Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
SQL Server
Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Managed Instance
Azure Synapse Analytics
Analytics Platform System (PDW)
SQL analytics endpoint in Microsoft Fabric
Warehouse in Microsoft Fabric
SQL database in Microsoft Fabric
Every SQL Server securable has associated permissions that can be granted to a principal. Permissions in the Database Engine are managed at the server level assigned to logins and server roles, and at the database level assigned to database users and database roles. The model for Azure SQL Database has the same system for the database permissions, but the server level permissions aren't available. This article contains the complete list of permissions. For a typical implementation of the permissions, see Get started with Database Engine permissions.
The total number of permissions for SQL Server 2022 (16.x) is 292. Azure SQL Database exposes 292 permissions. Most permissions apply to all platforms, but some don't. For example, most server level permissions can't be granted on Azure SQL Database, and a few permissions only make sense on Azure SQL Database. New permissions are being introduced gradually with new releases. SQL Server 2019 (15.x) exposes 248 permissions.SQL Server 2017 (14.x) exposed 238 permissions. SQL Server 2016 (13.x) exposed 230 permissions. SQL Server 2014 (12.x) exposed 219 permissions. SQL Server 2012 (11.x) exposed 214 permissions. SQL Server 2008 R2 (10.50.x) exposed 195 permissions. The sys.fn_builtin_permissions article specifies which permissions are new in recent versions.
In SQL database in Microsoft Fabric, only database-level users and roles are supported. Server-level logins, roles, and the sa account aren't available. In SQL database in Microsoft Fabric, Microsoft Entra ID for database users is the only supported authentication method. For more information, see Authorization in SQL database in Microsoft Fabric.
Once you understand the permissions required, you can apply server level permissions to logins or server roles, and database level permissions to users or database roles, by using the GRANT, REVOKE, and DENY statements. For example:
GRANT SELECT ON SCHEMA::HumanResources TO role_HumanResourcesDept;
REVOKE SELECT ON SCHEMA::HumanResources TO role_HumanResourcesDept;
For tips on planning a permissions system, see Get started with Database Engine permissions.
Permissions naming conventions
The following describes the general conventions that are followed for naming permissions:
CONTROL
Confers ownership-like capabilities on the grantee. The grantee effectively has all defined permissions on the securable. A principal that has been granted CONTROL can also grant permissions on the securable. Because the SQL Server security model is hierarchical, CONTROL at a particular scope implicitly includes CONTROL on all the securables under that scope. For example, CONTROL on a database implies all permissions on the database, all permissions on all assemblies in the database, all permissions on all schemas in the database, and all permissions on objects within all schemas within the database.
ALTER
Confers the ability to change the properties, except ownership, of a particular securable. When granted on a scope, ALTER also bestows the ability to alter, create, or drop any securable that is contained within that scope. For example, ALTER permission on a schema includes the ability to create, alter, and drop objects from the schema.
ALTER ANY <Server Securable>, where Server Securable can be any server securable.
Confers the ability to create, alter, or drop individual instances of the Server Securable. For example, ALTER ANY LOGIN confers the ability to create, alter, or drop any login in the instance.
ALTER ANY <Database Securable>, where Database Securable can be any securable at the database level.
Confers the ability to CREATE, ALTER, or DROP individual instances of the Database Securable. For example, ALTER ANY SCHEMA confers the ability to create, alter, or drop any schema in the database.
TAKE OWNERSHIP
Enables the grantee to take ownership of the securable on which it's granted.
IMPERSONATE <Login>
Enables the grantee to impersonate the login.
IMPERSONATE <User>
Enables the grantee to impersonate the user.
CREATE <Server Securable>
Confers to the grantee the ability to create the Server Securable.
CREATE <Database Securable>
Confers to the grantee the ability to create the Database Securable.
CREATE <Schema-contained Securable>
Confers the ability to create the schema-contained securable. However, ALTER permission on the schema is required to create the securable in a particular schema.
VIEW DEFINITION
Enables the grantee to access metadata.
REFERENCES
The REFERENCES permission on a table is needed to create a FOREIGN KEY constraint that references that table.
The REFERENCES permission is needed on an object to create a FUNCTION or VIEW with the
WITH SCHEMABINDINGclause that references that object.
Chart of SQL Server permissions
The following image shows the permissions and their relationships to each other. Some of the higher level permissions (such as CONTROL SERVER) are listed many times. In this article, the poster is far too small to read. You can download the full-sized Database Engine Permissions Poster in PDF format.
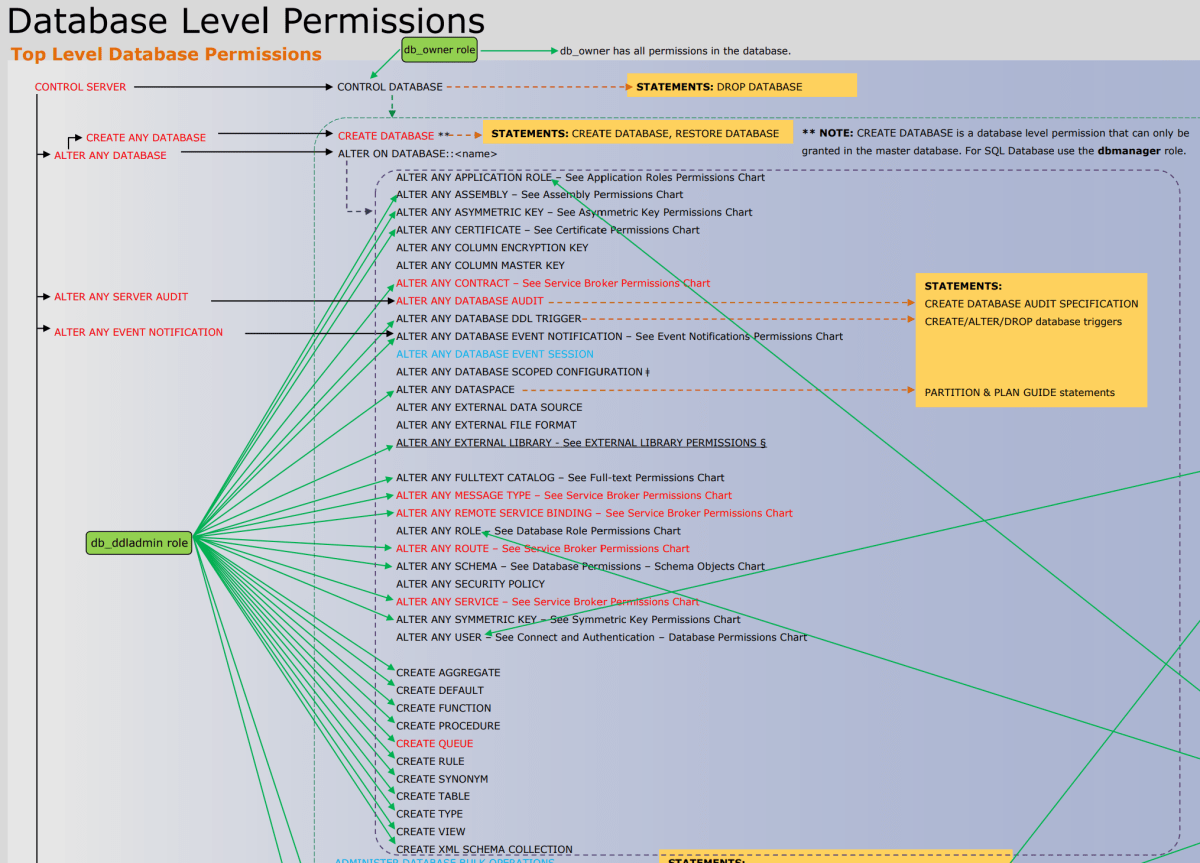
Permissions applicable to specific securables
The following table lists major classes of permissions and the kinds of securables to which they might be applied.
| Permission | Applies to |
|---|---|
| ALTER | All classes of objects except TYPE. |
| CONTROL | All classes of objects: AGGREGATE, APPLICATION ROLE, ASSEMBLY, ASYMMETRIC KEY, AVAILABILITY GROUP, CERTIFICATE, CONTRACT, CREDENTIALS, DATABASE, DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL, DEFAULT, ENDPOINT, FULLTEXT CATALOG, FULLTEXT STOPLIST, FUNCTION, LOGIN, MESSAGE TYPE, PROCEDURE, QUEUE, REMOTE SERVICE BINDING, ROLE, ROUTE, RULE, SCHEMA, SEARCH PROPERTY LIST, SERVER, SERVER ROLE, SERVICE, SYMMETRIC KEY, SYNONYM, TABLE, TYPE, USER, VIEW, and XML SCHEMA COLLECTION |
| DELETE | All classes of objects except DATABASE SCOPED CONFIGURATION, SERVER, and TYPE. |
| EXECUTE | CLR types, external scripts, procedures (Transact-SQL and CLR), scalar and aggregate functions (Transact-SQL and CLR), and synonyms |
| IMPERSONATE | Logins and users |
| INSERT | Synonyms, tables and columns, views and columns. Permission can be granted at the database, schema, or object level. |
| RECEIVE | Service Broker queues |
| REFERENCES | AGGREGATE, ASSEMBLY, ASYMMETRIC KEY, CERTIFICATE, CONTRACT, CREDENTIAL (applies to SQL Server 2022 (16.x) and later), DATABASE, DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL, FULLTEXT CATALOG, FULLTEXT STOPLIST, FUNCTION, MESSAGE TYPE, PROCEDURE, QUEUE, RULE, SCHEMA, SEARCH PROPERTY LIST, SEQUENCE OBJECT, SYMMETRIC KEY, TABLE, TYPE, VIEW, and XML SCHEMA COLLECTION |
| SELECT | Synonyms, tables and columns, views and columns. Permission can be granted at the database, schema, or object level. |
| TAKE OWNERSHIP | All classes of objects except DATABASE SCOPED CONFIGURATION, LOGIN, SERVER, and USER. |
| UPDATE | Synonyms, tables and columns, views and columns. Permission can be granted at the database, schema, or object level. |
| VIEW CHANGE TRACKING | Schemas and tables |
| VIEW DEFINITION | All classes of objects except DATABASE SCOPED CONFIGURATION, and SERVER. |
Caution
The default permissions that are granted to system objects at the time of setup are carefully evaluated against possible threats and need not be altered as part of hardening the SQL Server installation. Any changes to the permissions on the system objects could limit or break the functionality and could potentially leave your SQL Server installation in an unsupported state.
SQL Server permissions
The following table provides a complete list of SQL Server permissions. Azure SQL Database permissions are only available for base securables that are supported. Server level permissions can't be granted in Azure SQL Database, however in some cases database permissions are available instead.
| Base securable | Granular permissions on base securable | Permission type code | Securable that contains base securable | Permission on container securable that implies granular permission on base securable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| APPLICATION ROLE | ALTER | AL | DATABASE | ALTER ANY APPLICATION ROLE |
| APPLICATION ROLE | CONTROL | CL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| APPLICATION ROLE | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION |
| ASSEMBLY | ALTER | AL | DATABASE | ALTER ANY ASSEMBLY |
| ASSEMBLY | CONTROL | CL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| ASSEMBLY | REFERENCES | RF | DATABASE | REFERENCES |
| ASSEMBLY | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| ASSEMBLY | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION |
| ASYMMETRIC KEY | ALTER | AL | DATABASE | ALTER ANY ASYMMETRIC KEY |
| ASYMMETRIC KEY | CONTROL | CL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| ASYMMETRIC KEY | REFERENCES | RF | DATABASE | REFERENCES |
| ASYMMETRIC KEY | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| ASYMMETRIC KEY | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION |
| AVAILABILITY GROUP | ALTER | AL | SERVER | ALTER ANY AVAILABILITY GROUP |
| AVAILABILITY GROUP | CONTROL | CL | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| AVAILABILITY GROUP | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| AVAILABILITY GROUP | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | SERVER | VIEW ANY DEFINITION |
| CERTIFICATE | ALTER | AL | DATABASE | ALTER ANY CERTIFICATE |
| CERTIFICATE | CONTROL | CL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| CERTIFICATE | REFERENCES | RF | DATABASE | REFERENCES |
| CERTIFICATE | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| CERTIFICATE | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION |
| CONTRACT | ALTER | AL | DATABASE | ALTER ANY CONTRACT |
| CONTRACT | CONTROL | CL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| CONTRACT | REFERENCES | RF | DATABASE | REFERENCES |
| CONTRACT | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| CONTRACT | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION |
| CREDENTIAL | CONTROL | CL | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| CREDENTIAL | REFERENCES | RF | SERVER | ALTER ANY CREDENTIAL |
| DATABASE | ADMINISTER DATABASE BULK OPERATIONS | DABO | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER | AL | SERVER | ALTER ANY DATABASE |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY APPLICATION ROLE | ALAR | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY ASSEMBLY | ALAS | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY ASYMMETRIC KEY | ALAK | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY CERTIFICATE | ALCF | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY COLUMN ENCRYPTION KEY | ALCK Applies to SQL Server (SQL Server 2016 (13.x) through current), Azure SQL Database. |
SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY COLUMN MASTER KEY | ALCM Applies to SQL Server (SQL Server 2016 (13.x) through current), Azure SQL Database. |
SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY CONTRACT | ALSC | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY DATABASE AUDIT | ALDA | SERVER | ALTER ANY SERVER AUDIT |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY DATABASE DDL TRIGGER | ALTG | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT NOTIFICATION | ALED | SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT NOTIFICATION |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION | AADS | SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION ADD EVENT | LDAE | SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION ADD EVENT |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION ADD TARGET | LDAT | SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION ADD TARGET |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION DISABLE | DDES | SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION DISABLE |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION DROP EVENT | LDDE | SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION DROP EVENT |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION DROP TARGET | LDDT | SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION DROP TARGET |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION ENABLE | EDES | SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION ENABLE |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION OPTION | LDSO | SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION OPTION |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY DATABASE SCOPED CONFIGURATION | ALDC Applies to SQL Server (SQL Server 2016 (13.x) through current), Azure SQL Database. |
SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY DATASPACE | ALDS | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE | AEDS | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT | AEFF | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY EXTERNAL JOB | AESJ | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY EXTERNAL LANGUAGE | ALLA | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY EXTERNAL LIBRARY | ALEL | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY EXTERNAL STREAM | AEST | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY FULLTEXT CATALOG | ALFT | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY MASK | AAMK Applies to SQL Server (SQL Server 2016 (13.x) through current), Azure SQL Database. |
SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY MESSAGE TYPE | ALMT | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY REMOTE SERVICE BINDING | ALSB | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY ROLE | ALRL | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY ROUTE | ALRT | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY SCHEMA | ALSM | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY SECURITY POLICY | ALSP Applies to SQL Server (SQL Server 2016 (13.x) through current), Azure SQL Database. |
SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY SENSITIVITY CLASSIFICATION | AASC Applies to SQL Server (SQL Server 2019 (15.x) through current), Azure SQL Database. |
SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY SERVICE | ALSV | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY SYMMETRIC KEY | ALSK | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER ANY USER | ALUS | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | ALTER LEDGER | ALR | SERVER | CONTROL |
| DATABASE | ALTER LEDGER CONFIGURATION | ALC | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | AUTHENTICATE | AUTH | SERVER | AUTHENTICATE SERVER |
| DATABASE | BACKUP DATABASE | BADB | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | BACKUP LOG | BALO | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CHECKPOINT | CP | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CONNECT | CO | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CONNECT REPLICATION | CORP | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CONTROL | CL | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE AGGREGATE | CRAG | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION | CRDS | SERVER | CREATE ANY EVENT SESSION |
| DATABASE | CREATE ASSEMBLY | CRAS | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE ASYMMETRIC KEY | CRAK | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE CERTIFICATE | CRCF | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE CONTRACT | CRSC | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE DATABASE | CRDB | SERVER | CREATE ANY DATABASE |
| DATABASE | CREATE DATABASE DDL EVENT NOTIFICATION | CRED | SERVER | CREATE DDL EVENT NOTIFICATION |
| DATABASE | CREATE DEFAULT | CRDF | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE EXTERNAL LANGUAGE | CRLA | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE EXTERNAL LIBRARY | CREL | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE FULLTEXT CATALOG | CRFT | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE FUNCTION | CRFN | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE MESSAGE TYPE | CRMT | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE PROCEDURE | CRPR | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE QUEUE | CRQU | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE REMOTE SERVICE BINDING | CRSB | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE ROLE | CRRL | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE ROUTE | CRRT | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE RULE | CRRU | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE SCHEMA | CRSM | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE SERVICE | CRSV | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE SYMMETRIC KEY | CRSK | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE SYNONYM | CRSN | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE TABLE | CRTB | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE TYPE | CRTY | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE USER | CUSR | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE VIEW | CRVW | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | CREATE XML SCHEMA COLLECTION | CRXS | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | DELETE | DL | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | DROP ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION | DRDS | SERVER | DROP ANY EVENT SESSION |
| DATABASE | ENABLE LEDGER | EL | SERVER | CONTROL |
| DATABASE | EXECUTE | EX | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | EXECUTE ANY EXTERNAL ENDPOINT | EAEE | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | EXECUTE ANY EXTERNAL SCRIPT | EAES Applies to SQL Server (SQL Server 2016 (13.x) through current). |
SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | INSERT | IN | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | KILL DATABASE CONNECTION | KIDC Only applies to Azure SQL Database. Use ALTER ANY CONNECTION in SQL Server. |
SERVER | ALTER ANY CONNECTION |
| DATABASE | REFERENCES | RF | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | SELECT | SL | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | SHOWPLAN | SPLN | SERVER | ALTER TRACE |
| DATABASE | SUBSCRIBE QUERY NOTIFICATIONS | SUQN | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | UNMASK | UMSK Applies to SQL Server (SQL Server 2016 (13.x) through current), Azure SQL Database. |
SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | UPDATE | UP | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | VIEW ANY COLUMN ENCRYPTION KEY DEFINITION | VWCK Applies to SQL Server (SQL Server 2016 (13.x) through current), Azure SQL Database. |
SERVER | VIEW SERVER STATE |
| DATABASE | VIEW ANY COLUMN MASTER KEY DEFINITION | VWCM Applies to SQL Server (SQL Server 2016 (13.x) through current), Azure SQL Database. |
SERVER | VIEW SERVER STATE |
| DATABASE | VIEW ANY SENSITIVITY CLASSIFICATION | VASC | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | VIEW CRYPTOGRAPHICALLY SECURED DEFINITION | VCD | SERVER | VIEW ANY CRYPTOGRAPHICALLY SECURED DEFINITION |
| DATABASE | VIEW DATABASE PERFORMANCE STATE | VDP | SERVER | VIEW SERVER PERFORMANCE STATE |
| DATABASE | VIEW DATABASE SECURITY AUDIT | VDSA | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| DATABASE | VIEW DATABASE SECURITY STATE | VDS | SERVER | VIEW SERVER SECURITY STATE |
| DATABASE | VIEW DATABASE STATE | VWDS | SERVER | VIEW SERVER STATE |
| DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | SERVER | VIEW ANY DEFINITION |
| DATABASE | VIEW LEDGER CONTENT | VLC | SERVER | CONTROL |
| DATABASE | VIEW SECURITY DEFINITION | VWS | SERVER | VIEW ANY SECURITY DEFINITION |
| DATABASE | VIEW PERFORMANCE DEFINITION | VWP | SERVER | VIEW ANY PERFORMANCE DEFINITION |
| DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL | ALTER | AL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL | CONTROL | CL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL | REFERENCES | RF | DATABASE | REFERENCES |
| DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION |
| ENDPOINT | ALTER | AL | SERVER | ALTER ANY ENDPOINT |
| ENDPOINT | CONNECT | CO | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| ENDPOINT | CONTROL | CL | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| ENDPOINT | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| ENDPOINT | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | SERVER | VIEW ANY DEFINITION |
| FULLTEXT CATALOG | ALTER | AL | DATABASE | ALTER ANY FULLTEXT CATALOG |
| FULLTEXT CATALOG | CONTROL | CL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| FULLTEXT CATALOG | REFERENCES | RF | DATABASE | REFERENCES |
| FULLTEXT CATALOG | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| FULLTEXT CATALOG | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION |
| FULLTEXT STOPLIST | ALTER | AL | DATABASE | ALTER ANY FULLTEXT CATALOG |
| FULLTEXT STOPLIST | CONTROL | CL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| FULLTEXT STOPLIST | REFERENCES | RF | DATABASE | REFERENCES |
| FULLTEXT STOPLIST | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| FULLTEXT STOPLIST | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION |
| LOGIN | ALTER | AL | SERVER | ALTER ANY LOGIN |
| LOGIN | CONTROL | CL | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| LOGIN | IMPERSONATE | IM | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| LOGIN | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | SERVER | VIEW ANY DEFINITION |
| MESSAGE TYPE | ALTER | AL | DATABASE | ALTER ANY MESSAGE TYPE |
| MESSAGE TYPE | CONTROL | CL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| MESSAGE TYPE | REFERENCES | RF | DATABASE | REFERENCES |
| MESSAGE TYPE | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| MESSAGE TYPE | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION |
| OBJECT | ALTER | AL | SCHEMA | ALTER |
| OBJECT | CONTROL | CL | SCHEMA | CONTROL |
| OBJECT | DELETE | DL | SCHEMA | DELETE |
| OBJECT | EXECUTE | EX | SCHEMA | EXECUTE |
| OBJECT | INSERT | IN | SCHEMA | INSERT |
| OBJECT | RECEIVE | RC | SCHEMA | CONTROL |
| OBJECT | REFERENCES | RF | SCHEMA | REFERENCES |
| OBJECT | SELECT | SL | SCHEMA | SELECT |
| OBJECT | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | SCHEMA | CONTROL |
| OBJECT | UNMASK | UMSK | SCHEMA | UNMASK |
| OBJECT | UPDATE | UP | SCHEMA | UPDATE |
| OBJECT | VIEW CHANGE TRACKING | VWCT | SCHEMA | VIEW CHANGE TRACKING |
| OBJECT | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | SCHEMA | VIEW DEFINITION |
| REMOTE SERVICE BINDING | ALTER | AL | DATABASE | ALTER ANY REMOTE SERVICE BINDING |
| REMOTE SERVICE BINDING | CONTROL | CL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| REMOTE SERVICE BINDING | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| REMOTE SERVICE BINDING | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION |
| ROLE | ALTER | AL | DATABASE | ALTER ANY ROLE |
| ROLE | CONTROL | CL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| ROLE | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| ROLE | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION |
| ROUTE | ALTER | AL | DATABASE | ALTER ANY ROUTE |
| ROUTE | CONTROL | CL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| ROUTE | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| ROUTE | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION |
| SCHEMA | ALTER | AL | DATABASE | ALTER ANY SCHEMA |
| SCHEMA | CONTROL | CL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| SCHEMA | CREATE SEQUENCE | CRSO | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| SCHEMA | DELETE | DL | DATABASE | DELETE |
| SCHEMA | EXECUTE | EX | DATABASE | EXECUTE |
| SCHEMA | INSERT | IN | DATABASE | INSERT |
| SCHEMA | REFERENCES | RF | DATABASE | REFERENCES |
| SCHEMA | SELECT | SL | DATABASE | SELECT |
| SCHEMA | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| SCHEMA | UNMASK | UMSK | DATABASE | UNMASK |
| SCHEMA | UPDATE | UP | DATABASE | UPDATE |
| SCHEMA | VIEW CHANGE TRACKING | VWCT | DATABASE | VIEW CHANGE TRACKING |
| SCHEMA | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION |
| SEARCH PROPERTY LIST | ALTER | AL | SERVER | ALTER ANY FULLTEXT CATALOG |
| SEARCH PROPERTY LIST | CONTROL | CL | SERVER | CONTROL |
| SEARCH PROPERTY LIST | REFERENCES | RF | SERVER | REFERENCES |
| SEARCH PROPERTY LIST | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | SERVER | CONTROL |
| SEARCH PROPERTY LIST | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | SERVER | VIEW DEFINITION |
| SERVER | ADMINISTER BULK OPERATIONS | ADBO | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY AVAILABILITY GROUP | ALAG | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY CONNECTION | ALCO | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY CREDENTIAL | ALCD | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY DATABASE | ALDB | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY ENDPOINT | ALHE | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT NOTIFICATION | ALES | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION | AAES | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION ADD EVENT | LSAE | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION ADD TARGET | LSAT | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION DISABLE | DES | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION DROP EVENT | LSDE | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION DROP TARGET | LSDT | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION ENABLE | EES | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION OPTION | LESO | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY LINKED SERVER | ALLS | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY LOGIN | ALLG | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY SERVER AUDIT | ALAA | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER ANY SERVER ROLE | ALSR | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER RESOURCES | ALRS | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER SERVER STATE | ALSS | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER SETTINGS | ALST | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | ALTER TRACE | ALTR | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | AUTHENTICATE SERVER | AUTH | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | CONNECT ANY DATABASE | CADB | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | CONNECT SQL | COSQ | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | CONTROL SERVER | CL | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | CREATE ANY DATABASE | CRDB | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | CREATE AVAILABILITY GROUP | CRAC | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | CREATE DDL EVENT NOTIFICATION | CRDE | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | CREATE ENDPOINT | CRHE | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | CREATE SERVER ROLE | CRSR | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | CREATE TRACE EVENT NOTIFICATION | CRTE | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | EXTERNAL ACCESS ASSEMBLY | XA | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | IMPERSONATE ANY LOGIN | IAL | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | SELECT ALL USER SECURABLES | SUS | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | SHUTDOWN | SHDN | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | UNSAFE ASSEMBLY | XU | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | VIEW ANY DATABASE | VWDB | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | VIEW ANY DEFINITION | VWAD | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER | VIEW SERVER STATE | VWSS | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| SERVER ROLE | ALTER | AL | SERVER | ALTER ANY SERVER ROLE |
| SERVER ROLE | CONTROL | CL | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| SERVER ROLE | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | SERVER | CONTROL SERVER |
| SERVER ROLE | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | SERVER | VIEW ANY DEFINITION |
| SERVICE | ALTER | AL | DATABASE | ALTER ANY SERVICE |
| SERVICE | CONTROL | CL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| SERVICE | SEND | SN | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| SERVICE | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| SERVICE | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION |
| SYMMETRIC KEY | ALTER | AL | DATABASE | ALTER ANY SYMMETRIC KEY |
| SYMMETRIC KEY | CONTROL | CL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| SYMMETRIC KEY | REFERENCES | RF | DATABASE | REFERENCES |
| SYMMETRIC KEY | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| SYMMETRIC KEY | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION |
| TYPE | CONTROL | CL | SCHEMA | CONTROL |
| TYPE | EXECUTE | EX | SCHEMA | EXECUTE |
| TYPE | REFERENCES | RF | SCHEMA | REFERENCES |
| TYPE | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | SCHEMA | CONTROL |
| TYPE | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | SCHEMA | VIEW DEFINITION |
| USER | ALTER | AL | DATABASE | ALTER ANY USER |
| USER | CONTROL | CL | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| USER | IMPERSONATE | IM | DATABASE | CONTROL |
| USER | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | DATABASE | VIEW DEFINITION |
| XML SCHEMA COLLECTION | ALTER | AL | SCHEMA | ALTER |
| XML SCHEMA COLLECTION | CONTROL | CL | SCHEMA | CONTROL |
| XML SCHEMA COLLECTION | EXECUTE | EX | SCHEMA | EXECUTE |
| XML SCHEMA COLLECTION | REFERENCES | RF | SCHEMA | REFERENCES |
| XML SCHEMA COLLECTION | TAKE OWNERSHIP | TO | SCHEMA | CONTROL |
| XML SCHEMA COLLECTION | VIEW DEFINITION | VW | SCHEMA | VIEW DEFINITION |
New granular permissions added to SQL Server 2022
The following permissions are added to SQL Server 2022:
10 new permissions have been added to allow access to system metadata.
18 new permissions have been added for extended events.
9 new permissions have been added with regard to security-related objects.
4 permissions have been added for Ledger.
3 additional database permissions.
For more information, see New granular permissions for SQL Server 2022 and Azure SQL to improve adherence with PoLP.
Access to system metadata permissions
Server level:
- VIEW ANY SECURITY DEFINITION
- VIEW ANY PERFORMANCE DEFINITION
- VIEW SERVER SECURITY STATE
- VIEW SERVER PERFORMANCE STATE
- VIEW ANY CRYPTOGRAPHICALLY SECURED DEFINITION
Database level:
- VIEW DATABASE SECURITY STATE
- VIEW DATABASE PERFORMANCE STATE
- VIEW SECURITY DEFINITION
- VIEW PERFORMANCE DEFINITION
- VIEW CRYPTOGRAPHICALLY SECURED DEFINITION
Extended events permissions
Server level:
- CREATE ANY EVENT SESSION
- DROP ANY EVENT SESSION
- ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION OPTION
- ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION ADD EVENT
- ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION DROP EVENT
- ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION ENABLE
- ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION DISABLE
- ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION ADD TARGET
- ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION DROP TARGET
All of these permissions are under the same parent-permission: ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION
Database level:
- CREATE ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION
- DROP ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION
- ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION OPTION
- ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION ADD EVENT
- ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION DROP EVENT
- ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION ENABLE
- ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION DISABLE
- ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION ADD TARGET
- ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION DROP TARGET
All these permissions are under the same parent-permission: ALTER ANY DATABASE EVENT SESSION
Security-related object permissions
- CONTROL (CREDENTIAL)
- CREATE LOGIN
- CREATE USER
- REFERENCES (CREDENTIAL)
- UNMASK (OBJECT)
- UNMASK (SCHEMA)
- VIEW ANY ERROR LOG
- VIEW SERVER SECURITY AUDIT
- VIEW DATABASE SECURITY AUDIT
Ledger permissions
- ALTER LEDGER
- ALTER LEDGER CONFIGURATION
- ENABLE LEDGER
- VIEW LEDGER CONTENT
Other database permissions
- ALTER ANY EXTERNAL JOB
- ALTER ANY EXTERNAL STREAM
- EXECUTE ANY EXTERNAL ENDPOINT
Summary of the permission check algorithm
Checking permissions can be complex. The permission check algorithm includes overlapping group memberships and ownership chaining, both explicit and implicit permission, and can be affected by the permissions on securable classes that contain the securable entity. The general process of the algorithm is to collect all the relevant permissions. If no blocking DENY is found, the algorithm searches for a GRANT that provides sufficient access. The algorithm contains three essential elements, the security context, the permission space, and the required permission.
Note
You can't grant, deny, or revoke permissions to sa, dbo, the entity owner, information_schema, sys, or yourself.
Security context
This is the group of principals that contribute permissions to the access check. These are permissions that are related to the current login or user, unless the security context was changed to another login or user by using the EXECUTE AS statement. The security context includes the following principals:
The login
The user
Role memberships
Windows group memberships
If module signing is being used, any login or user account for the certificate used to sign the module that the user is currently executing, and the associated role memberships of that principal.
Permission space
This is the securable entity and any securable classes that contain the securable. For example, a table (a securable entity) is contained by the schema securable class and by the database securable class. Access can be affected by table-, schema-, database-, and server-level permissions. For more information, see Permissions Hierarchy (Database Engine).
Required permission
The kind of permission that is required. For example, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT, EXECUTE, ALTER, CONTROL, and so on.
Access can require multiple permissions, as in the following examples:
A stored procedure can require both EXECUTE permission on the stored procedure and INSERT permission on several tables that are referenced by the stored procedure.
A dynamic management view can require both VIEW SERVER STATE and SELECT permission on the view.
General steps of the algorithm
When the algorithm is determining whether to allow access to a securable, the precise steps that it uses can vary, depending on the principals and the securables that are involved. However, the algorithm performs the following general steps:
Bypass the permission check if the login is a member of the sysadmin fixed server role or if the user is the dbo user in the current database.
Allow access if ownership chaining is applicable and the access check on the object earlier in the chain passed the security check.
Aggregate the server-level, database-level, and signed-module identities that are associated with the caller to create the security context.
For that security context, collect all the permissions that are granted or denied for the permission space. The permission can be explicitly stated as a GRANT, GRANT WITH GRANT, or DENY; or the permissions can be an implied or covering permission GRANT or DENY. For example, CONTROL permission on a schema implies CONTROL on a table. And CONTROL on a table implies SELECT. Therefore, if CONTROL on the schema was granted, SELECT on the table is granted. If CONTROL was denied on the table, SELECT on the table is denied.
Note
A GRANT of a column-level permission overrides a DENY at the object level. For more information, see DENY Object Permissions.
Identify the required permission.
Fail the permission check if the required permission is directly or implicitly denied to any of the identities in the security context for the objects in the permission space.
Pass the permission check if the required permission wasn't denied and the required permission contains a GRANT or a GRANT WITH GRANT permission either directly or implicitly to any of the identities in the security context for any object in the permission space.
Special considerations for column level permissions
Column level permissions are granted with the syntax <table_name>(<column _name>). For example:
GRANT SELECT ON OBJECT::Customer(CustomerName) TO UserJoe;
A DENY on the table is overridden by a GRANT on a column. However, a subsequent DENY on the table will remove the column GRANT.
Examples
The examples in this section show how to retrieve permissions information.
A. Return the complete list of grantable permissions
The following statement returns all Database Engine permission by using the fn_builtin_permissions function. For more information, see sys.fn_builtin_permissions.
SELECT * FROM fn_builtin_permissions(default);
GO
B. Return the permissions on a particular class of objects
The following example uses fn_builtin_permissions to view all the permissions that are available for a category of securable. The example returns permissions on assemblies.
SELECT * FROM fn_builtin_permissions('assembly');
GO
C. Return the permissions granted to the executing principal on an object
The following example uses fn_my_permissions to return a list of the effective permissions that are held by the calling principal on a specified securable. The example returns permissions on an object named Orders55. For more information, see sys.fn_my_permissions.
SELECT * FROM fn_my_permissions('Orders55', 'object');
GO
D. Return the permissions applicable to a specified object
The following example returns permissions applicable to an object called Yttrium. The built-in function OBJECT_ID is used to retrieve the ID of object Yttrium.
SELECT * FROM sys.database_permissions
WHERE major_id = OBJECT_ID('Yttrium');
GO