User authentication
When it comes to user authentication, security should be the number one consideration that comes to mind. Strong security is essential. It seems like every month or so, a company reports a data breach. Credentials are stolen because of inefficient security processes, or simply because of a lack of up-to-date security features within the company. Establishing secure user authentication can be a difficult task if user adoption requires long and frustrating steps to authenticate.
GitHub Enterprise supports two recommended methods for secure user authentication:
- SAML Single Sign-On(SSO)
- Two-Factor Authentication(2FA)
SAML SSO Authentication
SAML(Security Assertion Markup Language) SSO integrates GitHub with your organization’s identity provider (IdP), allowing centralized access control, and improved compliance. When enabled, GitHub redirects users to the IdP for authentication before granting access to organization resources.
Enabling and Enforcing SAML SSO
You can configure SAML SSO at either the organization or enterprise level, depending on the scope of enforcement you require.
Organization-Level SAML SSO
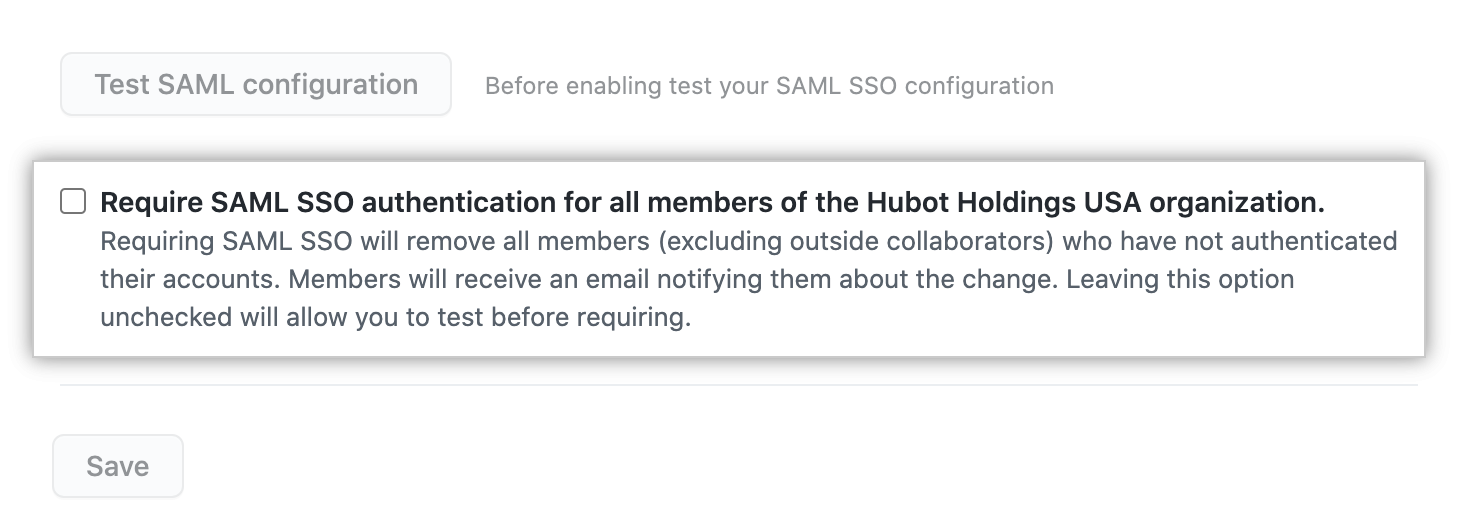
- Setup: In your org settings under Security, input your IdP’s SAML SSO URL and public certificate. Test and save the configuration.
- Enforcement: Select Require SAML SSO authentication to remove noncompliant members automatically.
- Use Case: Ideal for phased rollouts or testing with limited impact.
Note
GitHub removes only organization members who fail to authenticate. Enterprise members remain until they next access the resource.
Enterprise-Level SAML SSO
- Setup: In your enterprise account settings, enable SAML SSO similarly to org-level.
- Enforcement: Apply SSO across all organizations in your enterprise.
- Benefits: Ensures unified policies and reduces risk from fragmented configurations.
- Note: GitHub does not immediately remove noncompliant enterprise members. They are prompted to authenticate upon access.
Choosing the Right SSO Scope
| Criteria | Org-Level | Enterprise-Level |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Individual organization | Entire enterprise |
| User Removal | Immediate upon enforcement | Deferred until next access |
| Policy Consistency | Varies by org | Unified across enterprise |
| Setup Complexity | Lower | Higher |
| Use Case | Pilot/test | Broad compliance |
Step-by-Step: Enabling and Enforcing SAML SSO
| Scope | Steps |
|---|---|
| Organization | 1. Navigate to Your organizations → Settings → Security. 2. Enable SAML with your IdP’s details. 3. Test configuration and save. 4. Select Require SAML SSO, then remove noncompliant users. |
| Enterprise | 1. Navigate to Your enterprises → Settings → Security. 2. Enable SAML with your IdP’s details. 3. Test configuration and save. 4. Enforce SSO across all orgs and review noncompliant users. |
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
2FA adds a second verification step beyond username and password. You can require 2FA for organization members, outside collaborators, and billing managers.
Warning
When you require the use of two-factor authentication for your organization, all accounts that don't use 2FA is removed from the organization and lose access to its repositories. Accounts that are affected include bot accounts.
For more detailed information about 2FA, see Securing your account with two-factor authentication (2FA).
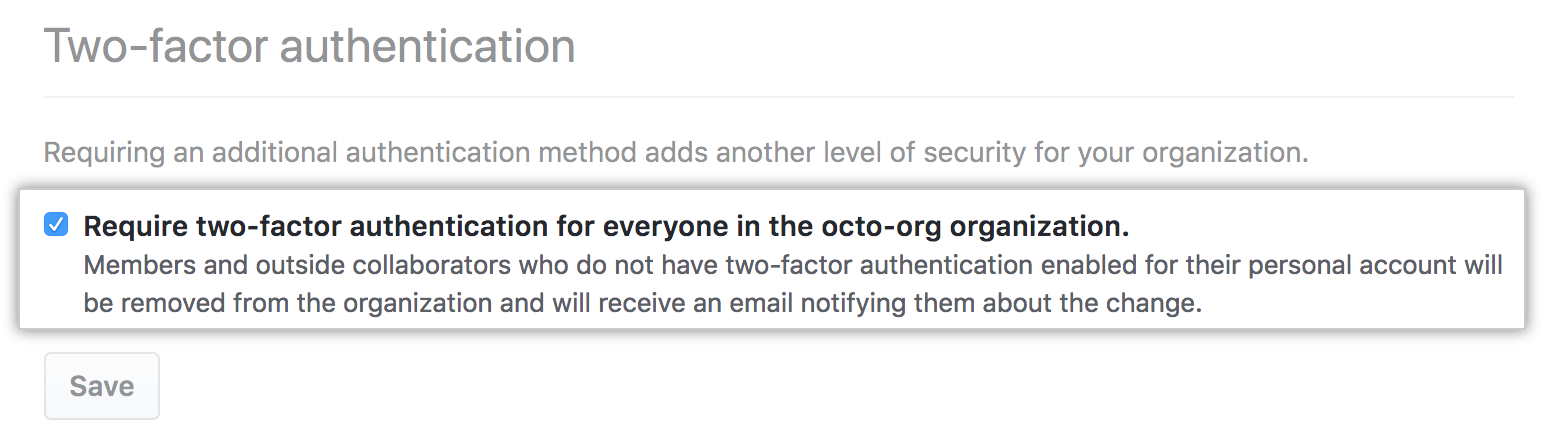
Enforcing 2FA
- Navigate to your org’s Security settings.
- Enable the checkbox labeled Require two-factor authentication.
- Communicate the requirement in advance to prevent loss of access.
2FA Methods in GitHub
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Security Keys | Most secure method. Physical USB or NFC devices that prevent phishing. Requires prior setup with TOTP(Time-based one-time passwords) or SMS(Short Message Service). |
| TOTP Apps | Recommended. Generates time-based one-time passwords, supports backup, and works offline. |
| SMS | Least secure. Should only be used where TOTP isn't viable. GitHub SMS support varies by region. |
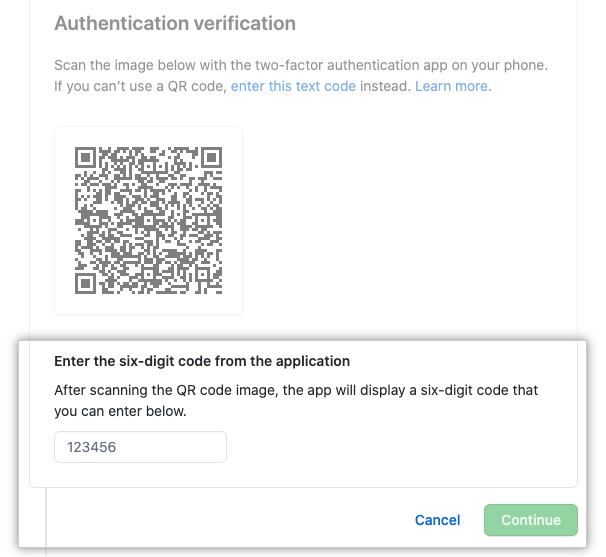
Time-based one-time passwords
GitHub SMS support
Note
Security keys store credentials locally and never expose secrets. GitHub recommends FIDO2/U2F keys.
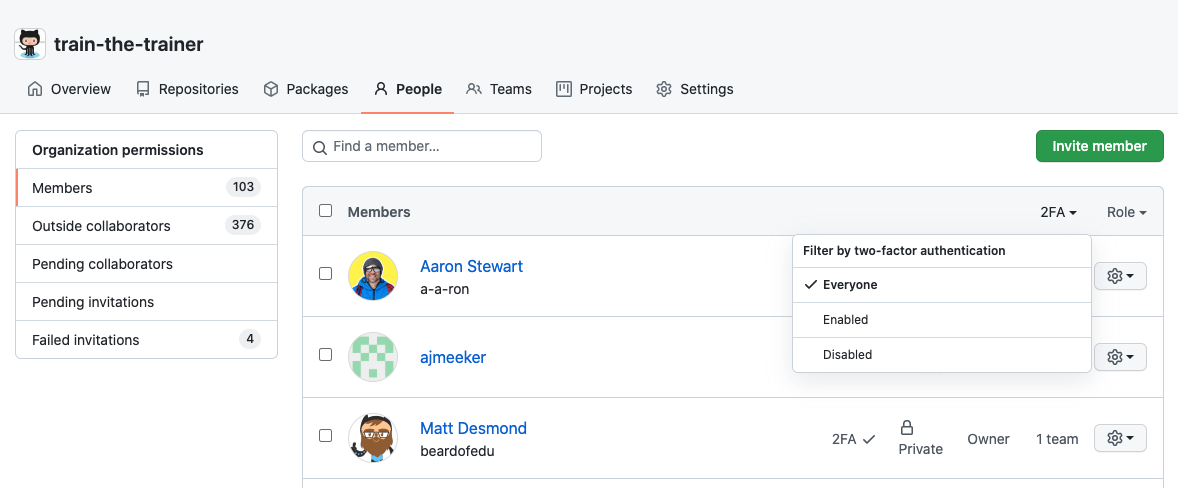
Auditing 2FA Compliance
To review who has enabled 2FA:
- Go to Your organizations → select org → People tab.
- Select the 2FA filter.
From here, you can identify noncompliant users and follow up outside of GitHub, typically via email.