Configure a nested VM as a host
Nested virtualization is a functionality in Windows Server 2016 and above that allows you to run Hyper-V inside a Hyper-V virtual machine. In other words, with nested virtualization, a Hyper-V host itself can be virtualized. Nested virtualization can be enabled out-of-band by using PowerShell and Hyper-V host configuration.
You can use this functionality to reduce your infrastructure expense for development and test scenarios without the need for individual hardware.
With System Center - Virtual Machine Manager (VMM), you can enable and disable the nested virtualization feature through VMM console. You can configure the nested Virtual Machine (VM) as a host in VMM and perform host operations from VMM, on this VM. For example, VMM dynamic optimization will consider a nested VM host for placement.
Enable the nested virtualization on a VM and then configure it as a host.
Note
Virtualization applications other than Hyper-V aren't supported in Hyper-V virtual machines and are likely to fail. This includes any software that requires hardware virtualization extensions.
Before you start
Ensure the following prerequisites are met:
- A Hyper-V host running Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2022.
- A Hyper-V VM running Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2022.
- A Hyper-V VM with configuration version 8.0 or greater.
- An Intel processor with VT-x and EPT technology.
Ensure the following prerequisites are met:
- A Hyper-V host running Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019.
- A Hyper-V VM running Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019.
- A Hyper-V VM with configuration version 8.0 or greater.
- An Intel processor with VT-x and EPT technology.
Enable network virtualization
Administrators/delegated administrators can configure nested virtualization by using VMM. Use the following procedures:
Enable nested virtualization on an existing virtual machine
Identify the VM that meets the above prerequisites.
Ensure the VM is in stopped state.
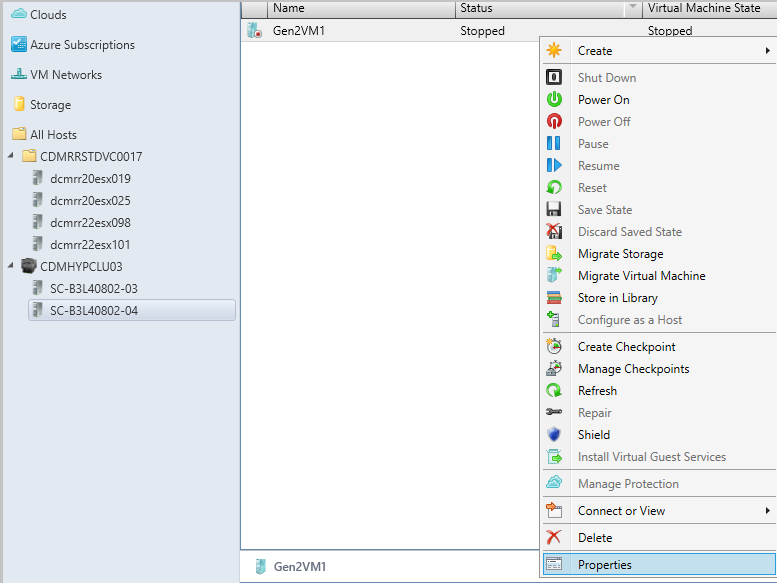
Browse the selected VM’s Properties.
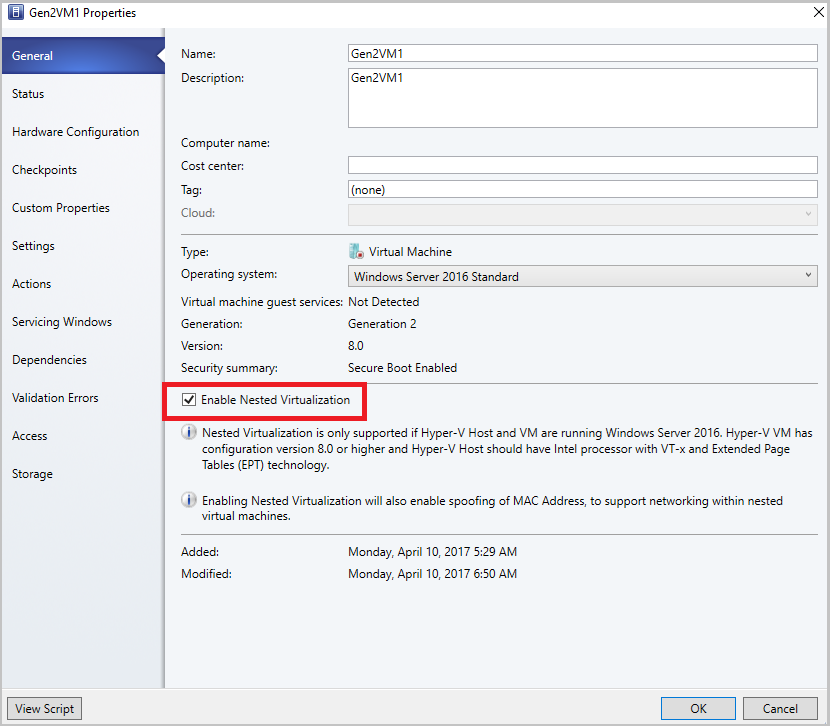
On General, select Enable Nested Virtualization.
Configure the nested VM as a host
Enable the following inbound and outbound firewall rules on the nested VM that you want to configure as the host.
Inbound Firewall rules
- File and printer sharing
- Windows remote management (HTTP-In)
- Windows management instrumentation
Outbound Firewall rules
- File and printer sharing
- Windows management instrumentation (WMI-Out)
Ensure the VM is in running state. Start the VM if it isn't running.
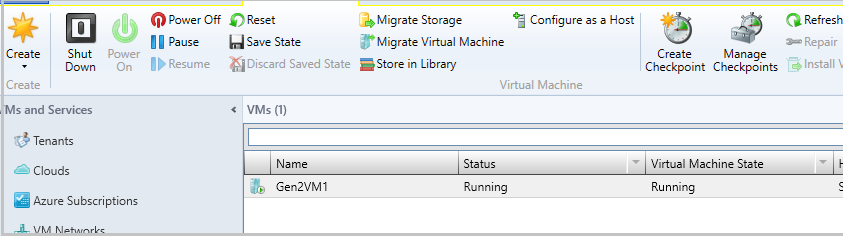
Right-click the VM and select Configure as a Host. The Add Resource wizard appears.
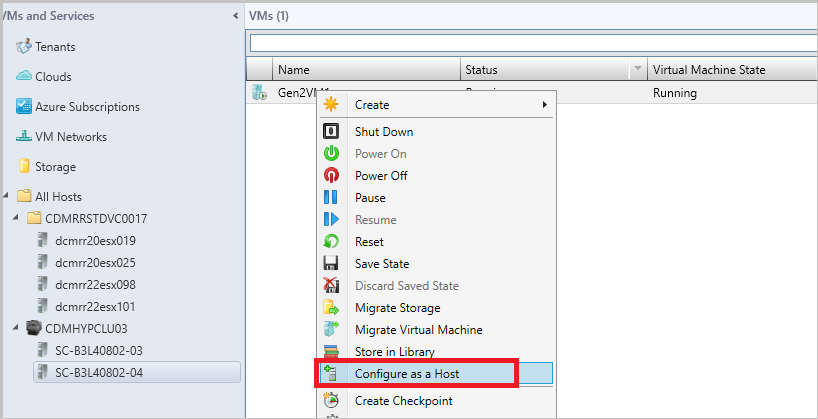
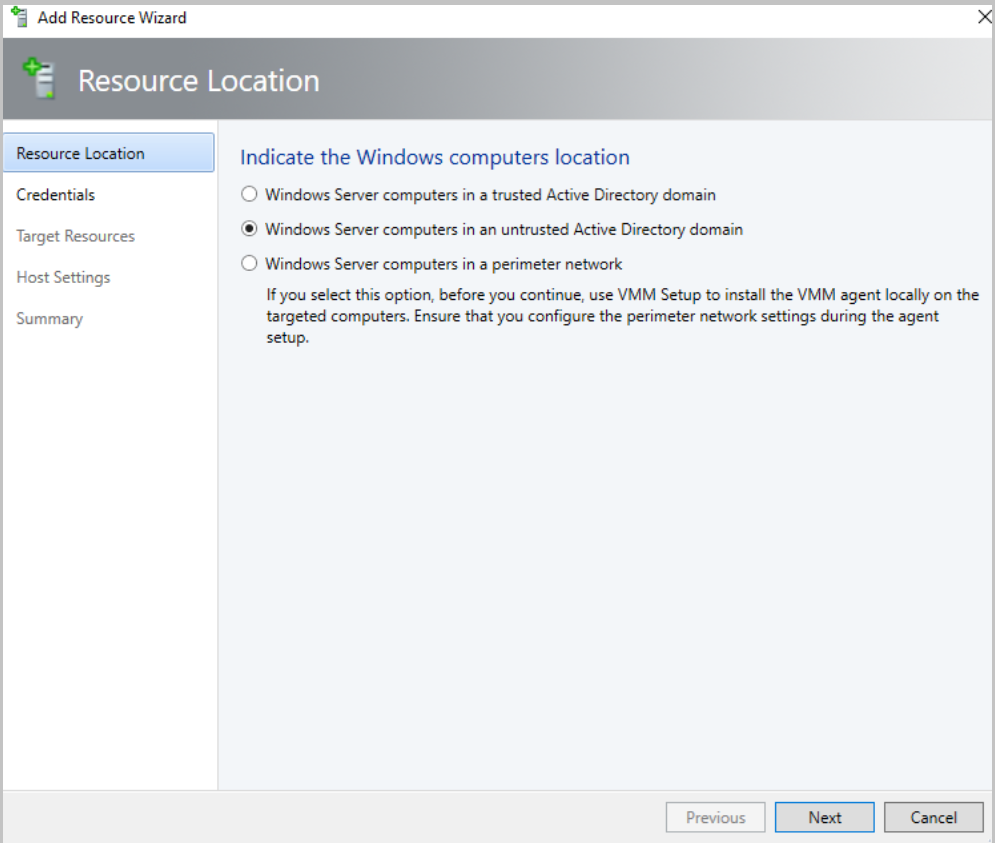
Run through the wizard, select the options as appropriate, and complete the wizard.
Disable nested virtualization
Select the host or VM for which nested virtualization is enabled.
Ensure the VM is in stopped state. Stop the VM if it's running.
Browse the VM Properties.
On General, clear the Enable Nested Virtualization check box.
Note
Check the note at the bottom of the wizard page before you disable nested virtualization.
Nested virtualization in 2019 ur1
With VMM 2019 UR1, in addition to enabling nested virtualization on an existing VM, you can also enable nested virtualization while creating new VMs through VM templates, service templates, or through VM creation wizard on VMM console.
Enable nested virtualization through VM templates
You can enable nested virtualization on VMs that are created through a VM template.
Note
Ensure the VMs that will be created using these templates meet the above prerequisites.
To enable nested virtualization, on the Create VM Template Wizard, select Select Source, and select Enable Nested Virtualization on the right pane of the wizard.
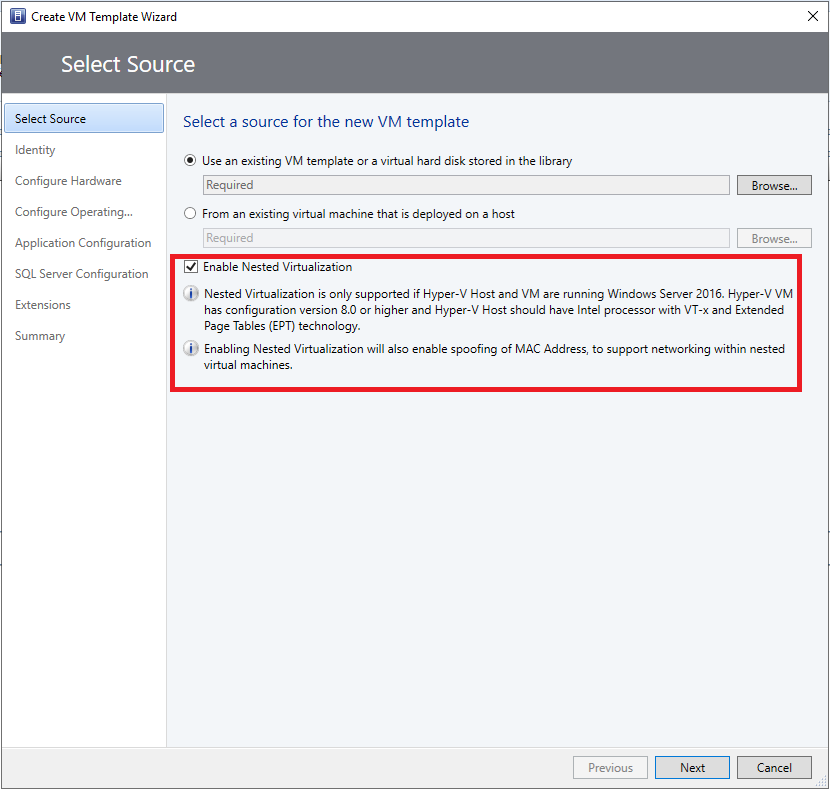
Enable nested virtualization through create virtual machines wizard
You can enable nested virtualization on VMs that are created through Create Virtual Machine wizard.
Note
Ensure the VMs that will be created using this wizard meet the above prerequisites.
To enable nested virtualization, on the Create Virtual Machines wizard, select Select Source, and select Enable Nested Virtualization on the right pane of the wizard.
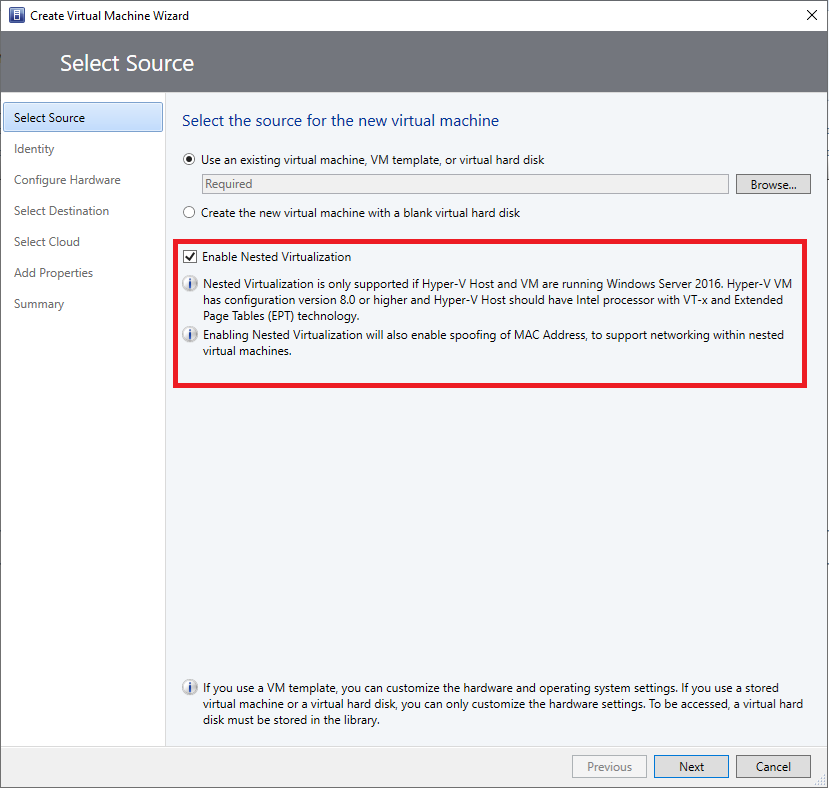
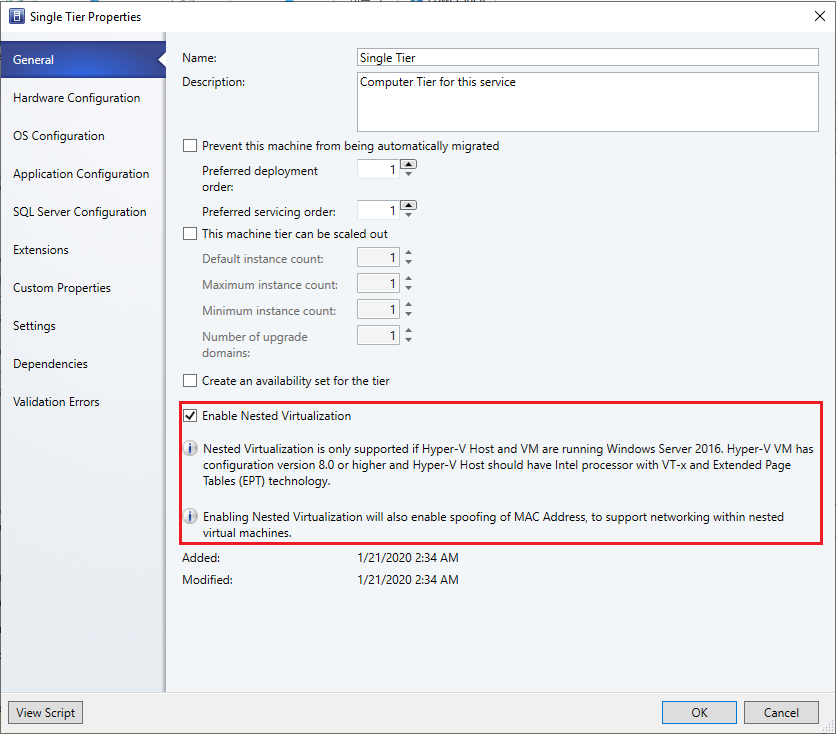
Enable nested virtualization through service template
You can enable nested virtualization on VMs that are created through service templates.
Note
Ensure the VMs that will be created using this template meet the above prerequisites.
To enable nested virtualization, from Single Tier Properties, select General, and select Enable Nested Virtualization on the right pane of the wizard.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for