Introduction
Introduction
Kubernetes allows you to manage the deployment lifecycle of cloud-native applications using a Kubernetes package manager. A Kubernetes package manager allows you to standardize, simplify, and implement reusable deployment strategies for your applications.
Example scenario
Let's say you work for a major pet store company called Contoso Pet Supplies. Your company sells pet supplies to customers worldwide. The solution is built and deployed as microservices and includes several major applications:
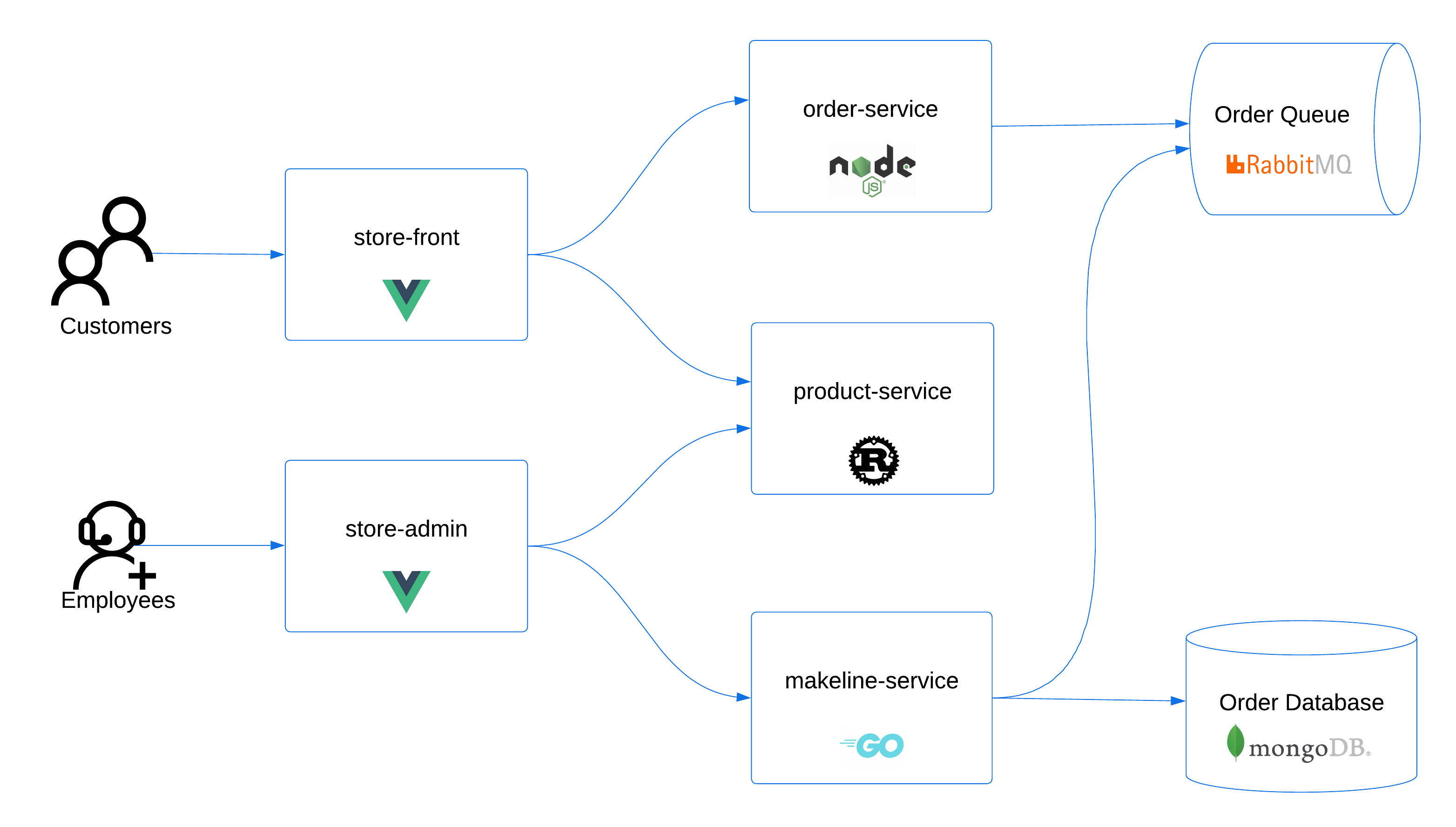
You use an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster to host the pet store front solution. The DevOps team uses standard declarative YAML files to deploy various services in the solution. In the current deployment workflow, the development teams create the deployment files for each application. Next, the DevOps team updates the deployment files to reflect production configuration settings where required. The manual management of many YAML files is proving a risk to the teams when efficiently deploying, operating, and maintaining systems and procedures. The DevOps team wants to use a Kubernetes package manager to standardize, simplify, and implement reusable deployment packages for all apps in the store front solution.
By the end of this module, you'll know how to create and manage a Kubernetes releases using Helm as a Kubernetes package manager.
Learning objectives
In this module, you'll learn how to:
- Describe the benefits of using Helm as a Kubernetes package manager
- Create a Helm chart for a cloud-native application
- Manage a cloud-native application release using Helm
Prerequisites
- Access to an Azure subscription
- Basic knowledge of executing commands using Azure CLI
- Knowledge of Kubernetes and its concepts
- Basic knowledge of creating Kubernetes YAML manifest files
- Basic knowledge of executing commands using Kubectl