectivity'set to an Azure Blob Storage provider. To find the value for providers, see PolyBase connectivity configuration. By Default, the Hadoop connectivity is set to7.-- Values map to various external data sources. -- Example: value 7 stands for Hortonworks HDP 2.1 to 2.6 on Linux, -- 2.1 to 2.3 on Windows Server, and Azure Blob Storage EXECUTE sp_configure @configname = 'hadoop connectivity', @configvalue = 7; GO RECONFIGURE;Restart SQL Server using services.msc. Restarting SQL Server restarts these services:
- SQL Server PolyBase Data Movement Service
- SQL Server PolyBase Engine
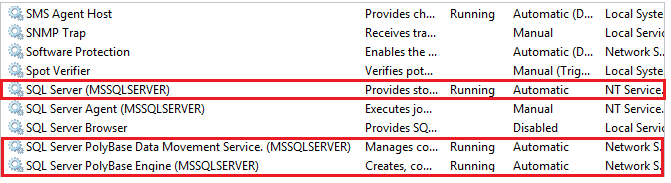
Restart SQL Server using services.msc. Restarting SQL Server restarts these services:
- SQL Server PolyBase Data Movement Service
- SQL Server PolyBase Engine

Configure an external table
To query the data in your Hadoop data source, you must define an external table to use in Transact-SQL queries. The following steps describe how to configure the external table.
Create a database master key (DMK) on the database. The DMK is required to encrypt the credential secret.
CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = '<strong password>';Create a database scoped credential for Azure Blob Storage;
IDENTITYcan be anything as it's not used.-- IDENTITY: any string (this is not used for authentication to Azure storage). -- SECRET: your Azure storage account key. CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL AzureStorageCredential WITH IDENTITY = 'user', SECRET = '<azure_storage_account_key>';Create an external data source with CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE. When you connect to Azure Storage via the
wasb[s]connector, authentication must be done with a storage account key, not with a shared access signature (SAS).-- LOCATION: Azure account storage account name and blob container name. -- CREDENTIAL: The database scoped credential created above. CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE AzureStorage WITH ( TYPE = HADOOP, LOCATION = 'wasbs://<blob_container_name>@<azure_storage_account_name>.blob.core.windows.net', CREDENTIAL = AzureStorageCredential );Create an external file format with CREATE EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT.
-- FORMAT TYPE: Type of format in Hadoop (DELIMITEDTEXT, RCFILE, ORC, PARQUET). CREATE EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT TextFileFormat WITH ( FORMAT_TYPE = DELIMITEDTEXT, FORMAT_OPTIONS (FIELD_TERMINATOR = '|', USE_TYPE_DEFAULT = TRUE) );Create an external table pointing to data stored in Azure storage with CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE. In this example, the external data contains car sensor data;
LOCATIONcan't be/but/Demo/as in this example doesn't need to exist previously.-- LOCATION: path to file or directory that contains the data (relative to HDFS root). CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [dbo].[CarSensor_Data] ( SensorKey INT NOT NULL, CustomerKey INT NOT NULL, GeographyKey INT NULL, Speed FLOAT NOT NULL, YearMeasured INT NOT NULL ) WITH ( DATA_SOURCE = AzureStorage, LOCATION = '/Demo/', FILE_FORMAT = TextFileFormat );Create statistics on an external table.
CREATE STATISTICS StatsForSensors ON CarSensor_Data(CustomerKey, Speed);
Create a database master key (DMK) on the database. The DMK is required to encrypt the credential secret.
CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = '<strong password>';Create a database scoped credential for Azure Blob Storage using a shared access signature (SAS);
IDENTITYcan be anything as it's not used.CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL AzureStorageCredential WITH IDENTITY = 'SHARED ACCESS SIGNATURE', -- Remove ? from the beginning of the SAS token SECRET = '<azure_shared_access_signature>';Create an external data source with CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE. When connecting to the Azure Storage via the WASB[s] connector, authentication with a shared access signature (SAS).
-- LOCATION: Azure account storage account name and blob container name. -- CREDENTIAL: The database scoped credential created above. CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE AzureStorage WITH ( LOCATION = 'wasbs://<blob_container_name>@<azure_storage_account_name>.blob.core.windows.net', CREDENTIAL = AzureStorageCredential );Create an external file format with CREATE EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT.
-- FORMAT TYPE: Type of format in Hadoop (DELIMITEDTEXT, RCFILE, ORC, PARQUET). CREATE EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT TextFileFormat WITH ( FORMAT_TYPE = DELIMITEDTEXT, FORMAT_OPTIONS (FIELD_TERMINATOR = '|', USE_TYPE_DEFAULT = TRUE) );Create an external table pointing to data stored in Azure storage with CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE. In this example, the external data contains car sensor data;
LOCATIONcan't be/but/Demo/as in this example doesn't need to exist previously.-- LOCATION: path to file or directory that contains the data (relative to HDFS root). CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [dbo].[CarSensor_Data] ( SensorKey INT NOT NULL, CustomerKey INT NOT NULL, GeographyKey INT NULL, Speed FLOAT NOT NULL, YearMeasured INT NOT NULL ) WITH ( DATA_SOURCE = AzureStorage, LOCATION = '/Demo/', FILE_FORMAT = TextFileFormat );Create statistics on an external table.
CREATE STATISTICS StatsForSensors ON CarSensor_Data(CustomerKey, Speed);
PolyBase queries
There are three functions that PolyBase is suited for:
- Ad hoc queries against external tables.
- Importing data.
- Exporting data.
The following queries provide example with fictional car sensor data.
Ad hoc queries
The following ad hoc query joins relational with Hadoop data. It selects customers who drive faster than 35 mph, and joins to structured customer data stored in SQL Server with car sensor data stored in Hadoop.
SELECT DISTINCT Insured_Customers.FirstName,
Insured_Customers.LastName,
Insured_Customers.YearlyIncome,
CarSensor_Data.Speed
FROM Insured_Customers,
CarSensor_Data
WHERE Insured_Customers.CustomerKey = CarSensor_Data.CustomerKey
AND CarSensor_Data.Speed > 35
ORDER BY CarSensor_Data.Speed DESC
OPTION (FORCE EXTERNALPUSHDOWN); -- or OPTION (DISABLE EXTERNALPUSHDOWN)
Import data with PolyBase
The following query imports external data into SQL Server. This example imports data for fast drivers into SQL Server to do more in-depth analysis. To improve performance, it uses columnstore technology.
SELECT DISTINCT Insured_Customers.FirstName,
Insured_Customers.LastName,
Insured_Customers.YearlyIncome,
Insured_Customers.MaritalStatus
INTO Fast_Customers
FROM Insured_Customers
INNER JOIN (SELECT *
FROM CarSensor_Data
WHERE Speed > 35
) AS SensorD
ON Insured_Customers.CustomerKey = SensorD.CustomerKey
ORDER BY YearlyIncome;
CREATE CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX CCI_FastCustomers
ON Fast_Customers;
Export data with PolyBase
The following query exports data from SQL Server to Azure Blob Storage. First enable PolyBase export. Then, create an external table for the destination before exporting data to it.
-- Enable INSERT into external table
EXECUTE sp_configure 'allow polybase export', 1;
RECONFIGURE;
GO
-- Create an external table.
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [dbo].[FastCustomers2009]
(
FirstName CHAR (25) NOT NULL,
LastName CHAR (25) NOT NULL,
YearlyIncome FLOAT NULL,
MaritalStatus CHAR (1) NOT NULL
)
WITH (
DATA_SOURCE = HadoopHDP2,
LOCATION = '/old_data/2009/customerdata',
FILE_FORMAT = TextFileFormat,
REJECT_TYPE = VALUE,
REJECT_VALUE = 0
);
-- Export data: Move old data to Hadoop while keeping it query-able via an external table.
INSERT INTO dbo.FastCustomer2009
SELECT T.*
FROM Insured_Customers AS T1
INNER JOIN CarSensor_Data AS T2
ON (T1.CustomerKey = T2.CustomerKey)
WHERE T2.YearMeasured = 2009
AND T2.Speed > 40;
PolyBase export with this method might create multiple files.
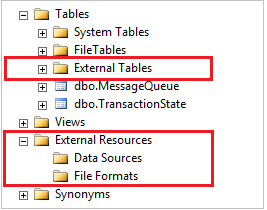
View PolyBase objects in SSMS
In SSMS, external tables are displayed in a separate folder External Tables. External data sources and external file formats are in subfolders under External Resources.