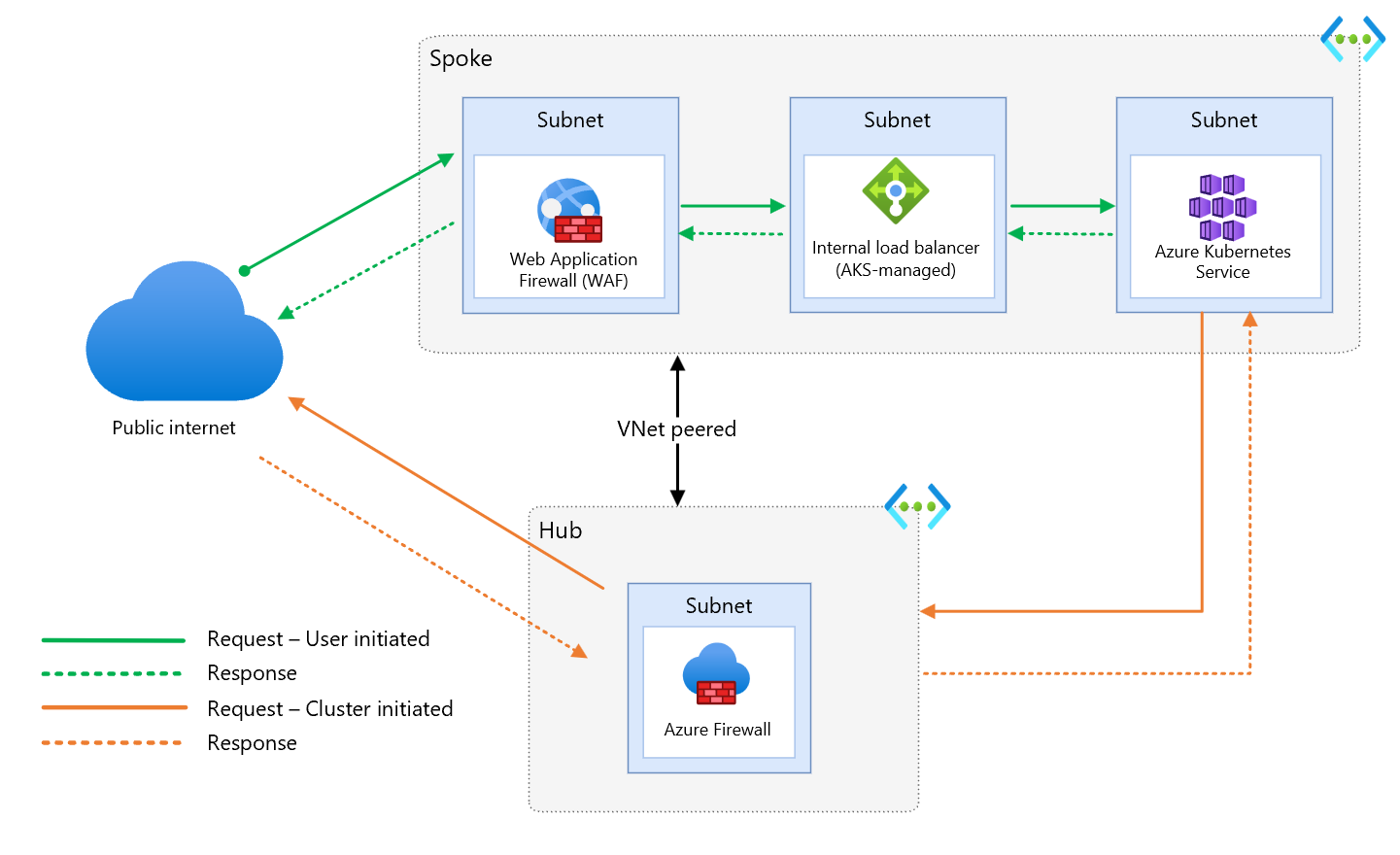
Secure the network flow
Network flow can be categorized as:
- Ingress traffic: From the client, to the workload running in the cluster.
- Egress traffic: From a pod or node, in the cluster to an external service.
- Pod-to-pod traffic: Communication between pods. This traffic includes communication between the ingress controller and the workload. Also, if your workload is composed of multiple applications deployed to the cluster, communication between those applications would fall into this category.
- Management traffic:Traffic that goes between the client and the Kubernetes API server.
This architecture has several layers of security to secure all types of traffic.
Ingress traffic flow
The architecture only accepts TLS encrypted requests from the client. TLS v1.2 is the minimum allowed version with a restricted set of cyphers. Server Name Indication (SNI) strict is enabled. End-to-end TLS is set up through Application Gateway by using two different TLS certificates, as shown in this image.
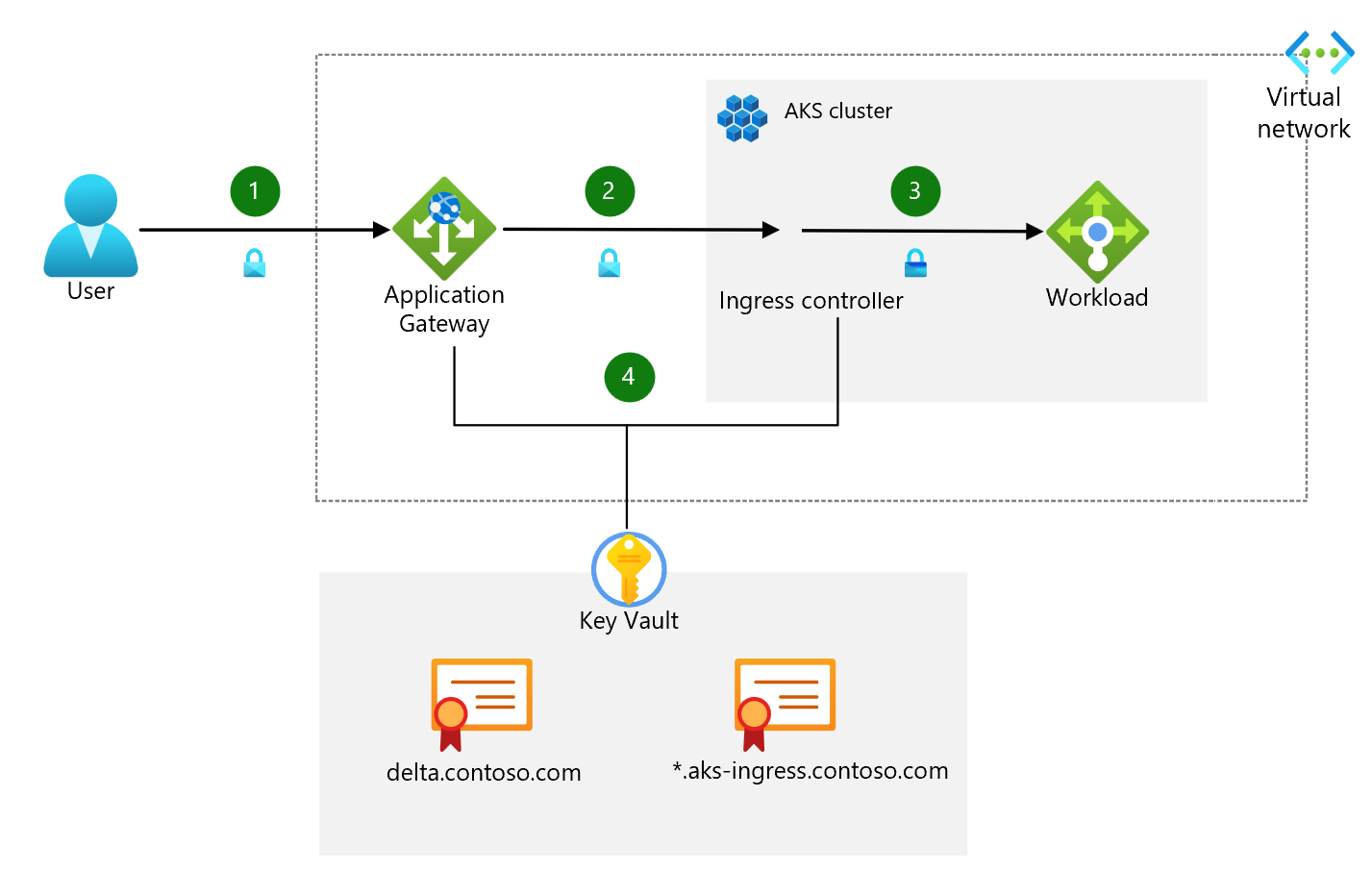
- The client sends an HTTPS request to the domain name: delta.contoso.com. That name is associated with through a DNS A record to the public IP address of Azure Application Gateway. This traffic is encrypted to make sure that the traffic between the client browser and gateway can't be inspected or changed.
- Application Gateway has an integrated web application firewall (WAF) and negotiates the TLS handshake for delta.contoso.com, allowing only secure ciphers. Application Gateway is a TLS termination point, as it's required to process WAF inspection rules, and execute routing rules that forward the traffic to the configured backend. The TLS certificate is stored in Azure Key Vault. It's accessed using a user-assigned managed identity integrated with Application Gateway.
- As traffic moves from Application Gateway to the backend, it's encrypted again with another TLS certificate (wildcard for *.aks-ingress.contoso.com) as it's forwarded to the internal load balancer. This re-encryption makes sure traffic that isn't secure doesn't flow into the cluster subnet.
- The ingress controller receives the encrypted traffic through the load balancer. The controller is another TLS termination point for *.aks-ingress.contoso.com and forwards the traffic to the workload pods over HTTP. The certificates are stored in Azure Key Vault and mounted into the cluster using the Container Storage Interface (CSI) driver.
You can implement end-to-end TLS traffic all at every hop the way through to the workload pod.