What is generative AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) imitates human behavior by using machine learning to interact with the environment and execute tasks without explicit directions on what to output.
What is generative AI?
Generative AI describes a category of capabilities within AI that create original content. These capabilities include taking in natural language input, and returning appropriate responses in a variety of formats such as natural language, images, code, and more. Let's take a look at a couple of examples:
Natural language generation
To generate a natural language response, you might submit a request such as "Write a cover letter for a person with a bachelor's degree in history."
A generative AI application might respond to such a request like this:
Dear Hiring Manager, I am writing to express my interest in the position of...
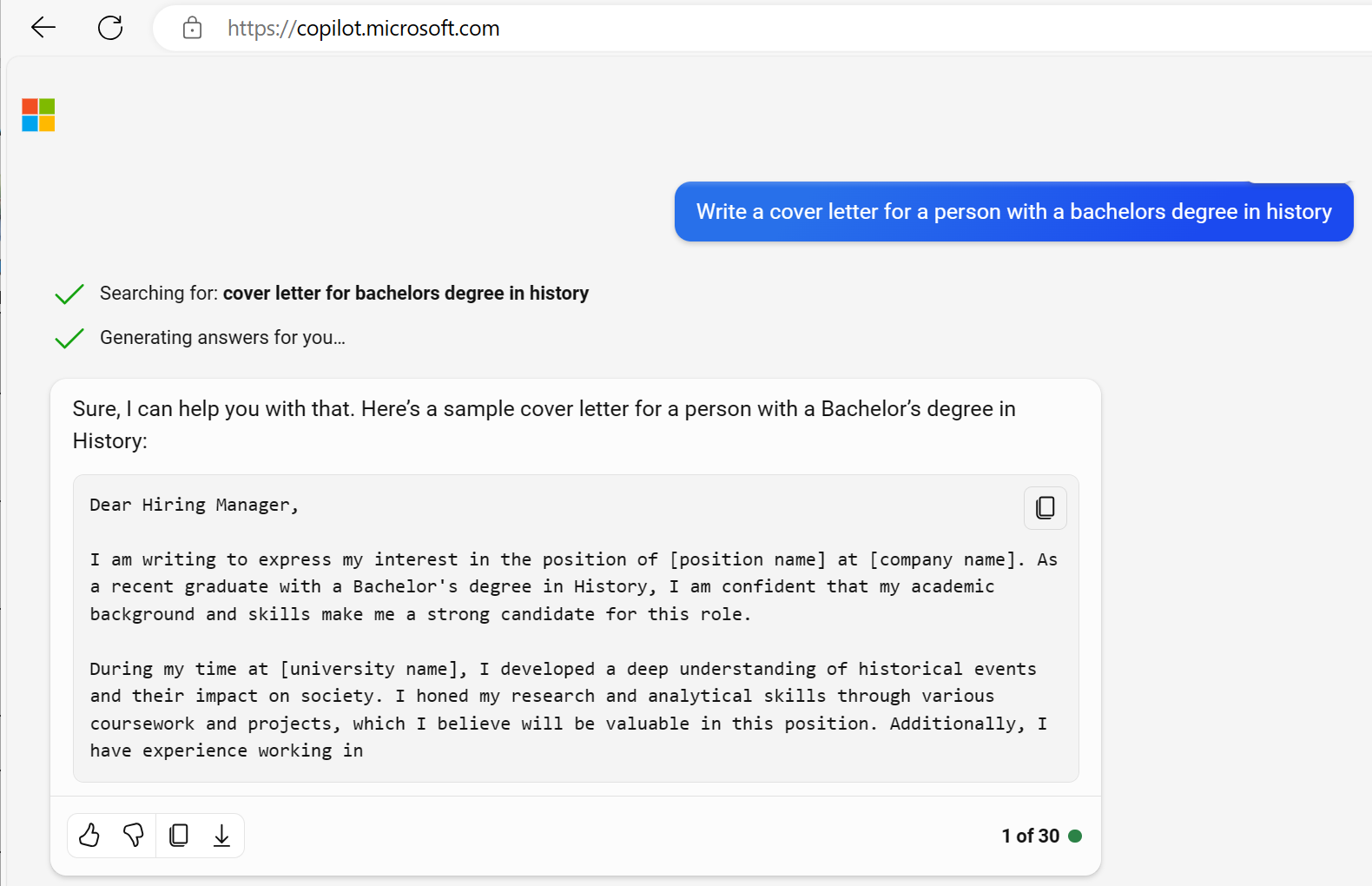
Image generation
Some generative AI applications can interpret a natural language request and generate an appropriate image. For example, you might submit a request like "Create a logo for a florist business."
A generative AI application could then return a new image based on the description you provided, like this:

Code generation
Some generative AI applications are designed to help software developers write code. For example, you could submit a request like "Write Python code to add two numbers." and generate the following response:
def add_numbers(a, b):
return a + b
Next, let's build an understanding of the language models that power generative AI.