Catching issues early and automating reviews with Copilot
GitHub Copilot reviews don't have to wait until you open a pull request. In VS Code or JetBrains IDEs, you can request Copilot to review changes before committing. This lets you address style violations, security gaps, or best practice issues earlier-saving cycles in the review process. You can also configure Copilot to review all pull requests automatically, scaling this approach across repositories and teams.
By the end of this unit, you'll be able to:
- Use Copilot reviews locally in VS Code or JetBrains IDEs.
- Customize Copilot's review behavior with repository and path-specific instructions.
- Leverage Premium Request Units (PRUs) for deeper analysis in your IDE.
- Configure automatic Copilot reviews for all pull requests.
- Combine Copilot with rulesets and status checks.
- Recognize the benefits of automation at scale.
Running Copilot reviews locally in your IDE
To guide reviews, create a .github/copilot-instructions.md file with rules such as:
- "Focus on security and avoid unsafe string interpolation."
- "Ensure functions have docstrings explaining parameters and return types."
Copilot then applies these rules automatically to reviews to analyze larger diffs and provide context-rich insights that align with your repo's style.
Use case: A developer adds repetitive code in a TypeScript service. Copilot flags it and suggests extracting a helper function. Instead of waiting for peers to point it out, the developer fixes it before pushing the code-reducing review noise later.
Creating path-specific custom instructions
You can use path-specific custom instructions to guide Copilot code review or the Copilot coding agent for specific files or folders. Here's how to set them up:
Create the instructions directory
In the root of your repository, add a folder named
.github/instructionsif it doesn't already exist.Add instruction files
Inside that folder, create one or more files ending in
.instructions.md(for example,security.instructions.md). The file name describes the purpose of the instructions.Define the paths to apply to
At the top of each file, add a frontmatter block with an applyTo keyword. Use glob syntax to target the files or directories where these instructions should apply.
Example - apply to Ruby models:
applyTo: "app/models/**/*.rb"Example - apply to TypeScript files:
applyTo: "**/*.ts,**/*.tsx"To apply to all files in the repository, use:
applyTo: "**"Write your custom guidance
Below the frontmatter, add your review guidance in plain language using Markdown. You can write it as a paragraph, on separate lines, or with blank lines for readability. Copilot will follow these instructions whenever it reviews or generates code for the matching paths.
You've seen how Copilot helps locally. Now let's explore how to scale reviews across teams and repositories.
Leverage PRUs for deeper analysis in your IDE
When you run Copilot reviews directly inside your IDE-such as Visual Studio Code or JetBrains-you're not limited to the lightweight checks available on GitHub.com. By allocating Premium Request Units (PRUs) to these local reviews, Copilot can tap into more advanced models that analyze larger diffs, apply your repository's custom instructions, and surface higher-quality suggestions before code ever reaches a pull request. This means you can spot style violations, security gaps, and best-practice issues earlier in the development cycle, saving time during formal reviews and reducing back-and-forth with teammates. PRU-powered reviews in your IDE give you a deeper, context-rich analysis right where you write and test code, while still leaving final judgment and sign-off to human reviewers.
Automating reviews and scaling with Rulesets
Manual reviews don't scale well in fast-moving teams. GitHub allows you to configure rulesets so Copilot is automatically assigned to all PRs targeting protected branches. This ensures every change gets reviewed-even if human reviewers are delayed.
Pair Copilot reviews with status checks like tests or code scanning. This creates a pipeline where:
- Copilot reviews for style and readability.
- Code scanning flags vulnerabilities.
- Tests validate functionality.
Because each Copilot review uses PRUs, organizations should budget PRU consumption to match review volume and perform automated reviews at appropriate times in the development process.. Tracking usage helps balance cost and coverage.
With automation, even small fixes or dependency updates are reviewed consistently, reducing the risk of unnoticed regressions.
Automation ensures reviews happen at scale. But what about implementing review comments? That's where Copilot shines as a coding partner.
Automatic reviews for your account
This option is only available if you are on the Copilot Pro or Copilot Pro+ plan.
When you turn this feature on in your personal Copilot settings, every PR you open will automatically be reviewed. This helps individual developers catch issues early across all their work.
Steps:
In the upper-right corner of any GitHub page, click your profile picture and select Your Copilot.
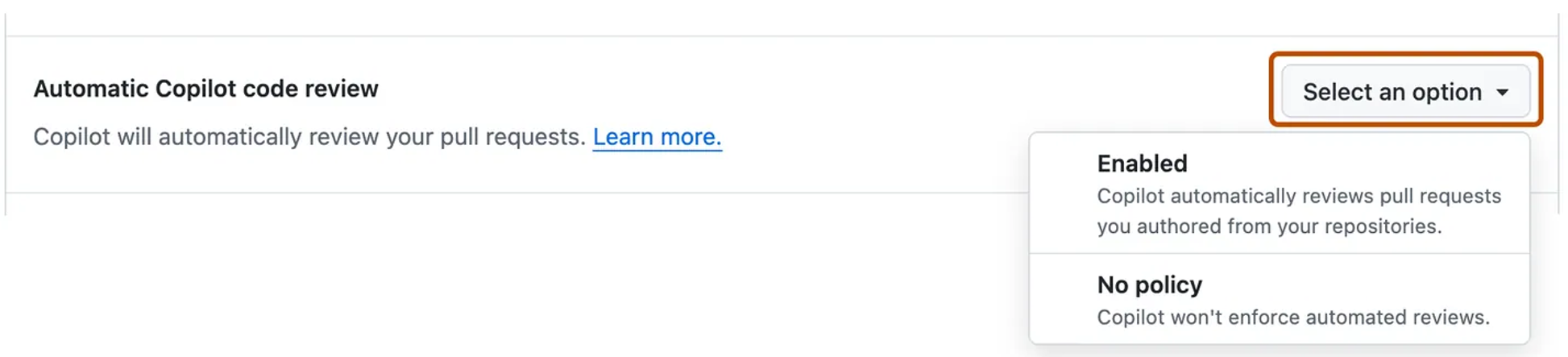
Find the Automatic Copilot code review option.
From the dropdown, select Enabled.
From now on, Copilot will always be added to your pull requests.
Automatic reviews for a repository
Sometimes you'll only want automatic reviews in certain repositories-like production services that require stricter quality control. Repository admins can enforce this by creating a branch ruleset.
Steps:
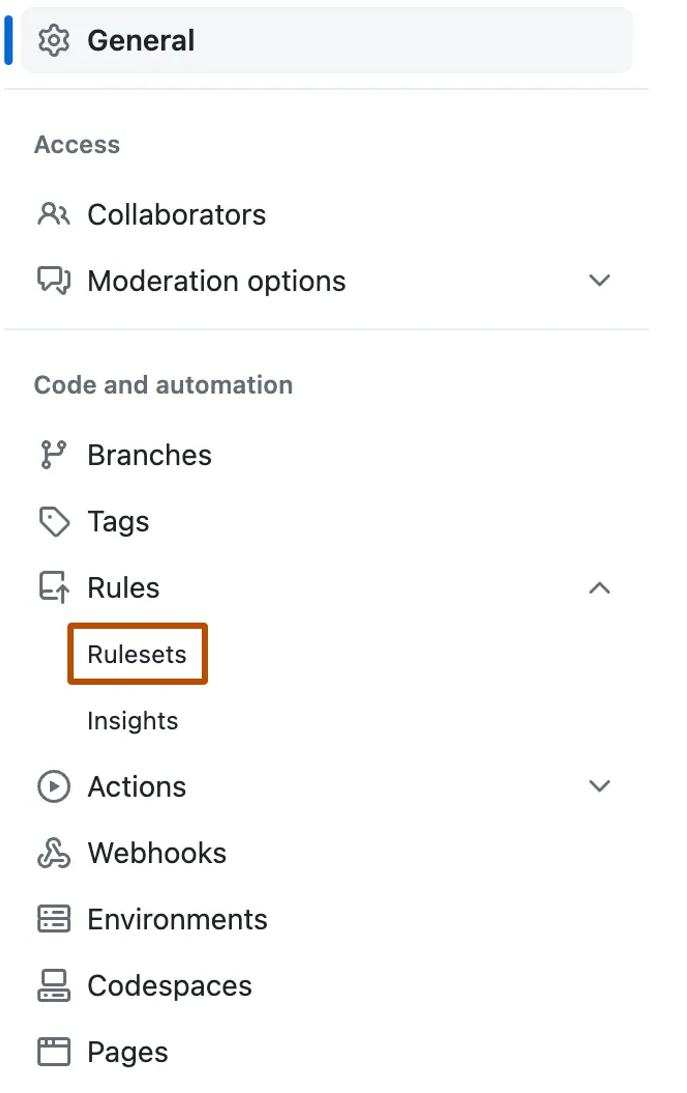
In the repository, click Settings.
In the left sidebar, expand Code and automation and select Rules → Rulesets.
Click New ruleset, then choose New branch ruleset.
Enter a name, set Enforcement status to Active, and select target branches (e.g., default branch).
Under Branch rules, check Require a pull request before merging.
In the expanded options, select Request pull request review from Copilot.
At the bottom, click Create.
Now every PR targeting the chosen branches will automatically include Copilot's review. Optionally, you can also enable “Require conversation resolution before merging” to encourage developers to read the feedback from Copilot.
Automatic reviews across an organization
For larger teams, you can scale this approach across multiple repositories at once. Organization owners can create rulesets that apply to selected repositories, based on name patterns or inclusion/exclusion rules.
In the upper-right corner of GitHub, click your profile picture, then select Your organizations.
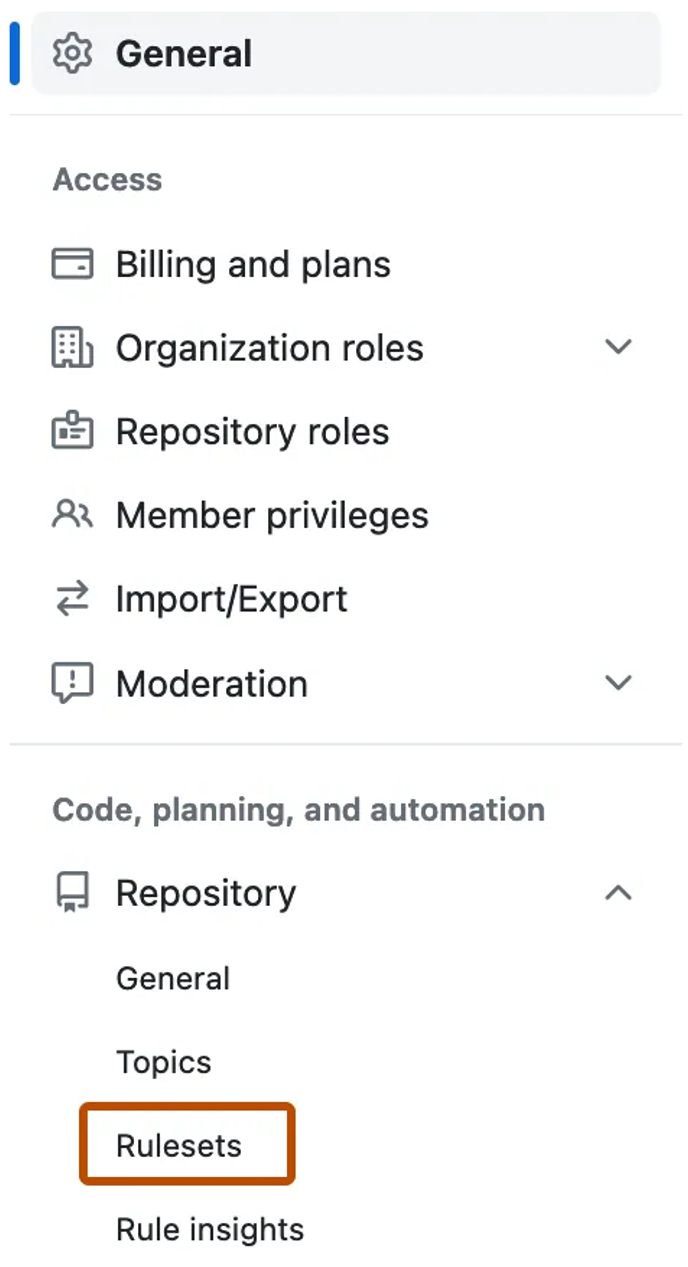
Choose the organization, then go to Settings.
In the sidebar, select Repository → Rulesets.
Click New ruleset → New branch ruleset.
Provide a ruleset name and set Enforcement status to Active.
Add target repositories by specifying inclusion or exclusion patterns (e.g., *service to match all service repos).
Define target branches.
Enable Require a pull request before merging, then check Request pull request review from Copilot.
Save by clicking Create.
This ensures consistent standards and reduces review times across the whole organization.