What is Bicep?
Bicep is a language for declaratively deploying Azure resources. Using Bicep, you can define how your Azure resources should be configured and deployed. You'll define your resources within a Bicep file, and submit the file to Azure Resource Manager. Resource Manager then takes responsibility for deploying each resource within the Bicep file on your behalf.
How is Bicep related to ARM templates?
You might already be familiar with Azure Resource Manager templates (ARM templates), which are files that represent Azure resources. Until Bicep was available, ARM templates had to be written in a special JSON format. One common problem with JSON templates is that they're difficult to work with because they have a complex syntax. It can be hard to get started with writing ARM templates in JSON.
Bicep solves these problems by using a much simpler language designed specifically to help you deploy resources to Azure.
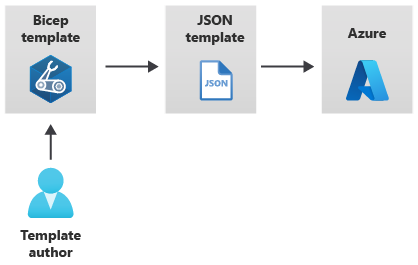
Behind the scenes, Resource Manager still operates based on the same JSON templates. When you submit a Bicep file to Resource Manager, the Bicep tooling converts your file to a JSON format in a process called transpilation. This process isn't something you typically have to think about, but you can view the JSON template file that's created from the Bicep file.
What do I need to install?
To get started with Bicep, you need to install some tooling. The easiest way is to install the latest version of the Azure CLI or Azure PowerShell. Both of these tools support Bicep files.
You also need a text editor to write your Bicep files. Visual Studio Code is a great text editor, and it has an extension for writing Bicep files. These tools provide language support and resource autocompletion. They help you to create and validate Bicep files, and they tell you when your code doesn't follow recommended practices.