Resource Governor
Applies to:
SQL Server
Azure SQL Managed Instance
SQL Server Resource Governor is a feature that you can use to manage SQL Server workload and system resource consumption. Resource Governor enables you to specify limits on the amount of CPU, physical I/O, and memory that incoming application requests can use.
Note
While Azure SQL Database leverages Resource Governor (among other techniques) to manage resources, user configuration of custom resource pools and workload groups in Azure SQL Database is not supported. Azure Synapse Analytics has a different implementation of similar Resource Governor behavior via the Workload Classification feature.
Benefits of Resource Governor
Resource Governor enables you to manage SQL Server workloads and resources by specifying limits on resource consumption by incoming requests. In the Resource Governor context, workload is a set of similarly sized queries or requests that can, and should be, treated as a single entity. This is not a requirement, but the more uniform the resource usage pattern of a workload is, the more benefit you are likely to derive from Resource Governor. Resource limits can be reconfigured in real time with minimal impact on workloads that are executing.
In an environment where multiple distinct workloads are present on the same server, Resource Governor enables you to differentiate these workloads and allocate shared resources as they are requested, based on the limits that you specify. These resources are CPU, physical I/O, and memory.
By using Resource Governor, you can:
Provide multitenancy and resource isolation on single instances of SQL Server that serve multiple client workloads. That is, you can divide the available resources on a server among the workloads and minimize the problems that can occur when workloads compete for resources.
Provide predictable performance and support SLAs for workload tenants in a multi-workload and multi-user environment.
Isolate and limit runaway queries or throttle I/O resources for operations such as DBCC CHECKDB that can saturate the I/O subsystem and negatively impact other workloads.
Add fine-grained resource tracking for resource usage chargebacks and provide predictable billing to the consumers of the server resources.
Resource Governor Constraints
This release of Resource Governor has the following constraints:
Resource management is limited to the SQL Server Database Engine. Resource Governor cannot be used for Analysis Services, Integration Services, and Reporting Services.
There is no workload monitoring or workload management between SQL Server instances.
Resource Governor can manage OLTP workloads but these types of queries, which are typically very short in duration, are not always on the CPU long enough to apply bandwidth controls. This may skew in the statistics returned for CPU usage percent.
The ability to govern physical I/O only applies to user operations and not system tasks. System tasks include write operations to the transaction log and Lazy Writer I/O operations. The Resource Governor applies primarily to user read operations because most write operations are typically performed by system tasks.
You cannot set I/O thresholds on the internal resource pool.
Resource Concepts
The following three concepts are fundamental to understanding and using Resource Governor:
Resource pools. A resource pool, represents the physical resources of the server. You can think of a pool as a virtual SQL Server instance inside of a SQL Server instance. Two resource pools (internal and default) are created when SQL Server is installed. Resource Governor also supports user-defined resource pools. For more information, see Resource Governor Resource Pool.
Workload groups. A workload group serves as a container for session requests that have similar classification criteria. A workload allows for aggregate monitoring of the sessions, and defines policies for the sessions. Each workload group is in a resource pool. Two workload groups (internal and default) are created and mapped to their corresponding resource pools when SQL Server is installed. Resource Governor also supports user-defined workload groups. For more information see, Resource Governor Workload Group.
Classification. The Classification process assigns incoming sessions to a workload group based on the characteristics of the session. You can tailor the classification logic by writing a user-defined function, called a classifier function. Resource Governor also supports a classifier user-defined function for implementing classification rules. For more information, see Resource Governor Classifier Function.
Note
Resource Governor does not impose any controls on a dedicated administrator connection (DAC). There is no need to classify DAC queries, which run in the internal workload group and resource pool.
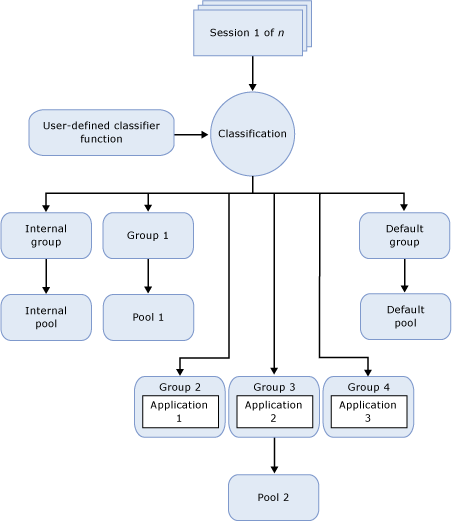
In the context of Resource Governor, you can treat the preceding concepts as components. The following illustration shows these components and their relationship with each other as they exist in the database engine environment. From a processing perspective, the simplified flow is as follows:
There is an incoming connection for a session (Session 1 of n).
The session is classified (Classification).
The session workload is routed to a workload group, for example, Group 4.
The workload group uses the resource pool it is associated with, for example, Pool 2.
The resource pool provides and limits the resources required by the application, for example, Application 3.
Resource Governor Tasks
| Task Description | Topic |
|---|---|
| Describes how to enable Resource Governor. | Enable Resource Governor |
| Describes how to disable Resource Governor. | Disable Resource Governor |
| Describes how to create, alter, and drop a resource pool. | Resource Governor Resource Pool |
| Describes how to create, alter, move, and drop a workload group. | Resource Governor Workload Group |
| Describes how to create and test a classifier user-defined function. | Resource Governor Classifier Function |
| Describes how to configure Resource Governor using a template. | Configure Resource Governor Using a Template |
| Describes how to view Resource Governor properties. | View Resource Governor Properties |
See Also
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for