Recommend a solution for database scalability
As the CTO for Tailwind Traders, you're interested in a low latency and high availability database solution to store relational data. After reviewing the five deployment options, you decide to implement Azure SQL Database for its fully managed service features. You're hoping to gain the high availability SLA offered in the Business Critical service tier when using availability zones.
Your next decision is how to support scalability for a relational database. You need a dynamically scalable solution that can handle an expanding number of requests over time without a negative effect on availability or performance.
Azure SQL Database and dynamic scalability
Azure SQL Database supports dynamic scalability. You can easily change resources allocated to your databases, such as CPU power, memory, I/O throughput, and storage with minimal downtime. Use the Azure portal to scale an Azure SQL Database without changing the existing infrastructure or purchasing new hardware.
Things to know about dynamic scalability
Review the following characteristics of dynamic scalability for an Azure SQL database:
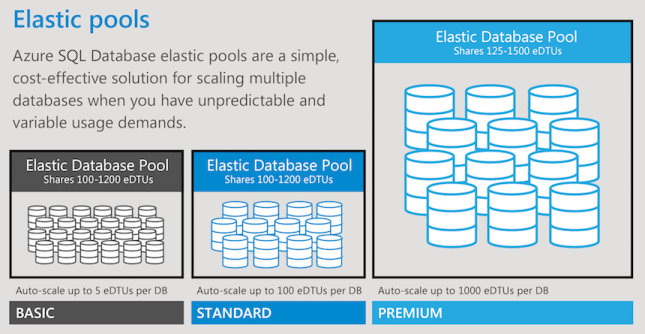
Choose DTU or vCore models, and define the maximum amount of resources to assign to each database with a single database implementation.
Use elastic database pools, and purchase resources for the group, and set minimum and maximum resource limits for the databases within the pool.
Implement vertical or horizontal scaling:
Vertical: Increase or decrease the compute size of an individual database, also called scaling up. Implement vertical scaling by using SQL Database elastic database pools. When you have low average utilization, but infrequent, high utilization spikes, you can allocate enough capacity in the pool to manage the spikes for the group.
Horizontal: Add or remove databases to adjust capacity or overall performance, also called scaling out. Apply horizontal scaling by using sharding to partition data or read scale-out provisioning.
Business scenario
Let's explore a business scenario for using vertical scaling. A small business experiences rapid growth globally. The company needs to maintain and scale separate SQL databases for each location. The rates of growth and database load vary significantly. Resource requirements are unpredictable. The ideal dynamic scaling solution is to use SQL elastic database pools with vertical scaling. You can scale, manage performance, and manage costs for a set of SQL databases. For more information, see SQL elastic database pools.
Things to consider when choosing scalability solutions
Review the following scaling scenarios, and think about which database scaling strategy can work for Tailwind Traders.
| Scenario | Scaling solution |
|---|---|
| Manage and scale multiple Azure SQL databases that have varying and unpredictable resource requirements | Elastic database pools and vertical scaling. Use elastic database pools to ensure databases get the performance resources they need when they need it. Elastic pools provide a simple resource allocation mechanism within a predictable budget. There's no per-database charge for elastic pools. You're billed for each hour a pool exists at the highest eDTU or vCores, regardless of usage or whether the pool was active for less than an hour. |
| Different sections of a database reside in different geographic locations for compliance reasons | Horizontal scaling and sharding. Use sharding to split your data into several databases and scale them independently. The shard map manager is a special database that maintains global mapping information about all shards (databases) in a shard set. The metadata allows an application to connect to the correct database based on the value of the sharding key. |
| Dependency support for commercial BI or data integration tools, where multiple databases contribute rows into a single overall result for use in Excel, Power BI, or Tableau | Elastic database tools and elastic query. Use the Elastic database tools elastic query feature to access data spread across multiple databases. Elastic query is available on the Standard tier. Querying can be done in T-SQL that spans multiple databases in Azure SQL Database. Run cross-database queries to access remote tables, and to connect tools (Excel, Power BI, Tableau, and so on) and query across data tiers. You can scale out queries to large data tiers and visualize the results in business intelligence reports. |