What is SSH?
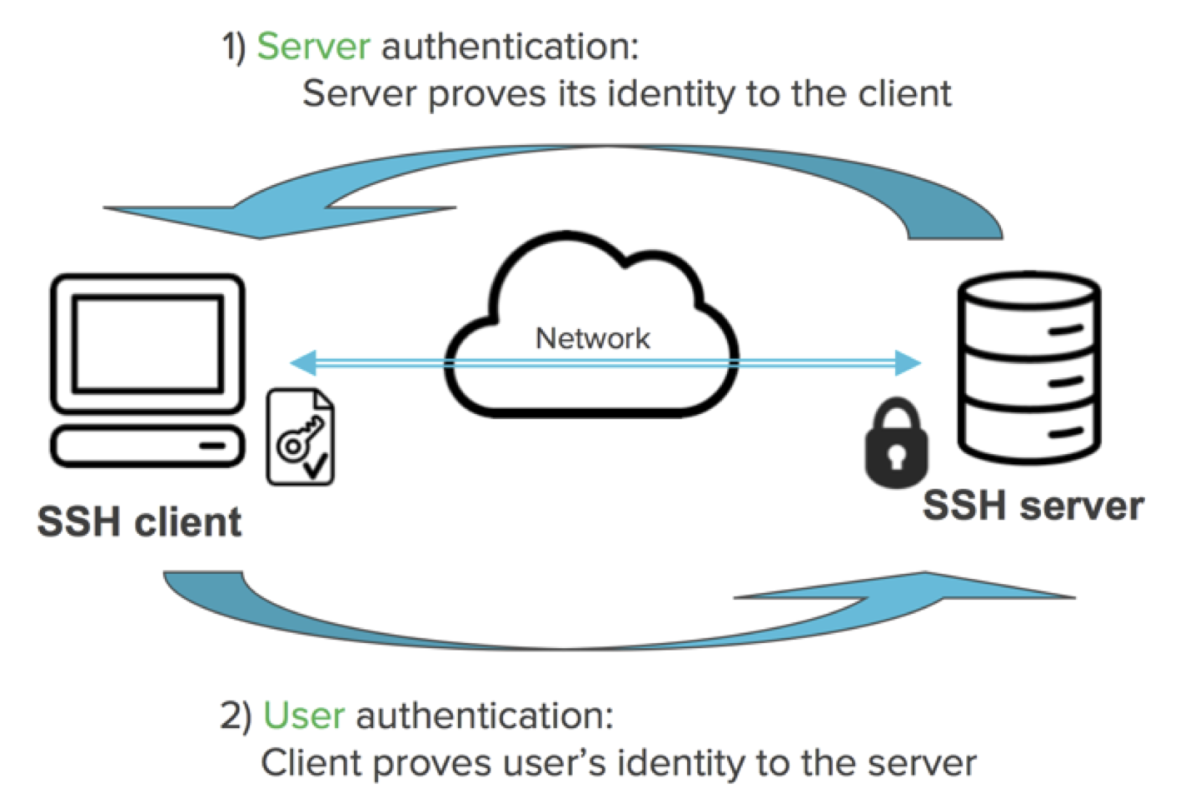
SSH stands for the secure shell protocol. SSH uses a client-server connection to set up a tunnel between a local machine (the client) and a remote machine (the server). SSH enables you to access a remote machine, virtual machine, or container securely over a network connection. You can think of the computer you're using right now as your local machine, and a virtual machine or physical machine in the office as the remote machine you need to access.
To connect using SSH, you must have a running SSH server. Most commonly, the connection is authenticated using SSH keys, which involves generating a public and private key pair. Once the key pair is generated, the public key is placed on the server and the private key is kept secret on the client. When a connection is initiated, the server verifies that the client has the correct private key. Once verified, the client is granted access to the server, and a secure connection is established.
Using SSH for development
You want to explore setting up a remote machine for each application your agency works on. Each machine is its own remote development environment that you can access without needing any application files on your local machine. Here are some ways that connecting to a remote machine using SSH can benefit your agency:
- Securely connect to the remote machine that has the same operating system where your application is deployed.
- Seamlessly switch between SSH connections depending on which application you're working on.
- Automatically have the right tools and dependencies installed on the remote machine.
- Access the remote development environment from your different machines or locations.
Configuring a remote machine for SSH
One way to set up a remote machine is to configure a virtual machine (VM) to use SSH. There are a lot of different configuration options for VMs, such as the operating system and size. The VM should be configured with the same properties you need for developing your agency's applications. For example, if the application is deployed on a Linux machine, you should use a Linux VM.
The VM must also be configured to use SSH by generating the SSH key pair and allowing inbound connections on port 22. Port 22 is the default port used for SSH connections. Once these SSH settings are configured on the VM, the VM becomes an SSH server with a unique public IP address for secure connections.
In the next section, you’ll configure a Linux VM to set up your own SSH server.