Track data changes on Azure SQL Database with change data capture (CDC)
Scenario
Let's remember our scenario, in which you're the CTO of a healthcare business that sells medical equipment in different regions around the country. You have different inventory databases in each region, and you want to ensure that these databases are all replicating data changes to a central country-wide inventory database that offers you a status on each sale. You might decide to use change data capture (CDC) and enable it on each of your regional inventory databases in order to track data changes on your source database, then you might decide to use a streaming service such as Azure Data Factory to consume changes from the CDC tables and stream them to the national/regional database.
Let's learn more about CDC.
How it works
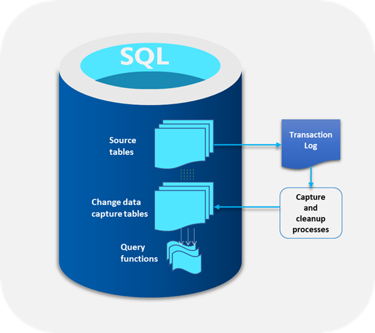
Once enabled on a table, change data capture (CDC) creates a record for insert, update, and delete activity that applies to the table. On SQL Server and Azure SQL Managed Instance, the SQL Server Agent runs CDC scan and cleanup jobs. However, on Azure SQL Database, a scheduler takes the place of the SQL Server Agent. The scheduler runs capture and cleanup jobs automatically within the database, without any external dependency for reliability or performance. Users still have the option to run capture and cleanup manually on demand.
The following steps highlight how CDC works on Azure SQL Database:
Enable CDC on the source database and tables that you want to track for Data Modification Language (DML) changes: insert, update, and delete.
Once you enable CDC on your source tables, associated change tables are created for each enabled source table. Change tables are system tables on your source database.
When you make DML changes on your CDC-enabled source table, these changes are reflected in the database transaction log. The CDC scan process picks up the committed changes from the transaction log and adds them to the change table associated to the CDC-enabled source table. The commit log sequence number (LSN) identifies changes that were committed in the same transaction and orders those transactions.
The cleanup process cleans the change tables on a retention-based policy set by the user. The default retention period is three days.
Query functions allow systematic access to the change data stored in the change tables.
The following illustration shows the principal data flow for CDC.
Enabling and disabling CDC
Access required for enabling / disabling CDC
The db_owner role is required to enable CDC for Azure SQL Database. Sysadmin permissions are required to enable change data capture for SQL Server or Azure SQL Managed Instance.
User interface options
You can use CDC by running T-SQL commands.
Enabling CDC on your database
In order to enable CDC on your Azure SQL Database, run the following:
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_db
GO
Enabling CDC on your tables
Once you've enabled CDC on the database, you should enable it on the tables that you want to be tracked.
To determine whether a source table has already been enabled for CDC, check the cdc.change_tables. Alternatively, you can also examine the is_tracked_by_cdc column in the sys.tables catalog view.
The following example shows how you can enable CDC on a table:
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_table
@source_schema = N'dbo',
@source_name = N'MyTable',
@role_name = N'MyRole',
@filegroup_name = N'MyDB_CT',
@supports_net_changes = 1,
@captured_column_list = N'Column1, Column2'
You can specify the following options when creating a capture instance:
By default, the change table is located in the database's default filegroup. Database owners who want to control the placement of individual change tables can use the @filegroup_name parameter to specify a particular filegroup for the change table associated with the capture instance. The named filegroup must already exist. Generally, we recommend that change tables be placed in a filegroup separate from source tables. In Azure SQL Database, users can't create their own filegroups, but since the Azure service adds and manages filegroups automatically as needed, it's possible to place individual change tables into different filegroups, if they exist.
If the parameter @supports_net_changes is set to 1, a net changes function is also generated for the capture instance. This function returns only one change for each distinct row changed in the interval specified in the call. To support net changes queries, the source table must have a primary key or unique index to uniquely identify rows. If a unique index is used, the name of the index must be specified using the @index_name parameter. The columns defined in the primary key or unique index must be included in the list of source columns to be captured.
By default, all of the columns in the source table are identified as captured columns. If only a subset of columns needs to be tracked, such as for privacy or performance reasons, use the @captured_column_list parameter to specify the subset of columns for which you want to track changes.
If you don't want to use a gating role, explicitly set the @role_name parameter to NULL (for example, @role_name=NULL).
Note
If CDC is enabled on a table with an existing primary key and the @index_name parameter is not used to identify an alternative unique index, the CDC feature will use the primary key. Subsequent changes to the primary key won't be allowed without first disabling CDC for the table. This is true regardless of whether support for net changes queries was requested when CDC was configured. If there's no primary key on a table at the time it's enabled for CDC, the subsequent addition of a primary key is ignored by CDC. Because CDC won't use a primary key that's created after the table was enabled, the key and key columns can be removed without restrictions.
Disabling CDC on your tables
Members of the db_owner fixed database role can remove a capture instance for individual source tables by using the stored procedure sys.sp_cdc_disable_table. To determine whether a source table has already been enabled for change data capture, check the cdc.change_tables. Alternatively, you can also examine the is_tracked_by_cdc column in the sys.tables catalog view. If there are no tables enabled for the database after the disabling takes place, the CDC jobs are also removed.
If a change data capture-enabled table is dropped, change data capture metadata that is associated with the table is automatically removed.
The following example shows how you can disable CDC on a table:
-- Connect to your target Azure SQL Database
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_disable_table
GO
Note
It's not necessary to disable individual tables before you disable the database.
Disabling CDC on your database
Disabling the CDC on the database removes all associated change data capture metadata, including the CDC user and schema and the CDC jobs. However, any gating roles CDC created will not be removed automatically and must be explicitly deleted. To determine if CDC is enabled on a database, query the is_cdc_enabled column in the sys.databases catalog view.
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_disable_db
GO
Note
If a change data capture enabled database is dropped, change data capture jobs are automatically removed.
Querying the change tables for changes
When a table is enabled for CDC, an associated capture instance is created to support the dissemination of the change data in the source table. The capture instance consists of a change table and up to two query functions. The requirements for the capture instance name are that it's a valid object name, and that it's unique across the database capture instances. By default, the name is schema name_table name of the source table. Its associated change table is named by appending _CT to the capture instance name.
Functions are provided to enumerate the changes that appear in the change tables over a specified range, returning the information in the form of a filtered result set. The filtered result set is typically used by an application process to update a representation of the source in some external environment. The function that is used to query for all changes is fn_cdc_get_all_changes_<capture_instance>.
If the capture instance is configured to support net changes, the net_changes query function fn_cdc_get_net_changes_<capture_instance> also gets created.
Next unit: Exercise - Work with change data capture
Having an issue? We can help!
- For issues related to this module, explore existing questions using the #SQL Server Training tag or Ask a question on Microsoft Q&A.
- For issues related to Certifications and Exams, post on Certifications Support Forums or visit our Credentials Help.