Develop intelligent applications with AI frameworks
Building production-ready AI applications requires more than just AI capabilities—it requires an approach that encompasses real-time data streaming, natural language interfaces, developer productivity tools, and cloud integration. SQL Server 2025 provides a platform for developing applications that scale from on-premises deployments to cloud-native architectures.
This integrated approach means you can build AI applications using tools and frameworks while using enterprise features for security, performance, and reliability. Whether you're building real-time recommendation engines, conversational AI assistants, or analytical dashboards powered by AI insights, SQL Server 2025 provides the foundation you need.
Build conversational AI interfaces
Natural language interfaces make enterprise data accessible to users without requiring SQL knowledge or technical expertise.
Design conversational query patterns
Conversational query patterns enable users to ask questions in natural language and receive data-driven answers by translating their queries into SQL using AI models like GPT-4.
Implement natural language to SQL (NL2SQL) capabilities:
-- Create a stored procedure that interprets natural language queries
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_ConversationalQuery
@user_question NVARCHAR(MAX),
@context NVARCHAR(MAX) OUTPUT,
@sql_query NVARCHAR(MAX) OUTPUT
AS
BEGIN
-- Build a prompt for the AI model to generate SQL
DECLARE @prompt NVARCHAR(MAX) = CONCAT(
'You are a SQL expert. Given the following database schema and user question, generate a SQL query.',
CHAR(10), CHAR(10),
'Schema:', CHAR(10),
'products (product_id INT, product_name NVARCHAR(100), price DECIMAL(10,2), category NVARCHAR(50))',
CHAR(10),
'sales (sale_id INT, product_id INT, quantity INT, sale_date DATE)',
CHAR(10), CHAR(10),
'Question: ', @user_question,
CHAR(10),
'Generate only the SQL query, no explanations.'
);
-- Call GPT-4 to generate SQL
DECLARE @request NVARCHAR(MAX) = JSON_OBJECT(
'messages': JSON_ARRAY(
JSON_OBJECT('role': 'system', 'content': 'You are a SQL query generator.'),
JSON_OBJECT('role': 'user', 'content': @prompt)
),
'max_tokens': 500
);
DECLARE @response NVARCHAR(MAX);
EXEC sp_invoke_external_rest_endpoint
@url = N'https://myopenai.openai.azure.com/openai/deployments/gpt-4/chat/completions?api-version=2024-02-15-preview',
@method = 'POST',
@credential = [MyAzureOpenAICredential],
@payload = @request,
@response = @response OUTPUT;
-- Extract the generated SQL
SET @sql_query = JSON_VALUE(@response, '$.result.choices[0].message.content');
SET @context = 'Query generated successfully';
END;
This stored procedure uses GPT-4 to translate natural language questions into SQL queries, enabling conversational access to your data.
Implement safety guardrails
Safety guardrails prevent AI-generated SQL queries from performing incorrect operations like deleting or modifying data, ensuring only read-only access to your database.
Add validation to ensure generated SQL is safe:
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_SafeConversationalQuery
@user_question NVARCHAR(MAX),
@results NVARCHAR(MAX) OUTPUT
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @sql_query NVARCHAR(MAX);
DECLARE @context NVARCHAR(MAX);
-- Generate SQL from natural language
EXEC sp_ConversationalQuery @user_question, @context OUTPUT, @sql_query OUTPUT;
-- Validate the generated SQL
IF @sql_query LIKE '%DROP%'
OR @sql_query LIKE '%DELETE%'
OR @sql_query LIKE '%UPDATE%'
OR @sql_query LIKE '%INSERT%'
OR @sql_query LIKE '%ALTER%'
OR @sql_query LIKE '%CREATE%'
BEGIN
SET @results = JSON_OBJECT('error': 'Generated query contains potentially unsafe operations');
RETURN;
END;
-- Execute the query safely (read-only)
BEGIN TRY
EXEC sp_executesql @sql_query;
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
SET @results = JSON_OBJECT(
'error': ERROR_MESSAGE(),
'query': @sql_query
);
END CATCH;
END;
This wrapper adds security checks to prevent destructive operations, ensuring users can only query data, not modify it.
Create multi-turn conversations
Multi-turn conversations allow users to have natural, contextual dialogues with your data by maintaining conversation history, enabling follow-up questions without repeating context.
The following example builds a conversational AI that maintains context across multiple interactions, enabling follow-up questions and natural dialogue with your data:
CREATE TABLE conversation_history (
conversation_id UNIQUEIDENTIFIER DEFAULT NEWID(),
user_id NVARCHAR(100),
turn_number INT,
user_message NVARCHAR(MAX),
assistant_message NVARCHAR(MAX),
timestamp DATETIME2 DEFAULT GETDATE(),
PRIMARY KEY (conversation_id, turn_number)
);
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_ConversationalChat
@conversation_id UNIQUEIDENTIFIER,
@user_id NVARCHAR(100),
@user_message NVARCHAR(MAX),
@response NVARCHAR(MAX) OUTPUT
AS
BEGIN
-- Get conversation history
DECLARE @history NVARCHAR(MAX);
SELECT @history = STRING_AGG(
JSON_OBJECT(
'role': CASE WHEN turn_number % 2 = 1 THEN 'user' ELSE 'assistant' END,
'content': CASE WHEN turn_number % 2 = 1 THEN user_message ELSE assistant_message END
),
','
)
FROM conversation_history
WHERE conversation_id = @conversation_id
ORDER BY turn_number;
-- Build messages array with history
DECLARE @messages NVARCHAR(MAX) = CONCAT('[', @history, ',',
JSON_OBJECT('role': 'user', 'content': @user_message), ']');
-- Call GPT-4 with conversation context
DECLARE @chat_request NVARCHAR(MAX) = JSON_OBJECT('messages': @messages);
EXEC sp_invoke_external_rest_endpoint
@url = N'https://myopenai.openai.azure.com/openai/deployments/gpt-4/chat/completions?api-version=2024-02-15-preview',
@method = 'POST',
@credential = [MyAzureOpenAICredential],
@payload = @chat_request,
@response = @response OUTPUT;
-- Extract and store the response
DECLARE @assistant_response NVARCHAR(MAX) = JSON_VALUE(@response, '$.result.choices[0].message.content');
-- Save to conversation history
DECLARE @next_turn INT = (SELECT ISNULL(MAX(turn_number), 0) + 1 FROM conversation_history WHERE conversation_id = @conversation_id);
INSERT INTO conversation_history (conversation_id, user_id, turn_number, user_message, assistant_message)
VALUES (@conversation_id, @user_id, @next_turn, @user_message, @assistant_response);
SET @response = @assistant_response;
END;
Enhance developer productivity with AI tools
SQL Server 2025 integrates with modern development tools to accelerate AI application development.
Use MSSQL extension for Visual Studio Code with GitHub Copilot
The MSSQL extension for Visual Studio Code includes GitHub Copilot integration, providing AI-powered assistance for database development.
Note
GitHub Copilot integration with the MSSQL extension is currently in preview. Features and functionality might change. For the latest information, see MSSQL extension documentation.
The GitHub Copilot integration provides code assistance for database development tasks:
- Query generation: Describe what you want in natural language, get T-SQL code
- Query optimization: Get suggestions for improving query performance
- Schema exploration: Ask questions about your database schema
- Migration assistance: Generate scripts for schema changes and data migrations
- Explanation: Understand complex queries with AI-generated explanations
The following example demonstrates how GitHub Copilot can generate a complete stored procedure from a natural language comment:
-- Type a comment describing what you want
-- Generate a stored procedure that finds products similar to a given product using vector search
-- GitHub Copilot suggests:
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_FindSimilarProducts
@product_id INT,
@top_n INT = 5
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @query_embedding VECTOR(1536);
-- Get the embedding of the reference product
SELECT @query_embedding = embedding
FROM products
WHERE product_id = @product_id;
-- Find similar products
SELECT TOP (@top_n)
product_id,
product_name,
category,
price,
VECTOR_DISTANCE('cosine', @query_embedding, embedding) AS similarity_score
FROM products
WHERE product_id != @product_id
ORDER BY similarity_score;
END;
Use Entity Framework Core with AI capabilities
Entity Framework Core can be used to build AI applications with SQL Server. You can use raw SQL queries to work with SQL Server's VECTOR data type and AI functions:
Since Entity Framework Core doesn't natively support the VECTOR data type, this example uses FromSqlRaw to execute T-SQL directly while benefiting from EF Core's async operations and object mapping. The method serializes a query embedding to JSON, executes a vector similarity search using VECTOR_DISTANCE, and returns products with similar embeddings—ideal for recommendation systems and semantic search.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using System.Text.Json;
public class Product
{
public int ProductId { get; set; }
public string ProductName { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
}
public class AppDbContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Product> Products { get; set; }
}
// Query with vector similarity using raw SQL
public async Task<List<Product>> FindSimilarProducts(float[] queryEmbedding, int topN = 5)
{
var embeddingJson = JsonSerializer.Serialize(queryEmbedding);
var similarProducts = await _context.Products
.FromSqlRaw(@"
SELECT TOP {0}
product_id,
product_name,
description,
price
FROM products
WHERE VECTOR_DISTANCE('cosine', CAST({1} AS VECTOR(1536)), embedding) < 0.5
ORDER BY VECTOR_DISTANCE('cosine', CAST({1} AS VECTOR(1536)), embedding)
", topN, embeddingJson)
.ToListAsync();
return similarProducts;
}
Integrate with Microsoft Fabric
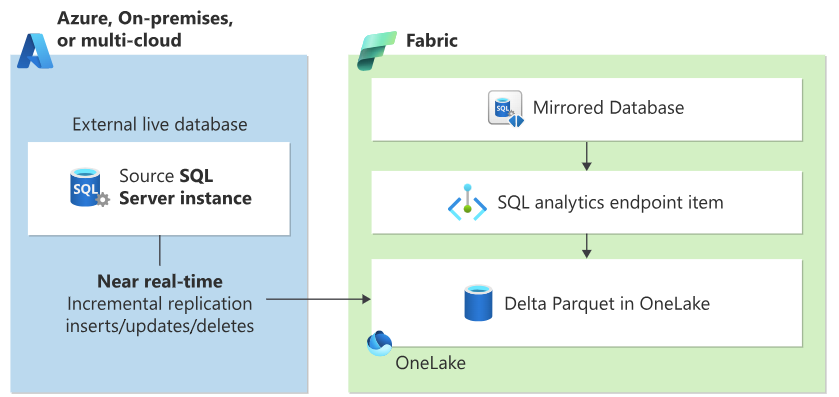
Microsoft Fabric provides a unified analytics platform that complements SQL Server's AI capabilities. SQL Server 2025 supports database mirroring to Microsoft Fabric, enabling near real-time analytics on operational data without the complexity of traditional ETL pipelines.
Diagram showing SQL Server 2025 database mirroring to Microsoft Fabric. On the left, a SQL Server 2025 database continuously replicates data to Microsoft Fabric OneLake. The diagram illustrates the zero-ETL architecture where operational data flows to the analytics platform.
Configure Fabric Mirroring
Fabric Mirroring is configured through the Microsoft Fabric portal using a visual interface. The mirroring feature continuously replicates your data to Fabric's OneLake in Delta Lake format, making it available for analytics without impacting your operational workloads.
Note
For step-by-step configuration instructions, see Tutorial: Configure Microsoft Fabric mirrored databases from SQL Server.
Some of the benefits of Fabric mirroring are:
- Near real-time analytics: Data changes are replicated continuously with minimal latency
- Zero-ETL architecture: No need to build and maintain complex data pipelines
- Open data format: Data is stored in Delta Lake format in OneLake for broad tool compatibility
- AI-ready analytics: Direct integration with Fabric's AI and machine learning capabilities
- SQL analytics endpoint: Query mirrored data using familiar T-SQL syntax
- No operational impact: Mirroring uses change tracking without affecting production workloads
Optimize mirroring performance
Once mirroring is configured, you can use SQL Server's Resource Governor to manage its performance effect on your operational workloads:
The following code example creates a Resource Governor configuration that limits the CPU and memory resources used by Fabric mirroring operations.
-- Create resource pool for mirroring
CREATE RESOURCE POOL FabricMirrorPool
WITH (
MIN_CPU_PERCENT = 5,
MAX_CPU_PERCENT = 20,
MIN_MEMORY_PERCENT = 5,
MAX_MEMORY_PERCENT = 20
);
-- Create workload group for mirroring
CREATE WORKLOAD GROUP FabricMirrorGroup
WITH (
IMPORTANCE = MEDIUM
)
USING FabricMirrorPool;
-- Apply classifier function
CREATE FUNCTION dbo.FabricMirrorClassifier()
RETURNS SYSNAME
WITH SCHEMABINDING
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @workload_group SYSNAME = 'default';
IF APP_NAME() LIKE '%Fabric Mirror%'
SET @workload_group = 'FabricMirrorGroup';
RETURN @workload_group;
END;
-- Enable resource governor
ALTER RESOURCE GOVERNOR
WITH (CLASSIFIER_FUNCTION = dbo.FabricMirrorClassifier);
ALTER RESOURCE GOVERNOR RECONFIGURE;
In the example, the resource pool FabricMirrorPool restricts mirroring to use between 5-20% of CPU and memory, preventing it from impacting production workloads. A classifier function identifies mirroring sessions based on the application name and routes them to the dedicated workload group, ensuring consistent resource allocation and predictable performance for both operational and analytics workloads.
Resource governor ensures Fabric mirroring doesn't affect your operational workloads.
Optimize AI application performance
Performance is critical for production AI applications.
Optimize vector search queries
Use query hints and index optimization:
Optimizing vector search performance is critical for production AI applications where response time directly impacts user experience.
The following example demonstrates two key optimization techniques: creating filtered vector indexes that target specific data subsets (like product categories), and using query hints to control execution behavior.
The filtered index idx_electronics_embedding accelerates searches within the Electronics category by indexing only relevant vectors, reducing search space and improving query speed. The MAXDOP 4 hint limits parallel processing to four threads, balancing performance with resource consumption—essential for preventing vector searches from monopolizing server resources and impacting other workloads.
-- Create filtered vector index for specific categories
CREATE VECTOR INDEX idx_electronics_embedding
ON products(embedding)
WHERE category = 'Electronics';
-- Use query hints for better performance
DECLARE @query_embedding VECTOR(1536) = AI_GENERATE_EMBEDDINGS(@user_query USE MODEL Ada2Embeddings);
SELECT TOP 10
product_id,
product_name,
VECTOR_DISTANCE('cosine', @query_embedding, embedding) AS score
FROM products WITH (INDEX(idx_electronics_embedding))
WHERE category = 'Electronics'
ORDER BY score
OPTION (MAXDOP 4);
You can use indexes and query hints optimize vector search for specific scenarios.
By following these practices and using SQL Server 2025's AI capabilities, you can build, deploy, and operate production-ready applications that deliver real business value while maintaining enterprise standards for security, performance, and reliability.