Explore data analytics
Data analytics is concerned with examining, transforming, and arranging data so that you can study it and extract useful information. Data analytics is a discipline that covers the entire range of data management tasks. These tasks not only include analysis, but also data collection, organization, storage, and all the tools and techniques used.
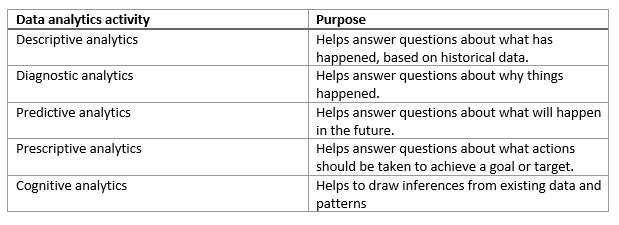
The term data analytics is a catch-all that covers a range of activities, each with its own focus and goals. You can categorize these activities as descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, prescriptive, and cognitive analytics.
In this unit, you'll learn about these categories of data analytics.
Descriptive analytics
Descriptive analytics helps answer questions about what has happened, based on historical data. Descriptive analytics techniques summarize large datasets to describe outcomes to stakeholders.
By developing KPIs (Key Performance Indicators), these strategies can help track the success or failure of key objectives. Metrics such as return on investment (ROI) are used in many industries. Specialized metrics are developed to track performance in specific industries.
Examples of descriptive analytics include generating reports to provide a view of an organization's sales and financial data.
Diagnostic analytics
Diagnostic analytics helps answer questions about why things happened. Diagnostic analytics techniques supplement more basic descriptive analytics. They take the findings from descriptive analytics and dig deeper to find the cause. The performance indicators are further investigated to discover why they got better or worse. This generally occurs in three steps:
- Identify anomalies in the data. These may be unexpected changes in a metric or a particular market.
- Collect data that's related to these anomalies.
- Use statistical techniques to discover relationships and trends that explain these anomalies.
Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics helps answer questions about what will happen in the future. Predictive analytics techniques use historical data to identify trends and determine if they're likely to recur. Predictive analytical tools provide valuable insight into what may happen in the future. Techniques include a variety of statistical and machine learning techniques such as neural networks, decision trees, and regression.
Prescriptive analytics
Prescriptive analytics helps answer questions about what actions should be taken to achieve a goal or target. By using insights from predictive analytics, data-driven decisions can be made. This technique allows businesses to make informed decisions in the face of uncertainty. Prescriptive analytics techniques rely on machine learning strategies to find patterns in large datasets. By analyzing past decisions and events, the likelihood of different outcomes can be estimated.
Cognitive analytics
Cognitive analytics attempts to draw inferences from existing data and patterns, derive conclusions based on existing knowledge bases, and then add these findings back into the knowledge base for future inferences--a self-learning feedback loop. Cognitive analytics helps you to learn what might happen if circumstances change, and how you might handle these situations.
Inferences aren't structured queries based on a rules database, rather they're unstructured hypotheses gathered from a number of sources, and expressed with varying degrees of confidence. Effective cognitive analytics depends on machine learning algorithms. It uses several NLP (Natural Language Processing) concepts to make sense of previously untapped data sources, such as call center conversation logs and product reviews.
Theoretically, by tapping the benefits of massive parallel/distributed computing and the falling costs of data storage and computing power, there's no limit to the cognitive development that these systems can achieve.