Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
SQL Server 2022 (16.x) and later.
This article describes how to authenticate with Microsoft Entra ID without setting up Azure Arc for your on-premises SQL Server 2022 and later versions. Microsoft Entra authentication is a cloud-based identity management service that provides secure access to SQL Server databases. This tutorial guides you through the process of setting up Microsoft Entra authentication for SQL Server on Windows without Azure Arc.
Note
Microsoft Entra ID was previously known as Azure Active Directory (Azure AD).
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Add a certificate for SQL Server.
- Install adal.dll used for connecting to SQL Server.
- Create and register a Microsoft Entra ID application.
- Grant application permissions.
- Upload the certificate to the application.
- Add registry values to enable Microsoft Entra authentication for SQL Server.
Prerequisites
- An on-premises SQL Server 2022 or later version.
- An active Microsoft Entra ID tenant.
- This setup uses an application registration to associate SQL Server with Microsoft Entra ID. Follow the guide to register an application in Microsoft Entra ID.
- Verify that the SQL Server has network connectivity to Azure, specifically to the following Microsoft Entra ID service and addresses:
- login.windows.net.
- login.microsoftonline.com.
- graph.microsoft.com.
- graph.windows.net.
- database.windows.net.
- The full list of IP addresses and URLs aren't needed, but can be found in the article, Microsoft 365 URLs and IP address ranges.
Obtain a certificate
- Obtain a certificate to use for the SQL Server and import it into the computer certificate store. We recommend a CA signed certificate.
Use a unique CN name for the certificate that doesn't match any certificates installed in the certificate store.
Install the certificate in the computer certificate store. For more information, see Import the certificate into the local computer store.
Add
Readpermissions for the SQL Server service account on the certificate.
Install adal.dll
Install adal.dll for SQL Server. This library is needed for connecting to your SQL Server with Microsoft Entra authentication. You can get adal.dll from the latest Microsoft OLE DB Driver for SQL Server install.
After installing the Microsoft OLE DB Driver for SQL Server, make sure that adal.dll is in the folder
C:\windows\system32.You should also have the registry key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\MSADALSQL\TargetDirwith the valueC:\windows\system32\adal.dll. If it doesn't exist, create it.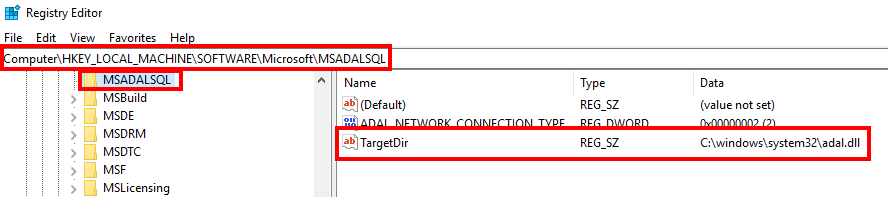
For more information on Windows registry, see Windows registry information for advanced users.
Create and register a Microsoft Entra ID application
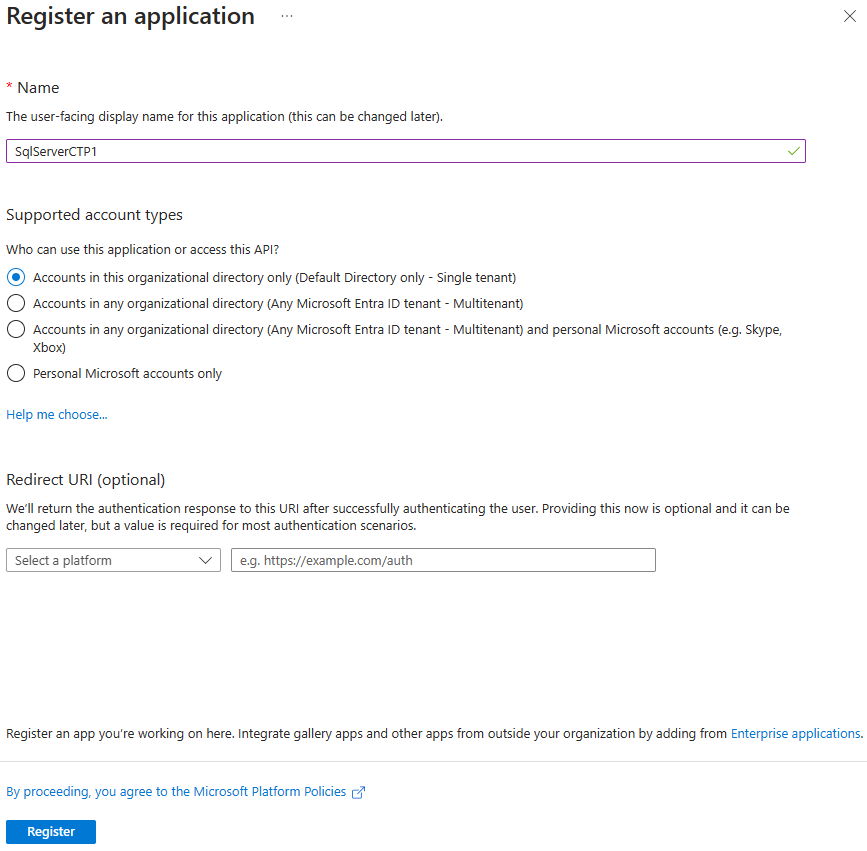
- Go to the Azure portal, select Microsoft Entra ID > App Registrations > New Registration.
- Specify a name - The example in this article uses SQLServer.
- Select Supported account types and use Accounts in this organization directory only
- Don't set a redirect URI
- Select Register
See the application registration below:
Grant application permissions
Select the newly created application, and on the left side menu, select API Permissions.
Select Add a permission > Microsoft Graph > Application permissions
- Check Directory.Read.All
- Select Add permissions
Or,
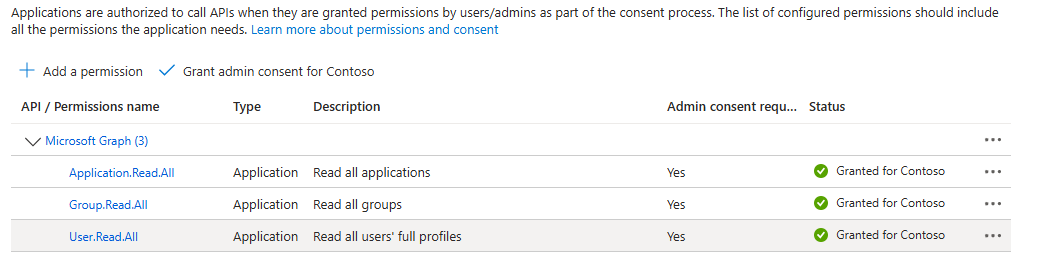
Select Add a permission > Microsoft Graph > Application permissions
Check Application.Read.All
Check Group.Read.All
Check User.Read.All
Select Add permissions
Select Grant admin consent
Note
To grant Admin consent to the permissions above, your Microsoft Entra account requires the Privileged Role Administrator role or higher permissions.
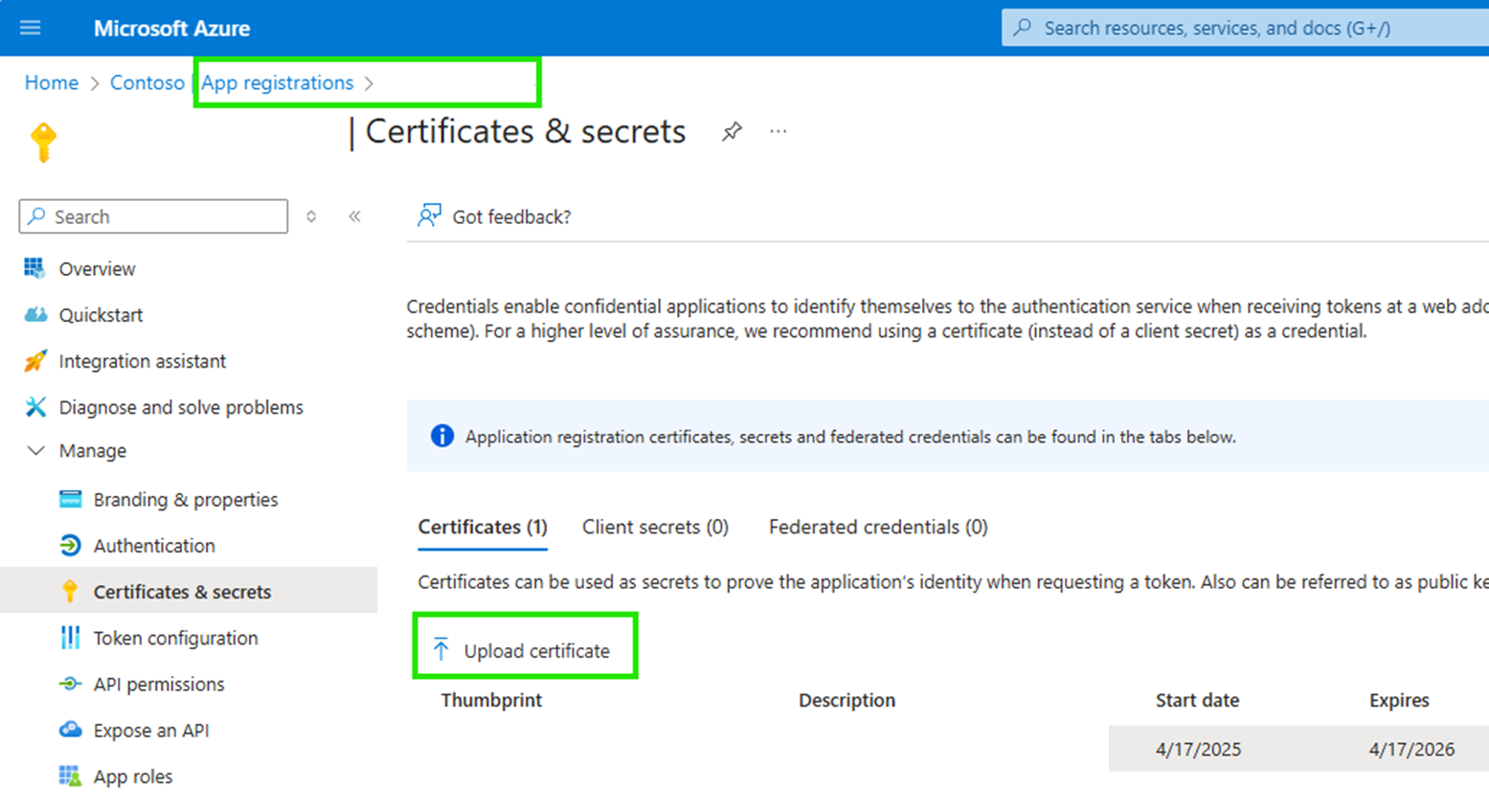
Upload the certificate
Upload the certificate you created in the section Obtain a certificate in the .cer or .pem format to the application registration in the Azure portal.
Add registry values to enable Microsoft Entra authentication for SQL Server
Update the registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL<version-number>.<instance-name>\MSSQLServer\FederatedAuthentication with the following values to enable Microsoft Entra authentication for SQL Server. An example of the registry key path for SQL Server 2022 is HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL16.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQLServer\FederatedAuthentication.
Warning
Serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly by using Registry Editor or by using another method. These problems might require that you reinstall the operating system. Microsoft can't guarantee that these problems can be solved. Modify the registry at your own risk.
- If the
FederatedAuthenticationkey doesn't exist, create it with all of the following values. - The first five entries listed need to be updated with the values from the application you created in the previous section. The rest of the entries are default values.
- The
<sql-server-certificate-name>is the name of the certificate you created in the section Obtain a certificate and uploaded to Azure. - The
<application-client-id>is the Application (client) ID from the application you created in the section Create and register a Microsoft Entra ID application. For more information on finding the client ID, see Client ID. - The
<tenant-id>is the tenant ID from your Azure tenant. You can find the tenant ID in the Azure portal under Microsoft Entra ID > Overview.
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL<version-number>.<instance-name>\MSSQLServer\FederatedAuthentication]
"AADCertSubjectName"="<sql-server-certificate-name>"
"AADTenantSpecificSQLServicePrincipalCertSubjectName"="<sql-server-certificate-name>"
"ClientId"="<application-client-id>"
"AADTenantSpecificSQLServicePrincipalClientId"="<application-client-id>"
"PrimaryAADTenant"="<tenant-id>"
"AADChannelMaxBufferedMessageSize"="200000"
"AADGraphEndPoint"="graph.windows.net"
"AADGroupLookupMaxRetryAttempts"="10"
"AADGroupLookupMaxRetryDuration"="30000"
"AADGroupLookupRetryInitialBackoff"="100"
"AuthenticationEndpoint"="login.microsoftonline.com"
"CacheMaxSize"="300"
"FederationMetadataEndpoint"="login.windows.net"
"GraphAPIEndpoint"="graph.windows.net"
"IssuerURL"="https://sts.windows.net/"
"MsGraphEndPoint"="graph.microsoft.com"
"OnBehalfOfAuthority"="https://login.windows.net/"
"SendX5c"="false"
"ServicePrincipalName"="https://database.windows.net/"
"ServicePrincipalNameForArcadia"="https://sql.azuresynapse.net"
"ServicePrincipalNameForArcadiaDogfood"="https://sql.azuresynapse-dogfood.net"
"ServicePrincipalNameNoSlash"="https://database.windows.net"
"STSURL"="https://login.windows.net/"
"ClientCertBlackList"=""
For more information on Windows registry, including backing up, editing, and restoring registry keys, see Windows registry information for advanced users.
Testing authentication
After setting up the server and editing the registry values, Microsoft Entra authentication should be functional. Test the setup by creating logins using the following T-SQL commands:
CREATE LOGIN [<admin@domain.com>] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER
Common issues
You might see the following error:
Keyset does not exist (AdalDll) with error code: 21
This error could be due to permission issues on the certificate. Make sure that the SQL Server service account has Read permissions on the certificate. If the issue persists, make sure that the certificate has a unique CN name that doesn't match any other certificates in the certificate store.