Describe customer journeys
A customer journey is a path a customer takes while interacting with your organization's marketing process. The goal of a completed journey is to generate revenue.
For example, a simple customer journey might look like this:
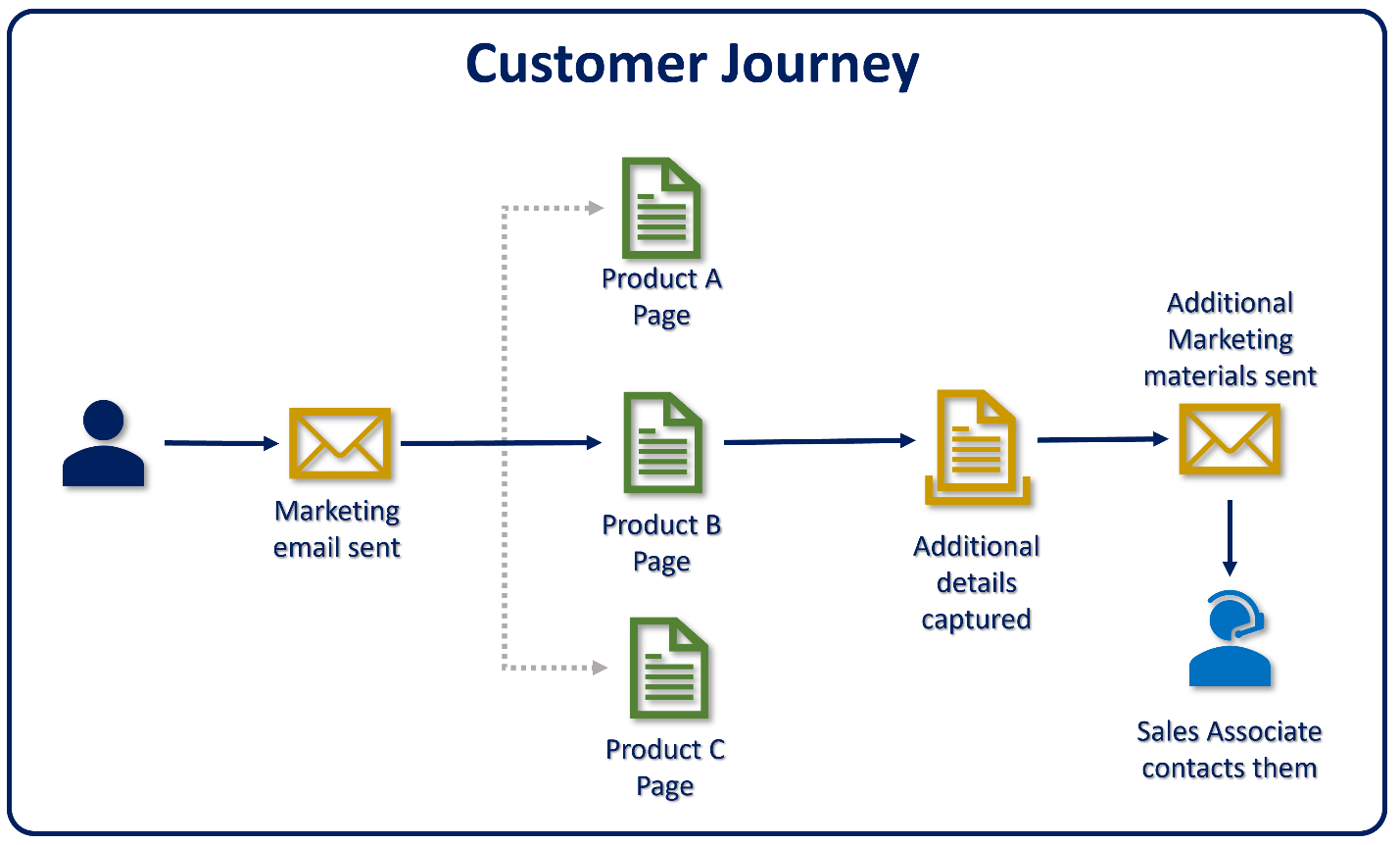
A potential customer opens a marketing email they received from Contoso Coffee.
The email includes multiple links the customer can click on to learn more about the different Contoso products highlighted in the email.
They're directed to a marketing page related to that product, based on the link they select.
The customer indicates they would like some additional information about the product they selected while they're on the marketing page.
The customer is sent targeted marketing materials, based on the request. A task is assigned to a Contoso Coffee sales associate to follow up with potential customers within a day or two, aiming to convert them into revenue.
Dynamics 365 Customer Insights - Journeys lets you create powerful customer journeys tailored to the products you're marketing and the objectives of your campaign. You can easily visualize and automate the journey customers take while interacting with your sales and marketing processes. From emails and task assignments to business workflows, decision points, and internal action items, journeys can be customized based on customer needs and preferences.
With customer journeys, you can:
Engage customers in real time
- With trigger-based customer journeys using email, text message, or push notification channels, organizations can trigger customer journeys in real time, pick the right channel for each individual, and react to customer-led actions in the moments that matter.
Win customers and earn loyalty faster
- Working across all customer touchpoints, real-time customer journeys are truly an end-to-end experience.
Personalize customer experiences with AI
- Turn insights into relevant action with AI-driven recommendations for content, channels, and analytics.
- Customer Insights - Data segment and profile integration allows organizations to seamlessly leverage the deep customer understanding in Customer Insights - Data.
Grow with a unified, adaptable platform
- Easily customize and connect with tools you already use.
- Efficiently manage compliance requirements and accessibility guidelines.
To get started, a basic customer journey needs at least two pieces of information:
Customers to target: You should have a segment containing the contacts to whom you want to send your email.
Marketing activities: You should include a marketing email that is both valid and live.
Depending on your desired complexity and specific goals, a customer journey can include various elements to guide engaged customers. These are represented in the journey’s visual designer as tiles.
Trigger-based journeys
Triggers represent actions taken by a customer such as a whitepaper download, a form submitted, or a Wi-Fi sign-up. They can also represent significant business events, such as a purchase that shipped or completion of an enrollment process. Trigger-based journeys are effective because they represent the ability to perform more targeted marketing based on customer related interactions and events.
Real-time marketing offers three types of triggers in the triggers catalog:
Custom triggers: These are triggers defined by real-time marketing users. They provide a flexible way to capture any customer action or significant business event.
Interaction triggers: These triggers are customer interactions with journey elements such as email, text message, and push channels. They don’t start or stop journeys. They're used within a journey and represent a logical continuation of a preceding step. When a journey sends an email, triggers like Email delivered, Email bounced, or Email opened become available to journey authors, helping them decide the next steps.
Business triggers: These triggers represent changes in Dynamics 365 applications such as Sales or Service. These changes can reflect either the creation of a new record or an update to an existing one. A business trigger occurs when a contact is created or when an email address, phone number, or physical address is updated.