Connect devices to networks with Point-to-site VPN connections
A Point-to-Site (P2S) VPN gateway connection lets you create a secure connection to your virtual network from an individual client computer.
A P2S connection is established by starting it from the client computer. This solution is useful for telecommuters who want to connect to Azure VNets from a remote location, such as from home or a conference. P2S VPN is also a useful solution to use instead of S2S VPN when you have only a few clients that need to connect to a VNet.
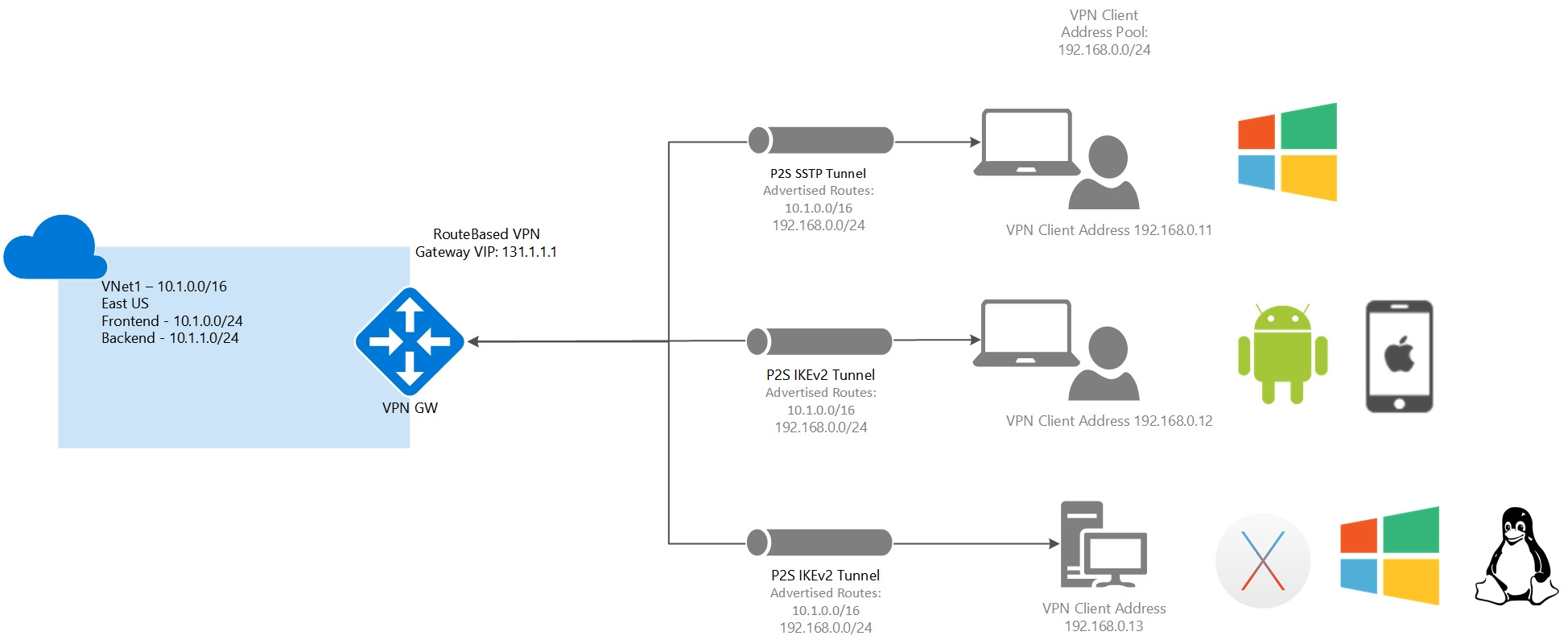
Point-to-site protocols
Point-to-site VPN can use one of the following protocols:
- OpenVPN® Protocol, an SSL/TLS based VPN protocol. A TLS VPN solution can penetrate firewalls, since most firewalls open TCP port 443 outbound, which TLS uses. OpenVPN can be used to connect from Android, iOS (versions 11.0 and above), Windows, Linux, and Mac devices (macOS versions 10.13 and above).
- Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP), a proprietary TLS-based VPN protocol. A TLS VPN solution can penetrate firewalls, since most firewalls open TCP port 443 outbound, which TLS uses. SSTP is only supported on Windows devices. Azure supports all versions of Windows that have SSTP (Windows 7 and later).
- IKEv2 VPN, a standards-based IPsec VPN solution. IKEv2 VPN can be used to connect from Mac devices (macOS versions 10.11 and above).
Point-to-site authentication methods
The user must be authenticated before Azure accepts a P2S VPN connection. The two most common authentication methods are: Entra ID authentication and on-premises Active Directory Domain Services authentication.
Authenticate using native Microsoft Entra ID authentication
Native authentication allows users to connect to Azure using their Microsoft Entra ID credentials. Native authentication is only supported for OpenVPN protocol and Windows and requires the use of the Azure VPN Client. With this authentication, you can use conditional access and multifactor authentication (MFA) features for VPN.
Authenticate using Active Directory Domain Services
This authentication is a popular option because it allows users to connect to Azure using their organization domain credentials. It requires a RADIUS server that integrates with the server. Organizations can also use their existing RADIUS deployment.
The RADIUS server is deployed either on-premises or in your Azure VNet. During authentication, the Azure VPN Gateway passes authentication messages back and forth between the RADIUS server and the connecting device. Thus, the Gateway must be able to communicate with the RADIUS server. If the RADIUS server is present on-premises, then a VPN S2S connection from Azure to the on-premises site is required for reachability.