Get network security recommendations with Microsoft Defender for Cloud
- 7 minutes
Network security covers various technologies, devices, and processes. Security provides a set of rules and configurations designed to protect the integrity, confidentiality, and accessibility of computer networks and data. Every organization, regardless of size, industry, or infrastructure, requires a degree of network security solutions. These solutions protect from the ever-growing risks of attacks.
Network security provides controls to secure and protect Azure networks. These controls include securing virtual networks, establishing private connections, preventing and mitigating external attacks, and securing DNS.
A full description of the network security controls can be found at Security Control V3: Network Security on Microsoft Learn.
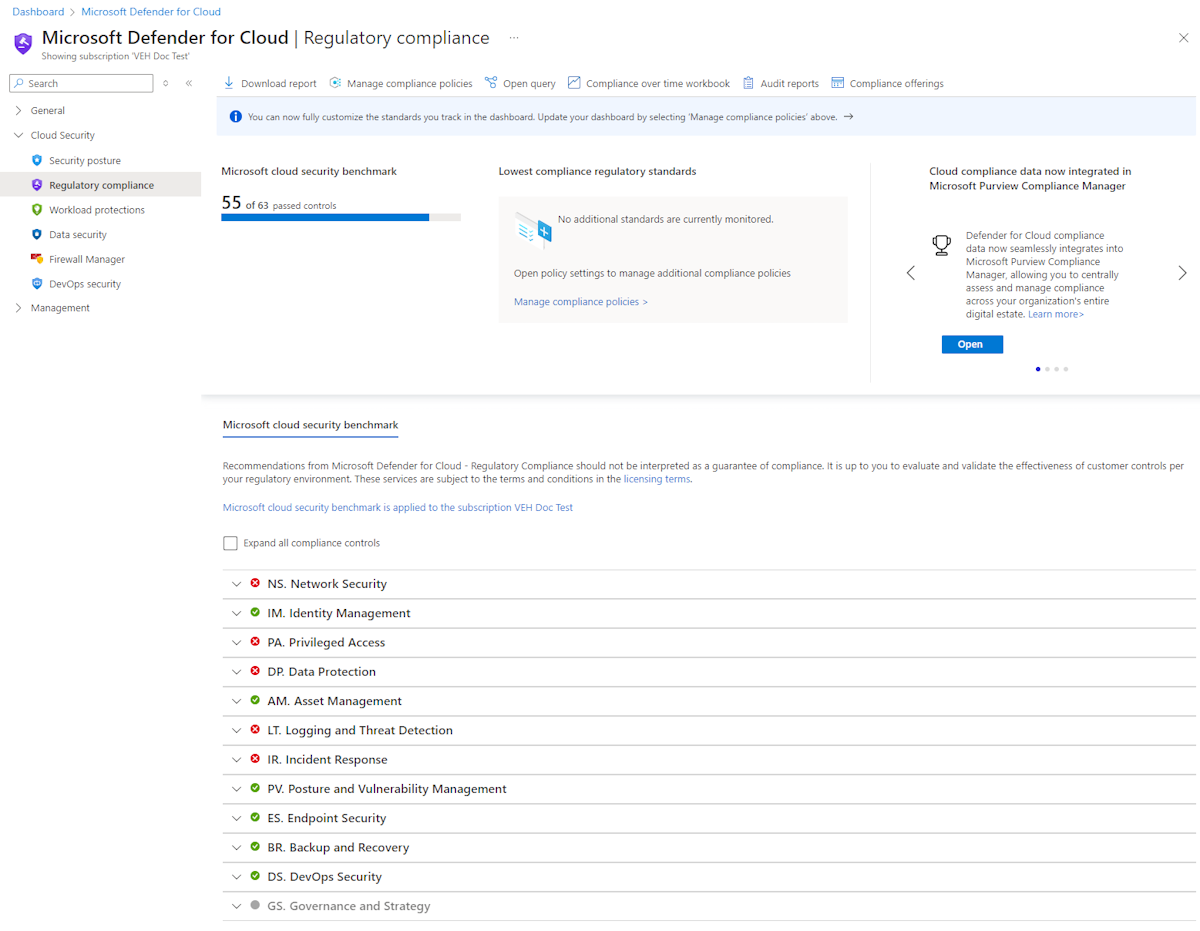
Using Microsoft Defender for Cloud for regulatory compliance
Microsoft Defender for Cloud helps streamline the process for meeting network regulatory compliance requirements.
The regulatory compliance dashboard shows the status of all the assessments within your environment for your chosen standards and regulations. As you act on the recommendations and reduce risk factors in your environment, your compliance posture improves. You can also view the overall compliance score, and the number of passing vs. failing assessments associated with each standard.
Compliance controls
For each security control, you can drill down into more information.
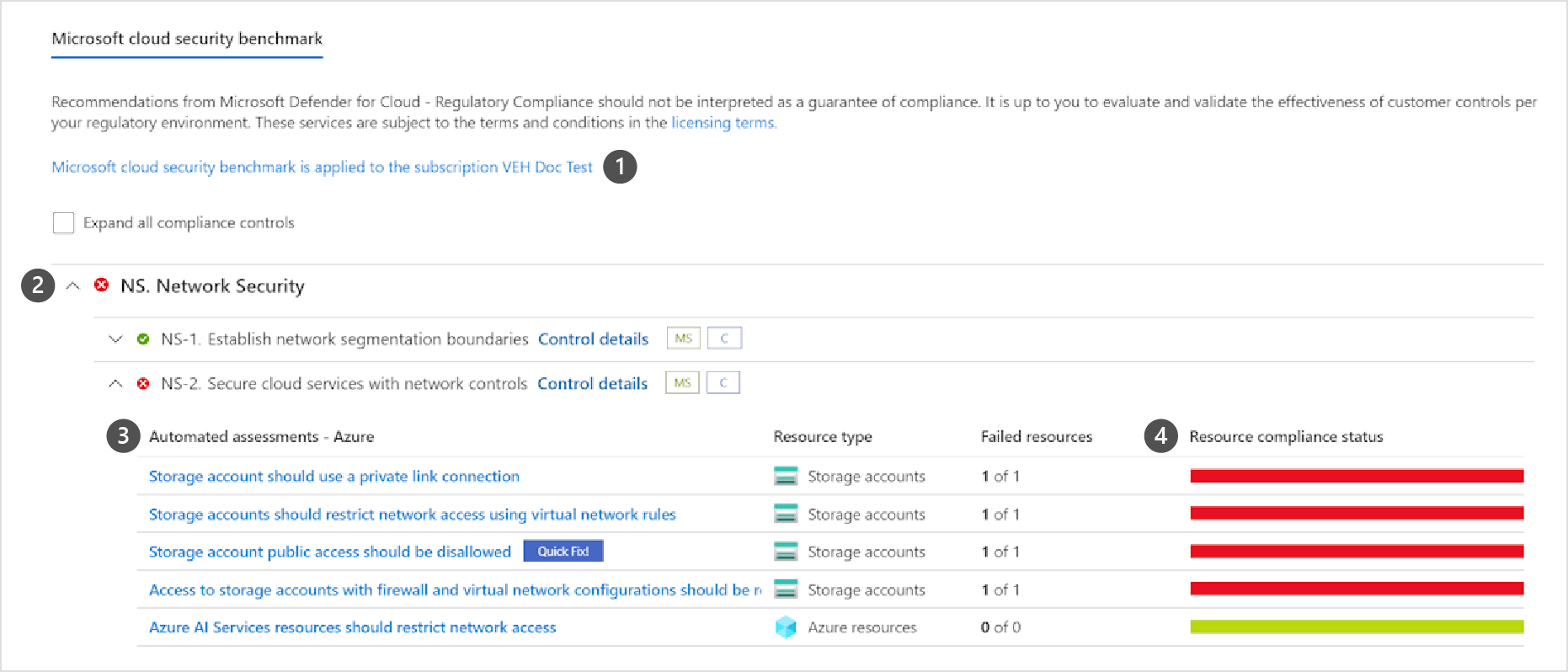
- Subscriptions the standard is applied on.
- List of all controls for that standard.
- View the details of passing and failing assessments associated with that control.
- Number of affected resources.
- Severity of the alert.
Tip
Learn more with the Examine Defender for Cloud regulatory compliance standards module.