Design a caching solution
Caching is a common technique that aims to improve the performance and scalability of a system. Caching temporarily copies frequently accessed data to fast storage located close to the application. When the fast data storage is located closer to an application than its original data store, caching can significantly improve response times for client applications by serving data more quickly.
Caching is most effective when a client instance repeatedly reads the same data, especially when the following conditions apply to the original data store:
- The original data store remains relatively static.
- It's subject to a high level of contention.
- It's far away, and network latency can result in slow access to the store.
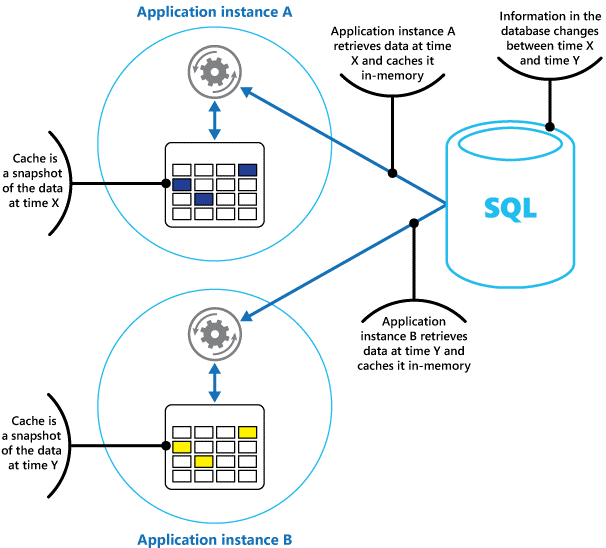
Suppose Tailwind Traders is adding a new feature to the product demo application to increase customer traffic to their retail website. The event feature adds a banner to the top of the mobile app to announce special offers and limited product discounts. New offers are posted on the hour, and the remaining product availability for each offer is updated after every order is processed. The first customer to respond to a new offer receives a double discount! Customers are encouraged to check their mobile app frequently for updates to the offers and product availability. To implement this new feature, you need to design a caching solution that can support in-memory fast read and writes.
Things to know about Azure Cache for Redis
Azure Cache for Redis provides an in-memory data store based on the Redis software. Redis improves the performance and scalability of an application that uses back-end data stores heavily. It's able to process large volumes of application requests by keeping frequently accessed data in the server memory, which can be written to and read from quickly. Redis brings a critical low-latency and high-throughput data storage solution to modern applications.
Let's review the characteristics of the service:
Azure Cache for Redis offers two implementation options for developers:
- The Redis open source (OSS Redis)
- A commercial product from Redis Labs (Redis Enterprise) as a managed service
Azure Cache for Redis provides secure and dedicated Redis server instances and full Redis API compatibility.
You can use Azure Cache for Redis as a distributed data or content cache, session store, or message broker.
Deploy Azure Cache for Redis as a standalone or with other Azure database services, such as Azure SQL or Azure Cosmos DB.
How Azure Cache for Redis works
Azure Cache for Redis is hosted on Azure, and usable by any application within or outside of Azure. As indicated in the following graphic, Azure Cache for Redis can help improve performance in apps that interface with many database solutions, including Azure SQL Database, Azure Cosmos DB, and Azure Database for MySQL.
Things to consider when using Azure Cache for Redis
Azure Cache for Redis improves application performance by supporting common application architecture patterns. As you review the following patterns, consider patterns that might be exhibited in the Tailwind Traders application architecture. Think about how Azure Cache for Redis can supply the pattern requirements.
| Pattern | Scenario | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Data cache | Databases are often too large to load directly into a cache. | It's common to use the cache-aside pattern to only load data into the cache as needed. When the system makes changes to the data, the system can also update the cache, which is then distributed to other clients. Additionally, the system can set an expiration on data, or use an eviction policy to trigger data updates into the cache. |
| Content cache | Many web pages are generated from templates that use static content such as headers, footers, banners. These static items shouldn't change often. | Using an in-memory cache provides quick access to static content compared to back-end datastores. This pattern reduces processing time and server load and allows web servers to be more responsive. A content cache can allow you to reduce the number of servers needed to handle loads. Azure Cache for Redis provides the Redis Output Cache Provider to support this pattern with ASP.NET. |
| Session store | A session store is commonly used with shopping carts and other user history data that a web application might associate with user cookies. Storing too much in a cookie can have a negative effect on performance as the cookie size grows and is passed and validated with every request. | A typical solution uses the cookie as a key to query the data in a database. It's faster to use an in-memory cache like Azure Cache for Redis to associate information with a user than interacting with a full relational database. |
| Job and message queuing | Some application operations take significant time to complete, which might prevent other unrelated jobs or messages from starting. | Applications often add tasks to a queue when the operations associated with the request take time to execute. Longer running operations are queued to be processed in sequence, often by another server. This method of deferring work is called task queuing. Azure Cache for Redis provides a distributed queue to enable this pattern in your application. |
| Distributed transactions | Applications sometimes require a series of commands against a back-end datastore to execute as a single atomic operation. All commands must succeed, or all commands must be rolled back to the initial state. | Azure Cache for Redis supports executing a batch of commands as a single transaction. |