Explore the resource hierarchy
The Azure Cosmos DB account is the fundamental unit of global distribution and high availability. Your Azure Cosmos DB account contains a unique Domain Name System (DNS) name and you can manage an account by using the Azure portal or the Azure CLI, or by using different language-specific SDKs. For globally distributing your data and throughput across multiple Azure regions, you can add and remove Azure regions to your account at any time.
Elements in an Azure Cosmos DB account
An Azure Cosmos DB container is the fundamental unit of scalability. You can virtually have an unlimited provisioned throughput (RU/s) and storage on a container. Azure Cosmos DB transparently partitions your container using the logical partition key that you specify in order to elastically scale your provisioned throughput and storage.
Currently, you can create a maximum of 50 Azure Cosmos DB accounts under an Azure subscription (can be increased via support request). After you create an account under your Azure subscription, you can manage the data in your account by creating databases, containers, and items.
The following image shows the hierarchy of different entities in an Azure Cosmos DB account:
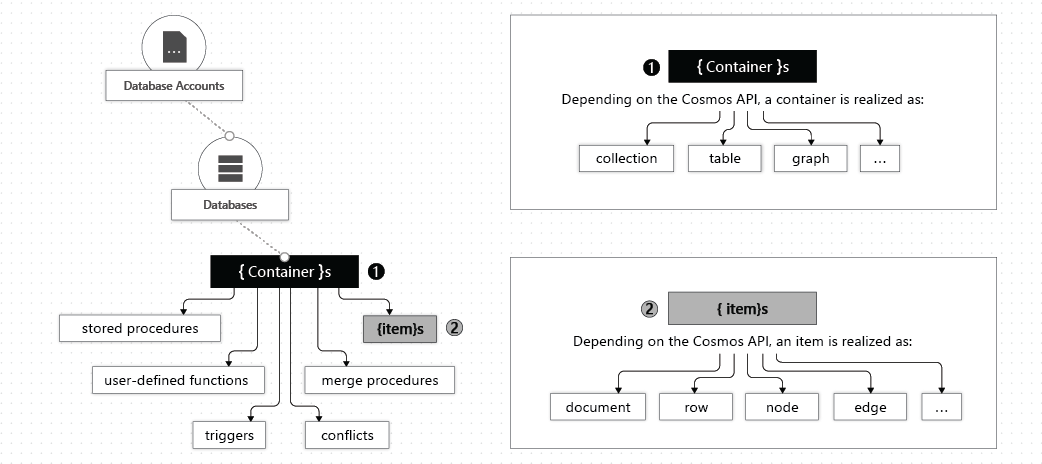
Azure Cosmos DB databases
You can create one or multiple Azure Cosmos DB databases under your account. A database is analogous to a namespace. A database is the unit of management for a set of Azure Cosmos DB containers.
Azure Cosmos DB containers
An Azure Cosmos DB container is where data is stored. Unlike most relational databases, which scale up with larger sizes of virtual machines, Azure Cosmos DB scales out.
Data is stored on one or more servers called partitions. To increase partitions, you increase throughput, or they grow automatically as storage increases. This relationship provides a virtually unlimited amount of throughput and storage for a container.
When you create a container, you need to supply a partition key. The partition key is a property that you select from your items to help Azure Cosmos DB distribute the data efficiently across partitions. Azure Cosmos DB uses the value of this property to route data to the appropriate partition to be written, updated, or deleted. You can also use the partition key in the WHERE clause in queries for efficient data retrieval.
The underlying storage mechanism for data in Azure Cosmos DB is called a physical partition. Physical partitions can have a throughput amount up to 10,000 Request Units per second, and they can store up to 50 GB of data. Azure Cosmos DB abstracts this partitioning concept with a logical partition, which can store up to 20 GB of data.
When you create a container, you configure throughput in one of the following modes:
Dedicated throughput: The throughput on a container is exclusively reserved for that container. There are two types of dedicated throughput: standard and autoscale.
Shared throughput: Throughput is specified at the database level and then shared with up to 25 containers within the database. Sharing of throughput excludes containers that are configured with their own dedicated throughput.
Azure Cosmos DB items
Depending on which API you use, individual data entities can be represented in various ways:
| Azure Cosmos DB entity | API for NoSQL | API for Cassandra | API for MongoDB | API for Gremlin | API for Table |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Azure Cosmos DB item | Item | Row | Document | Node or edge | Item |