Back up and restore a database for SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance
Back up and restore on SQL Server PaaS offering work differently than on IaaS. Backups are generated automatically for Azure SQL Database, and Azure SQL Managed Instance. A full backup is created once a week, a differential every 12 hours, and transaction log backups every 5 to 10 minutes. All backups are located in read-access, geo-redundant (RA-GRS) blobs replicated to a datacenter that is paired based on Azure rules. That means backups are safe from an outage in a single data center.
Database backup and restore for SQL Database
Database backups are an essential part of any business continuity and disaster recovery strategy because they help protect your data from corruption or deletion.
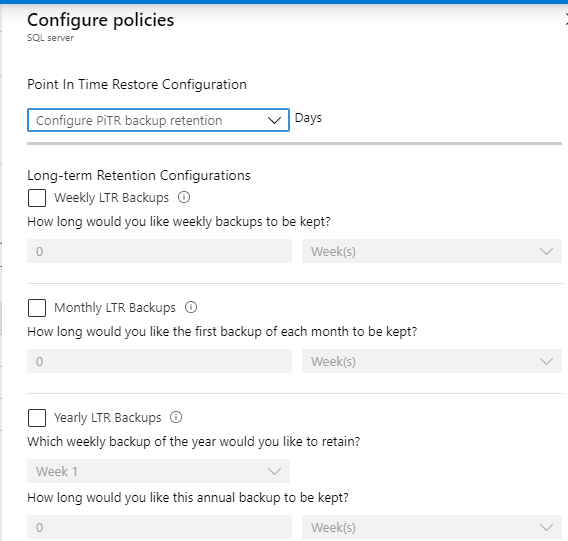
SQL Database can assist you to be compliant with mandatory backups for regulatory purposes with retention policies. Backup policies can be configured per database as shown in the following image:
If the server containing the database is deleted, all backups are deleted at the same time, and there's no way to recover them. If the server isn't deleted but the database is, you can restore the database normally.
Both SQL Database, and SQL Managed Instance have a feature called Accelerated Database Recovery (ADR). This feature is enabled by default, and its purpose is to decrease the time it takes to deal with long running transactions so they don't affect the recovery time. Although Accelerated Database Recovery was developed for Azure and was originally an Azure-based feature, ADR was implemented in SQL Server 2019 as well.
Note
You can't restore SQL Database Azure SQL Managed Instance backups on SQL Database.
Automated database backups are also avaialable on Azure SQL Managed Instance. SQL Server database engine backups are automatically managed by Microsoft, and stored on Microsoft-managed Azure storage accounts.
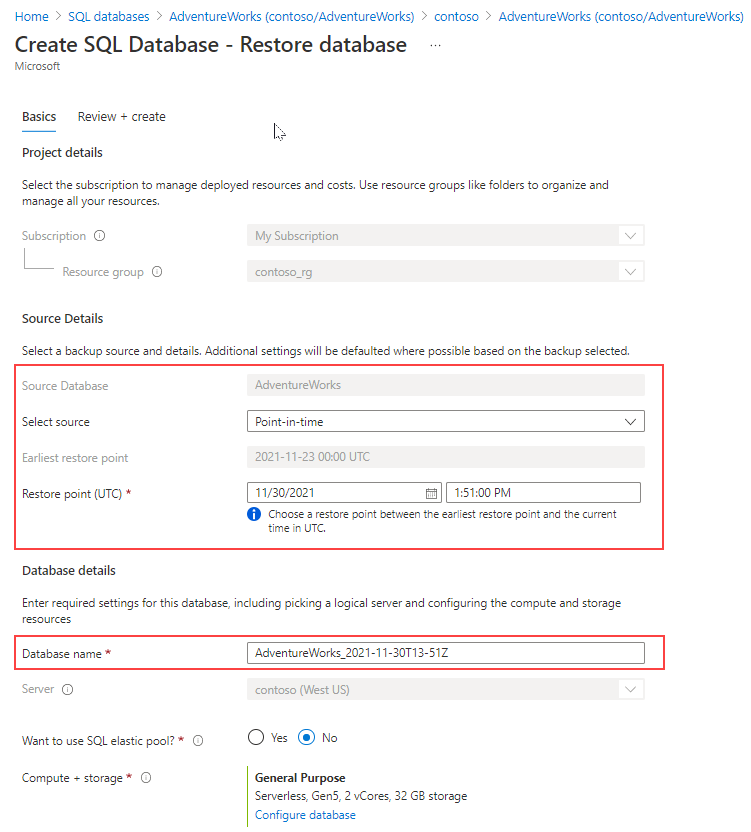
Point in time restore
To restore a database to a specific point in time on SQL Database, you can use either Azure portal, Azure PowerShell, Azure CLI, or REST API.
The following image shows the SQL Database restore page on Azure portal, where you can restore a database to a specific point in time.
Restore in place isn't supported on SQL Database, and SQL Managed Instance. You need to make sure the database doesn't exist before attempting the restore operation. By default, point in time retention policy is set to seven days, and you can change it to up to 35-days.
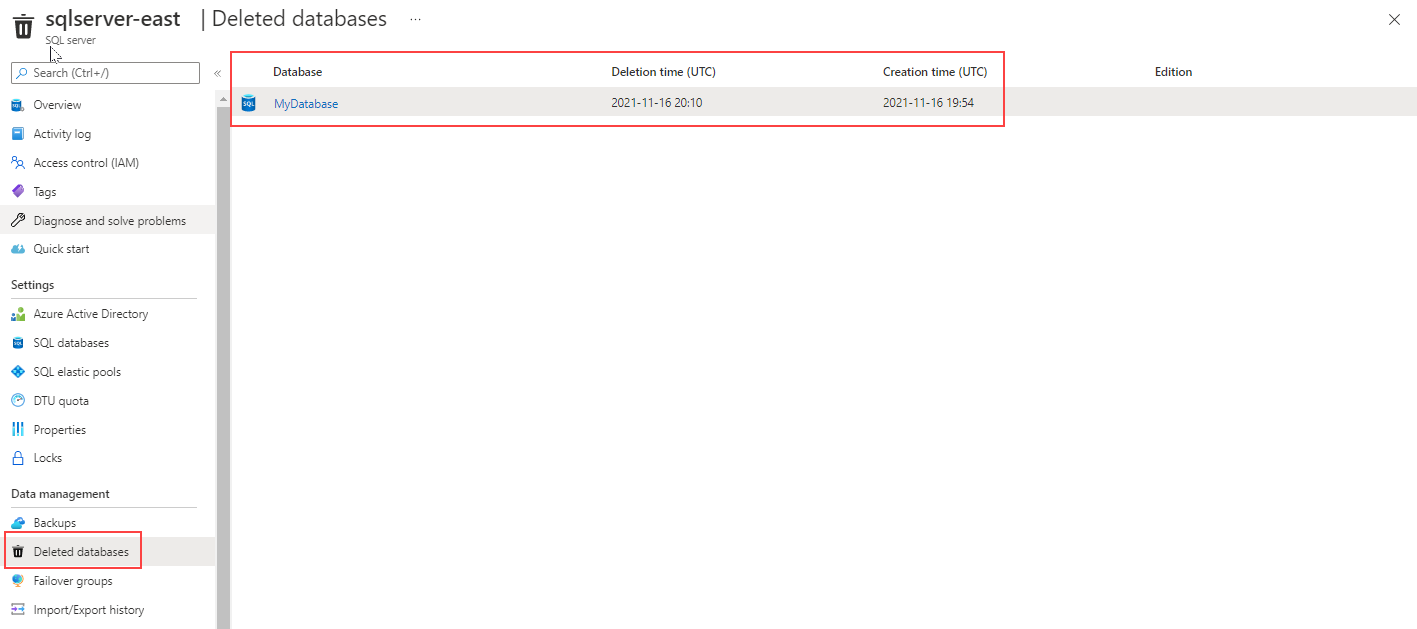
Restore a deleted database
Both SQL Database, and SQL Managed Instance have a feature to restore a deleted database to the last point in time available before the DROP DATABASE took place. To recover a deleted database to the deletion time by using the Azure portal, open the server's overview page and select Deleted databases. Select a deleted database that you want to restore, and then enter the name for the new database that will be created with data restored from the backup.
The image shows how to restore a deleted database on SQL Database. The deleted databases page shows a list of deleted databases available to restore, the database deletion time in UTC, and the database creation time in UTC. Once you select the database, the Create SQL Database - Restore database page opens. On that page you find the earliest restore point in time available for the selected database.
Database backup and restore for SQL Managed Instance
Azure manages backups for databases in SQL Managed Instance automatically, and they operate similar to SQL Database.
You can also manually back up, and restore databases with SQL Managed Instance using the same backup to URL/restore from URL functionality found in SQL Server covered earlier. That requires the use of credentials to access the Azure Blob Storage container. SQL Database doesn't support this feature.
You can only generate a COPY_ONLY backup since SQL Managed Instance is maintaining the log chain. A sample backup statement would look like:
BACKUP DATABASE contoso
TO URL = 'https://myacc.blob.core.windows.net/mycontainer/contoso.bak'
WITH COPY_ONLY
Note
You can't restore SQL Database SQL Managed Instance backups on SQL Database.