Razor class library creation and concepts
- 5 minutes
Components in web applications give developers the ability to reuse portions of an application user interface throughout the application. By using Razor class libraries, developers can share and reuse these components across many applications.
In this unit, you learn how to create a Razor class library. You then use it to share rendered and static content for Blazor applications to customize and display.
Razor class libraries
A Razor class library is a .NET project type. It contains Razor components, pages, HTML, Cascading Style Sheet (CSS) files, JavaScript, images, and other static web content that a Blazor application can reference. Like other .NET class library projects, Razor class libraries can be bundled as a NuGet package and shared on NuGet package repositories such as NuGet.org.
Let's look at the default template for creating a Razor class library.
Create a project by using the default template
You can optionally begin creating a Razor class library in Visual Studio by selecting File > New Project.
You can also create projects on a command-line interface by running the following command:
dotnet new razorclasslib -o MyProjectName
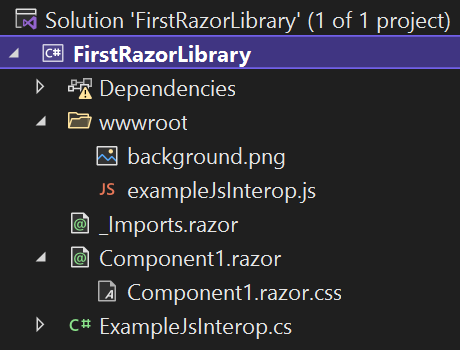
This template delivers an initial component named Component1, which contains several important features that your components can use:
- An isolated cascading style sheet named Component1.razor.css, which is stored in the same folder as Component1.razor. The Component1.razor.css file is conditionally included in a Blazor application that references Component1.
- Static content, such as images and JavaScript files, which is available to a Blazor application at runtime and referenced within Component1. This content is delivered in a wwwroot folder that behaves in the same way as a wwwroot folder in an ASP.NET Core or Blazor application.
- .NET code, which executes functions that reside in the included JavaScript file.
Differences between a class library and a Razor class library
A class library is a common package delivery structure in .NET applications, and a Razor class library is similar in structure with a few other features configured in the project file.
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Razor">
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>net8.0</TargetFramework>
<Nullable>enable</Nullable>
<ImplicitUsings>enable</ImplicitUsings>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<SupportedPlatform Include="browser" />
</ItemGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Web" Version="8.0.0" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>
- The project file contains an SDK reference to Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Razor to declare that it contains and creates Razor content as a Razor class library.
- The
SupportedPlatformentry declares that this library can be used in abrowserplatform, namely WebAssembly. - The
PackageReferenceto theMicrosoft.AspNetCore.Components.Weblibrary gives access to the base Blazor components that are shipped with the framework. This access lets you use those simple components to help you build more complex components.
Razor component contents
This initial Razor component is simple. It contains only an HTML div element with a short block of text:
<div class="my-component">
This component is defined in the <strong>FirstRazorLibrary</strong> library.
</div>
This component interacts with other Blazor components and pages that reference it in the same way that you would expect a component delivered in the same project to behave. That is, the CSS isolated script in the Component1.razor.css file is rendered inline with the rest of the application's CSS in the application.css file.
Static asset delivery
You can reference the contents of the wwwroot folder relatively among the other contents of that folder. You can also relatively reference the components' individual CSS files, such as Component1.razor.css, as files in the same base folder. For example, the default CSS adds a two pixel dashed red border and a background image style that uses the background.png image in the wwwroot folder. No path is required to make this reference from the CSS to the content that resides in the wwwroot folder.
.my-component {
border: 2px dashed red;
padding: 1em;
margin: 1em 0;
background-image: url('background.png');
}
The contents of the wwwroot folder are available for referencing by hosted Blazor applications with an absolute folder reference in the format:
/_content/{PACKAGE_ID}/{PATH_AND_FILENAME_INSIDE_WWWROOT}
Reference a Razor class library
In a .NET solution, where the Razor class library resides on the disk next to a Blazor application that references the library, you can update the Blazor application to reference the Razor class library by using the standard Visual Studio Add Reference dialog and by using the .NET CLI add reference command, as shown here:
dotnet add reference ../MyClassLibrary
For libraries that are delivered in NuGet package form, you can add a reference by using the Visual Studio NuGet package installer or by using the .NET CLI add package command, as shown here:
dotnet add package MyClassLibrary