Topology
Azure Network Watcher’s Topology functionality provides a visualization of the entire network for understanding network configuration. It provides an interactive interface to view resources and their relationships in Azure spanning across multiple subscriptions, resource groups, and locations. You can also drill down to a resource view for resources to view their component level visualization.
The following are the resource types supported by topology:
- Application gateways
- Azure Bastion hosts
- Azure Front Door profiles
- ExpressRoute circuits
- Load balancers
- Network interfaces
- Network security groups
- Private endpoints
- Private Link services
- Public IP addresses
- Virtual machines
- Virtual network gateways
- Virtual networks
To view a topology, follow these steps:
- In the search box at the top of the Azure portal, enter Monitor. Select Monitor from the search results.
- Under Insights, select Networks.
- In Networks, select Topology.
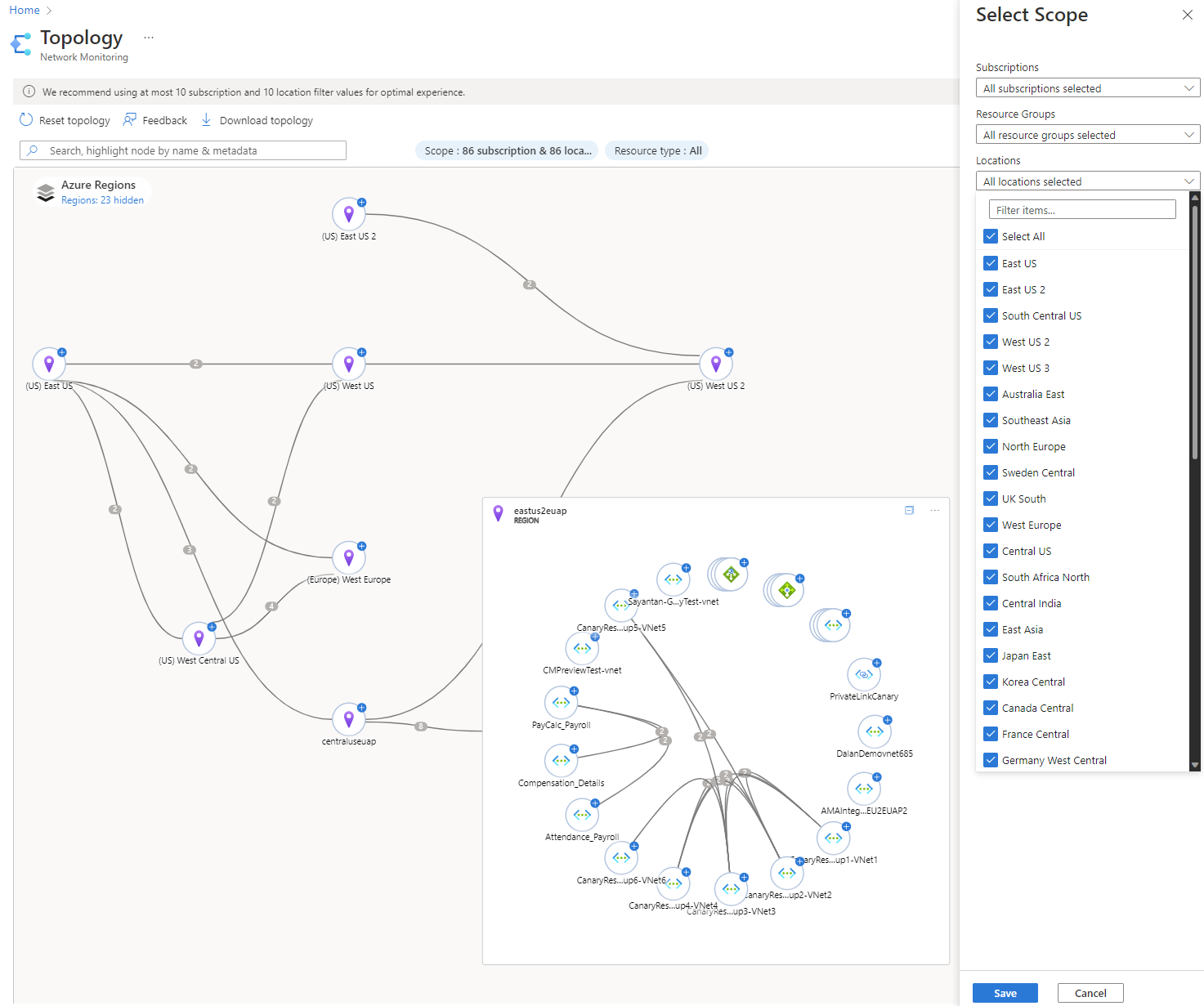
- Select Scope to define the scope of the Topology.
- In the Select scope pane, select the list of Subscriptions, Resource groups, and Locations of the resources for which you want to view the topology. Select Save.
- Select the Resource type that you want to include in the topology and select Apply.
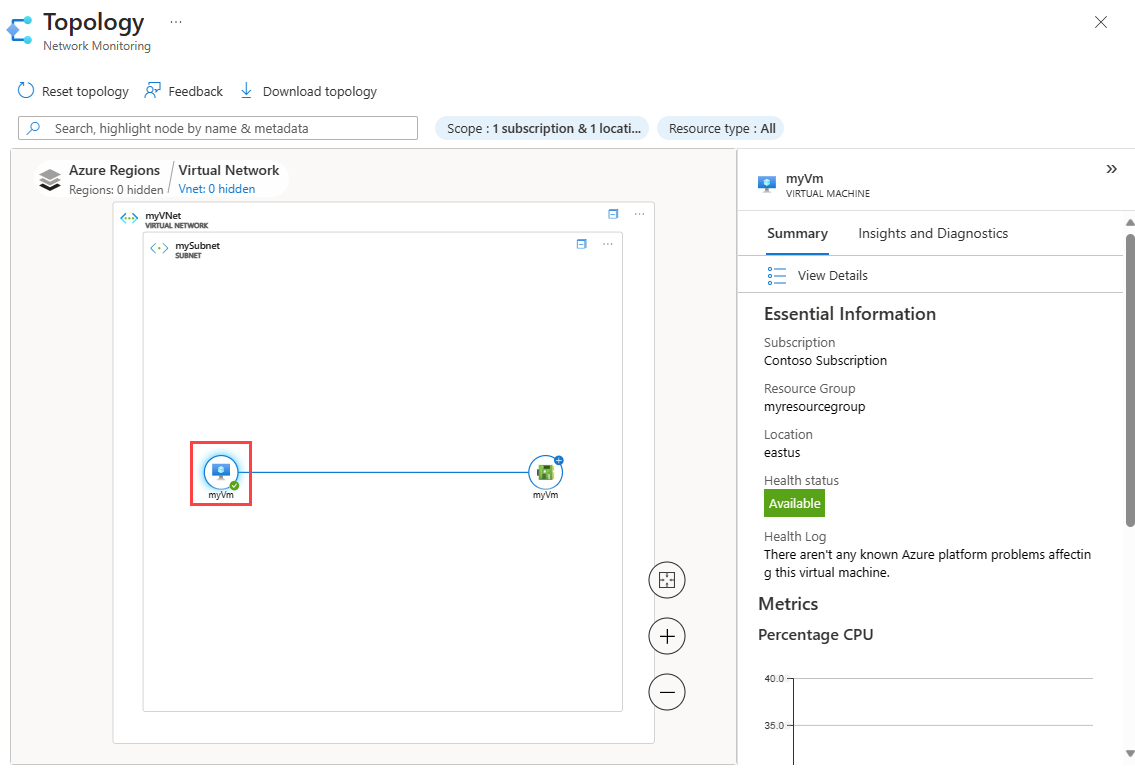
To drill down to the basic unit of each network, select the plus sign on each resource. When you hover on the resource, you can see the details of that resource. Selecting a resource displays a pane on the right with a summary of the resource. When you drill down to a VM within the topology, you can see details about the VM in the summary tab.
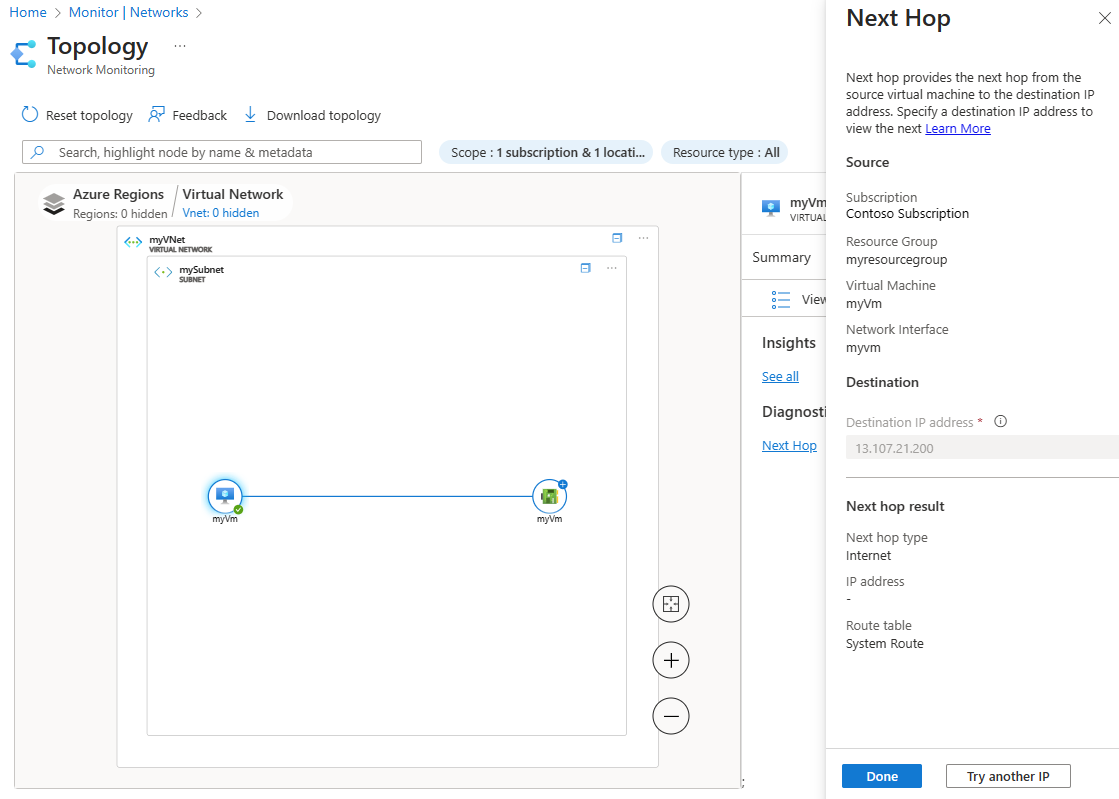
The Next hop capability of Network Watcher checks if the destination IP address is reachable from the source VM. Azure Network Watcher next hop gives you the Next hop type, IP address, and Route table ID of a specific destination IP address. Knowing the next hop helps you determine if traffic is being directed to the intended destination, or whether the traffic is being sent nowhere. An improper configuration of routes, where traffic is directed to an on-premises location, or a network virtual appliance, can lead to connectivity issues. If the route is defined using a user-defined route, the route table that has the route is returned. Otherwise, next hop returns System Route as the route table. The result shows the Next hop type and route table used to route traffic from the VM.