Optimize temporary table usage
This unit explains temporary tables, the different types of temporary tables, and when they should be used.
Temporary tables allow you to efficiently create and clean up temporary data. The two types of temporary tables are:
InMemoryTempDB
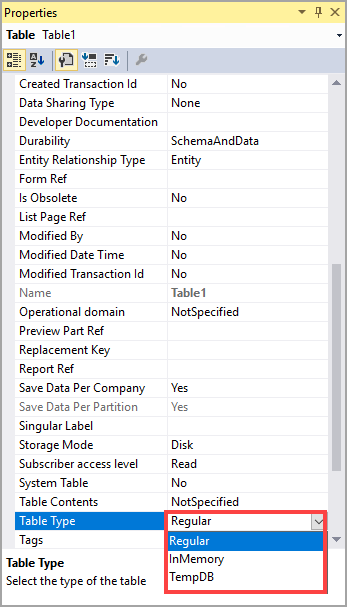
The table type can be determined on the table's TableType
property.
InMemory tables use an indexed sequential access method
(ISAM) file that exists on the client tier or the AOS tier. Microsoft
SQL Server has no connection to the ISAM file. The data is stored in
memory until it reaches 128 KB, and then the dataset is written to a
disk file on the server tier. InMemory tables are
instantiated when the first record is inserted. The table exists and
memory is only allocated to the table while a record buffer exists.
An InMemory table might be used when you need to store and
retrieve data without writing data to the database. This is like a
container, but InMemory tables allow you to use indexes to
speed up data retrieval. If you are only using a few records, you should
use a container, not an InMemory table. You can use X++
SQL syntax to join an InMemory table, however, joins and SQL
operations are usually inefficient.
TempDB tables use the TempDB database of the
SQL Server. This type of table causes the data to be removed when it is
no longer used by the current method or when the system is restarted. Regular tables are automatically turned into TempDB tables by
disabling the configuration key for the table, which allows references
to the disabled table in the system to continue to compile and run.
Additionally, TempDB tables are commonly used on reports to manipulate data.
The capabilities of TempDB tables include the following:
- Joining to regular tables.
- Using foreign keys.
- Being per company or global.
- Having indexes.
- Having methods but an inability to override the methods.
- Instantiating from the client or server tier.
- Being used as a query.
- Having no requirements for a configuration key.
TempDB tables also have the following limitations:
- Inability to manage date-effective data.
- They do not contain delete actions.
- Record Level Security does not apply.
- You cannot use them in views.