Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Increased sensitivity to sensory stimuli (hypersensitive) or diminished ability to detect sensory stimuli (hyposensitive).
The way our bodies interpret noises, smells, textures, and visual stimuli varies greatly from person to person. In general, someone can be “hypersensitive“ with all of their senses. Noises at “normal” volume levels may be bothersome or painful. Certain clothing and object textures may be irritating to wear or interact with. Brighter colors or stronger odors, enjoyable to some, may be overwhelming and cause nausea or headaches in others. The material used on a piece of hardware, the “clickiness” of keys on a keyboard, or the bright colors used on a website are all aspects of technology that can negatively impact a user who has hypersensitivity. In the same way that some are hypersensitive to noises, touch, light, or smell in their environments, others may be hyposensitive—or less receptive—to these experiences. Someone with diminished sensation may not feel a hot surface or friction on their skin from contact with a device.
Sensory limitations can occur in people with autism, sensory processing disorders, or any condition or injury that affects sensory nerves.
Barriers
- The color, texture, or material of device hardware
- Haptic feedback during an experience
- Noises emitted from a product
- Lights, colors, or brightness emitted during an experience
- Experiences that emit sensory stimuli that may potentially be harmful if someone cannot detect them on their own (such as emittance of heat from a device, sharp edges on a device, textured materials)
Facilitators
- A wide variety of options for purchasing products made of different materials (such as Alcantara vs. aluminum)
- Setting options that allow a user to adjust device specifications (for example, being able to change color scheme, lessen screen brightness, or adjust volume settings)
- Adequate warning of potential hazards (for example, including stickers on a device or designing software notifications)
Examples
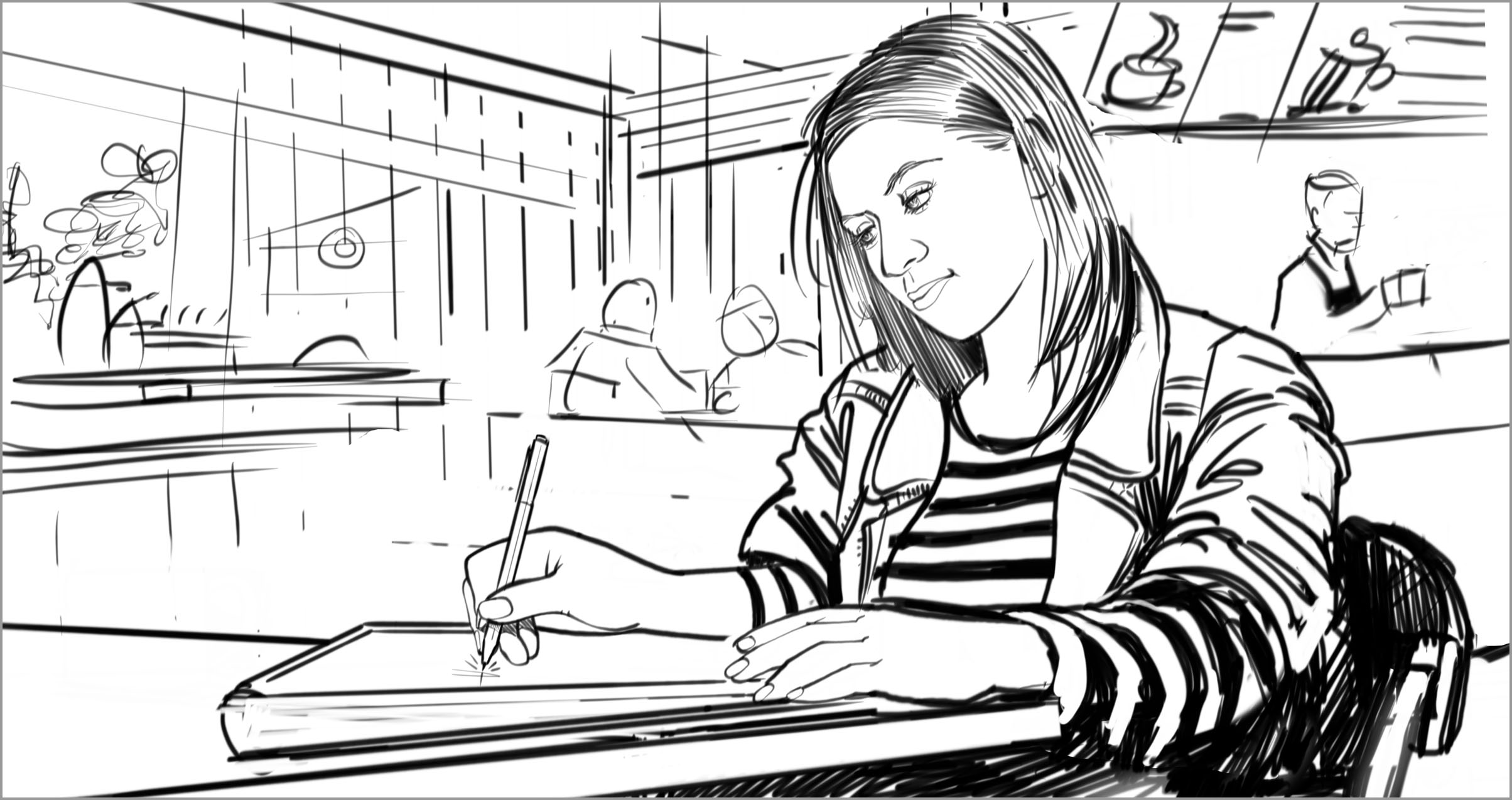

BARRIER — Noises emitted from a device like a fine-tip digital pen scratching across a screen can be disruptive or irritating to a user who is hypersensitive to sound.
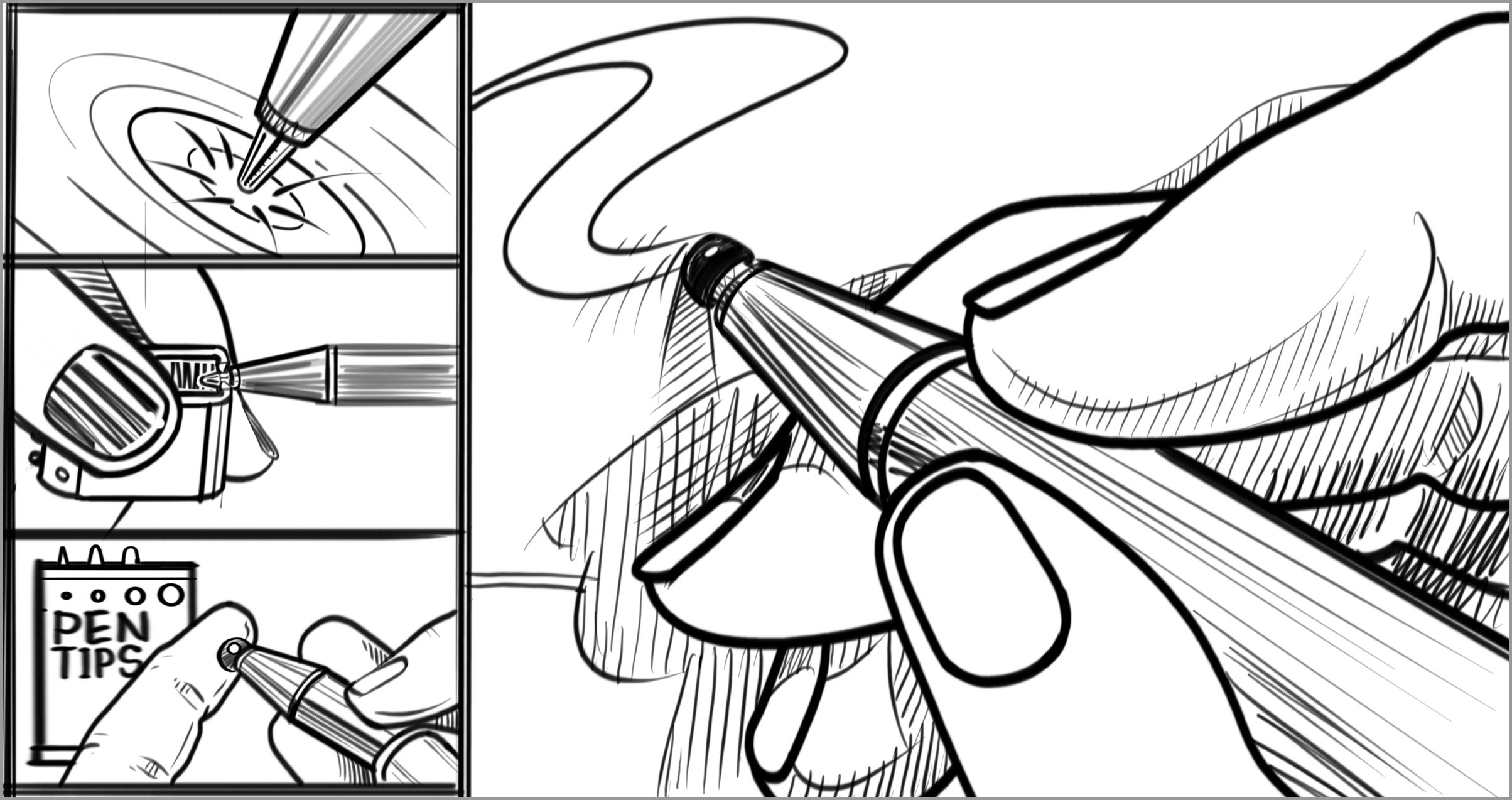
FACILITATOR — Providing optional softer pen tips can reduce the noise emitted from a digital pen gliding along a tablet screen.
The purpose of this reference is to provide concepts people can use to document and discuss aspects of function. Design should happen with people with disabilities, this reference is meant to support that activity, not replace it.