Create custom domain names
When you create a web app, Azure assigns the app to a subdomain of azurewebsites.net. Suppose your web app is named contoso. Azure creates a URL for your web app as contoso.azurewebsites.net. Azure also assigns a virtual IP address for your app. For a production web app, you might want users to see a custom domain name.
What is a custom domain?
A domain name is the address people type into a web browser to reach your website. A custom domain is a domain name that you own and configure to point to your Azure-hosted app, replacing the default Azure domain.
For example:
- Default Azure domain:
myapp-00000.westus.azurewebsites.net - Custom domain:
www.contoso.com
Using a custom domain allows you to:
- Establish a branded, user-friendly web address.
- Improve trust and credibility with customers.
- Manage and secure traffic to your application.
Steps to configure a custom domain name for your app
Creating a custom domain name requires providers, security, and naming information.
There are three steps to create a custom domain name.
Reserve your domain name. The easiest way to set up a custom domain is to buy one directly in the Azure portal. (This name isn't the Azure assigned name of
\*.azurewebsites.net.) The registration process enables you to manage your web app's domain name directly in the Azure portal instead of going to a third-party site. Configuring the domain name in your web app is also a simple process in the Azure portal.Create DNS records to map the domain to your Azure web app. The Domain Name System (DNS) uses data records to map domain names to IP addresses. There are several types of DNS records.
For web apps, you create either an
A(Address) record or aCNAME(Canonical Name) record.- An
Arecord maps a domain name to an IP address. - A
CNAMErecord maps a domain name to another domain name. DNS uses the second name to look up the address. Users still see the first domain name in their browser. As an example, you could mapcontoso.comto yourwebapp.azurewebsites.netURL.
- An
If the IP address changes, a
CNAMEentry is still valid, whereas anArecord must be updated.Some domain registrars don't allow
CNAMErecords for the root domain or for wildcard domains. In such cases, you must use anArecord.
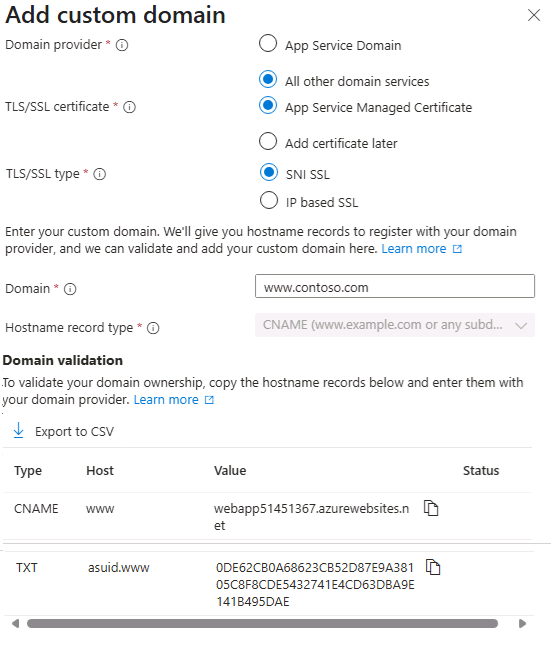
Enable the custom domain. After you have your domain and create your DNS record, use the Azure portal to validate your custom domain and add it to your web app. Be sure to test your domain before publishing.
Important
To map a custom DNS name to your app, you need a paid tier of an App Service plan for your app.