Configure managed identity
Managed identity allows Azure services to authenticate and access other Azure resources securely without needing to manage credentials. It automatically handles the creation and management of the identity, making it easier and more secure to connect services.
Authentication with managed identities for Azure resources is the recommended authentication method for programmatic access to SQL.
When using Microsoft Entra authentication with Azure SQL Database, you must assign a system-assigned managed identity when Azure service principals are used to create Microsoft Entra users in SQL Database. Previously, only a system-assigned managed identity could be assigned to the Azure SQL Database server identity, but now a user-assigned managed identity can also be assigned as the server identity.
System-assigned managed identity
When you enable a system-assigned managed identity on an Azure resource like a SQL logical server, a special service principal is created in Microsoft Entra ID. This service principal is tied to the resource's lifecycle, meaning it's automatically deleted when the resource is deleted. This type of managed identity can't be shared and is only associated with a single Azure resource. It's commonly used for workloads contained within a single resource that need independent identities, like an application running on a single virtual machine.
Use system-assigned manage identity
Imagine a scenario where you need to enable system-assigned managed identity for your Azure Web App. You need to start by accessing the Azure portal and finding your Web App. Once there, navigate to the Settings section found in the left-hand menu and select Identity.
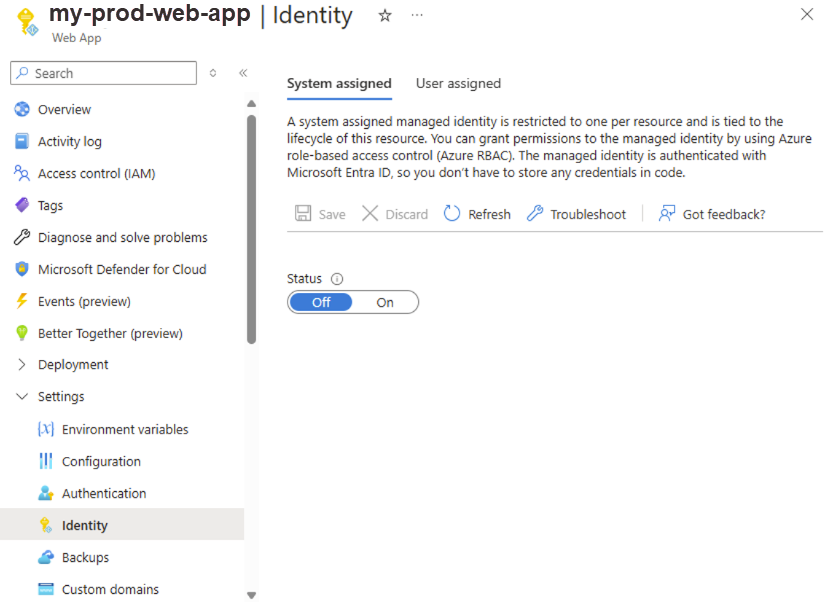
Within the System assigned tab, you'll need to switch the Status to On and then save your changes.
To enable your application to access the database using a system-managed identity, you also need to create a user with the appropriate permissions on your database.
CREATE USER [my-prod-web-app] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;
ALTER ROLE db_datareader ADD MEMBER [my-prod-web-app];
ALTER ROLE db_datawriter ADD MEMBER [my-prod-web-app];
Then, in your application code, you need to use the following connection string to connect to Azure SQL Database using a system-assigned managed identity.
Server=myserver.database.windows.net;Authentication=Active Directory Managed Identity; Encrypt=True;Database=my-db
User-assigned managed identity
A user-assigned managed identity is created as an independent Azure resource. This type of managed identity can be assigned to multiple instances of various Azure services, making it suitable for workloads that run on multiple resources and can share a single identity.
User-assigned managed identity is also useful for workloads that need pre-authorization to a secure resource as part of a provisioning flow, or where resources are frequently recycled but permissions need to remain consistent.
Use user-assigned manage identity
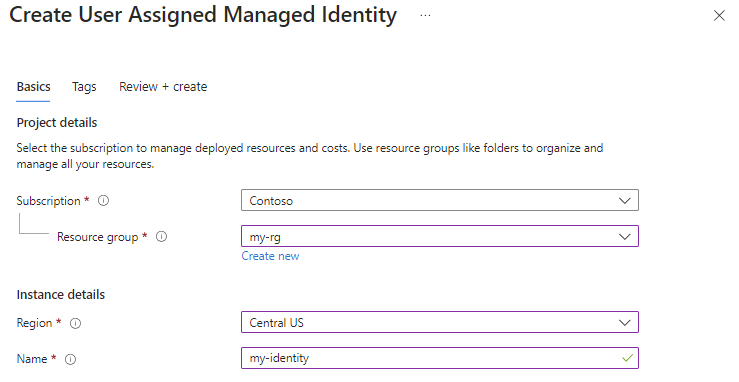
To use managed identities for Azure resources, first we need to create a user-managed identity in Azure.
You can start by navigating to the Azure portal. Select Managed Identities, then select + Create. Complete the required fields on the Create User Assigned Managed Identity page.
Next, similar to a system-managed identity, you need to assign the user-managed identity to the Azure resource. In this example, you would assign it to the Azure Web App, under the User managed tab.
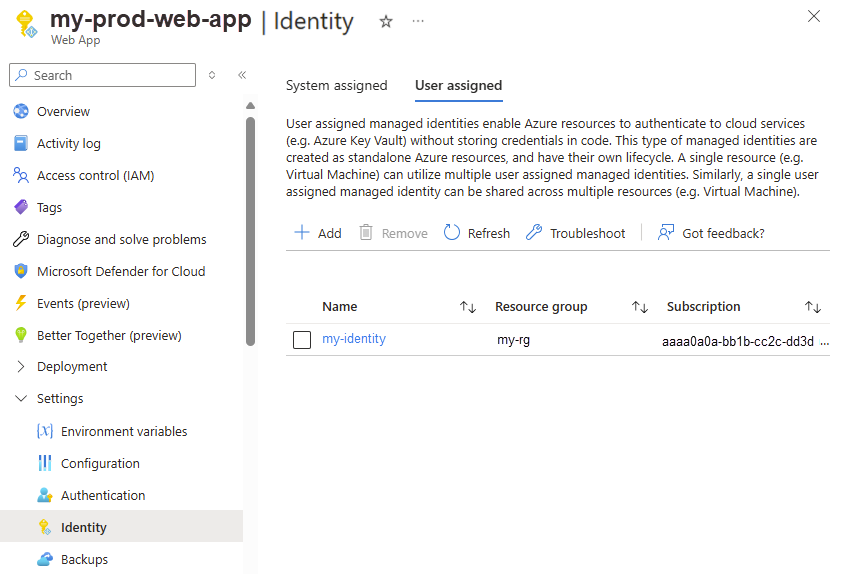
Finally, create a SQL user from the managed identity in the target database using the CREATE USER statement. In this example, our managed identity name is my-identity.
CREATE USER [my-identity] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;
ALTER ROLE db_datareader ADD MEMBER [my-identity];
ALTER ROLE db_datawriter ADD MEMBER [my-identity];
The following connection string shows how to connect to Azure SQL Database using a user-assigned managed identity.
Server=myserver.database.windows.net;Authentication=Active Directory Managed Identity; Encrypt=True;User Id=my-identity; Database=my-db
This flexibility makes user-assigned managed identities a versatile and secure option for managing access across different services within your Azure environment.