What is a runbook?
Runbooks serve as repositories for your custom scripts and workflows.
They also typically reference Automation shared resources such as credentials, variables, connections, and certificates.
Runbooks can also contain other runbooks, allowing you to build more complex workflows.
You can invoke and run runbooks on-demand or according to a schedule using Automation Schedule assets.
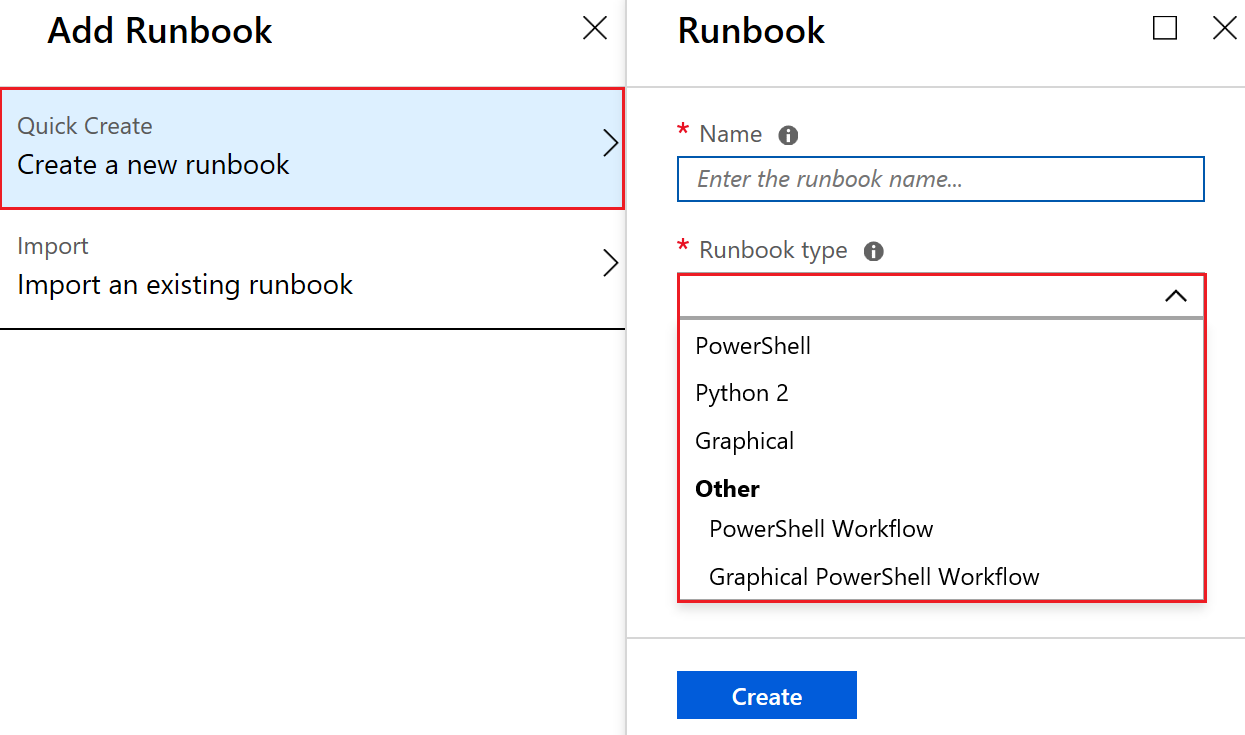
Creating runbooks
When creating runbooks, you have two options. You can either:
- Create your runbook and import it. For more information about creating or importing a runbook in Azure Automation, go to Start a runbook in Azure Automation.
- Modify runbooks from the runbook gallery. It provides a rich ecosystem of runbooks that are available for your requirements. Visit Runbook and module galleries for Azure Automation for more information.
A vibrant open-source community also creates runbooks you can apply directly to your use cases.
You can choose from different runbook types based on your requirements and Windows PowerShell experience.
If you prefer to work directly with Windows PowerShell code, you can use a PowerShell runbook or a PowerShell Workflow runbook.
You can edit offline or with the textual editor in the Azure portal using either of these.
If you prefer to edit a runbook without exposure to the underlying code, you can create a graphical runbook using the Azure portal's graphic editor.
Graphical runbooks
Graphical runbooks and Graphical PowerShell Workflow runbooks are created and edited with the graphic editor in the Azure portal.
You can export them to a file and import them into another automation account, but you can't create or edit them with another tool.
PowerShell runbooks
PowerShell runbooks are based on Windows PowerShell. You edit the runbook code directly using the text editor in the Azure portal.
You can also use any offline text editor and import the runbook into Azure Automation. PowerShell runbooks don't use parallel processing.
PowerShell Workflow runbooks
PowerShell Workflow runbooks are text runbooks based on Windows PowerShell Workflow.
You directly edit the runbook code using the text editor in the Azure portal.
You can also use any offline text editor and import the runbook into Azure Automation.
PowerShell Workflow runbooks use parallel processing to allow for the simultaneous completion of multiple tasks.
Workflow runbooks take longer to start than PowerShell runbooks because they must be compiled before running.
Python runbooks
You can directly edit the code of the runbook using the text editor in the Azure portal, or you can use any offline text editor and import the runbook into Azure Automation.
You can also use Python libraries. You must first import the package into the Automation Account to use third-party libraries.
Note
You can't convert runbooks from graphical to textual type and vice versa.
For more information on the different types of runbooks, visit Azure Automation runbook types.