Design for Azure Batch solutions
Azure Batch runs large-scale applications efficiently in the cloud. You can schedule compute-intensive tasks and dynamically adjust resources for your solution without managing infrastructure. Azure Batch can create and manage a pool of compute nodes (virtual machines). Azure Batch can also install the application you want to run, and schedule jobs to run on the compute nodes.
Things to know about Azure Batch
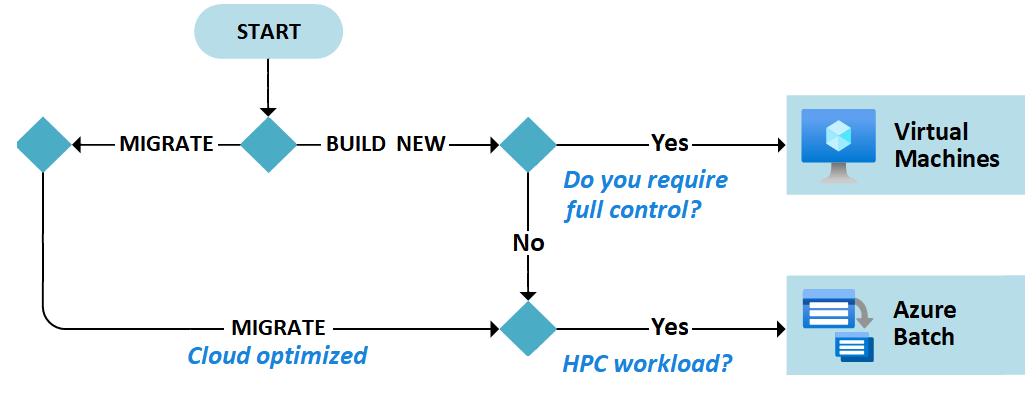
There are many scenarios where Azure Batch can be an ideal compute solution for your infrastructure. Azure Batch is similar to Azure Virtual Machines and can be used to build new workloads and migrate data.
Azure Batch works well with applications that run independently (parallel workloads).
Azure Batch is effective for applications that need to communicate with each other (tightly coupled workloads). You can use Batch to build a service that runs a Monte Carlo simulation for a financial services company or a service to process images.
Azure Batch enables large-scale parallel and high-performance computing (HPC) batch jobs with the ability to scale to tens, hundreds, or thousands of virtual machines. When you're ready to run a job, Azure Batch:
- Starts a pool of compute virtual machines for you.
- Installs applications and staging data.
- Runs jobs with as many tasks as you have.
- Identifies failures, requeues work, and scales down the pool as work completes.
How Azure Batch works
A typical real-world scenario for Azure Batch requires data and application files. The Batch workflow begins with uploading the data and application files to an Azure storage account. Based on the demand, you create a Batch pool with as many Windows or Linux virtual compute nodes as needed. If the demand increases, compute nodes can be automatically scaled.
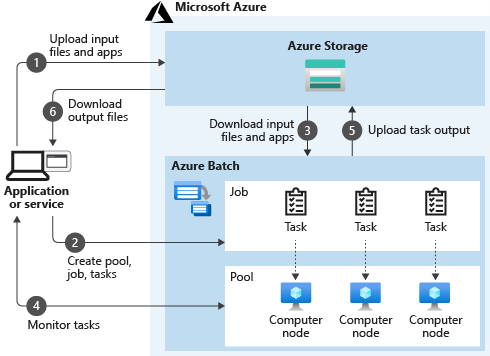
As you plan for your own configuration, you can separate aspects of the scenario into two parts: your service and the Azure Batch compute.
Your service uses Azure as the platform. The platform is used for completing computationally intensive work and retrieving results. You can also monitor jobs and task progress.
Azure Batch operates as the compute platform behind your service. Batch uses Azure Storage to fetch applications or data needed to complete a task. Azure Batch writes output to Azure Storage. Behind the scenes, there are collections (pools) of virtual machines. Pools are the resources that jobs and tasks are executed on.
Things to consider when using Azure Batch
Let's look at some best practices for using Azure Batch. As you review the suggestions, think about what scenarios can be accomplished by integrating Azure Batch in the Tailwind Traders infrastructure.
Consider pools. If your jobs consist of short-running tasks, don't create a new pool for each job. The overhead to create new pools diminishes the run time of the job. Also, it's best to have your jobs use pools dynamically. If your jobs use the same pool for everything, there's a higher chance of failure.
Consider nodes. Individual nodes aren't guaranteed to always be available. If your Azure Batch workload requires deterministic, guaranteed progress, you should allocate pools with multiple nodes. Consider using isolated virtual machine sizes for workloads with compliance or regulatory requirements.
Consider jobs. Uniquely name your jobs so you can accurately monitor and log the activity. Consider grouping your tasks into efficiently sized jobs. It's more efficient to use a single job that contains 1,000 tasks rather than creating 100 jobs that have 10 tasks each.