Design for Azure Policy
Azure Policy is a service in Azure that enables you to create, assign, and manage policies to control or audit your resources. These policies enforce different rules over your resource configurations so the configurations stay compliant with corporate standards.
Things to know about Azure Policy
As you plan the governance strategy for Tailwind Traders, consider these characteristics of Azure Policy:
Azure Policy lets you define both individual policies and groups of related policies, called initiatives. Azure Policy comes with many built-in policy and initiative definitions.
Azure policies are inherited down the hierarchy.
You can scope and enforce Azure policies at different levels in the organizational hierarchy.
Azure Policy evaluates all resources in Azure and Arc-enabled resources (specific resource types that are hosted outside of Azure).
Azure Policy highlights resources that aren't compliant with the current policies.
Use Azure Policy to prevent noncompliant resources from being created, and automatically remediate noncompliant resources.
Azure Policy integrates with Azure Pipelines by applying predeployment and post-deployment policies.
Things to consider when using Azure Policy
You're ready to consider how to apply Azure Policy settings to your Tailwind Traders applications. You apply some policies at the Production management group level. Other policies can be assigned at the application level.
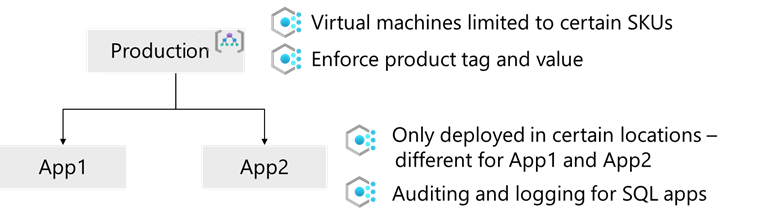
Consider using the Azure Policy compliance dashboard. Use the Azure Policy compliance dashboard to analyze the overall state of the environment. The dashboard offers an aggregated view where you can drill down to see Tailwind Traders policies for each resource and level. The tool provides bulk remediation for existing resources and automatic remediation for new resources, to resolve issues rapidly and effectively.
Consider when Azure Policy evaluates resources. Plan for how Azure Policy evaluates your Tailwind Traders resources at specific times. Understand when and how evaluations are triggered. There might be a delay in identifying noncompliant resources. The following events or times trigger an evaluation:
A resource is created, deleted, or updated in scope with a policy assignment.
A policy or an initiative is newly assigned to a scope.
An assigned policy or initiative for a scope is updated.
The standard compliance evaluation cycle (occurs once every 24 hours).
Consider how to handle a noncompliant resource. Determine how you're going to handle noncompliant resources for Tailwind Traders. An organization can have a different way of handling noncompliance depending on the resource. Here are some examples:
Deny changes to the resource.
Log changes to the resource.
Alter the resource before or after the change.
Deploy related compliant resources.
Consider when to automatically remediate noncompliant resources. Decide if you want Azure Policy to do automatic remediation for noncompliant resources. Remediation is especially useful in resource tagging. Azure Policy can tag resources and reapply tags that are removed. You can use Azure Policy to ensure all resources in a certain resource group are tagged with a specific tag like
Locationto identify the region.Consider how Azure Policy is different from role-based access control (RBAC). It's important to understand that Azure Policy and Azure RBAC are different. For your Tailwind Traders strategy, Azure RBAC and Azure Policy should be used together to achieve full scope control.
You use Azure Policy to ensure the resource state is compliant with the organization's business rules. Compliance doesn't depend on who made the change or who has permission to make changes. Azure Policy evaluates the state of a resource, and acts to ensure the resource stays compliant.
You implement Azure RBAC to focus on user actions at different scopes. Azure RBAC manages who can access Azure resources, what they can do with those resources, and what areas they can access. If actions need to be controlled, use Azure RBAC. If a user has access to complete an action, but the result is a noncompliant resource, Azure Policy still blocks the action.
Control resource access
After you determine your identity management solution for Tailwind Traders, it's time to think about resource access. What resources should these identities be able to access? How do you enforce that access? How do you monitor and review the access?
A user's identity goes through several phases. Initially, the user has no access. Access can be granted through RBAC and verified with Microsoft Entra Conditional Access. Microsoft Entra ID Protection can be used to monitor the user's access. Periodically, Microsoft Entra access reviews confirm the access is still required.