What is an AI application?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to systems designed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence—such as reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and language understanding. Responsible AI: Emphasizes fairness, transparency, and ethical use of AI technologies.
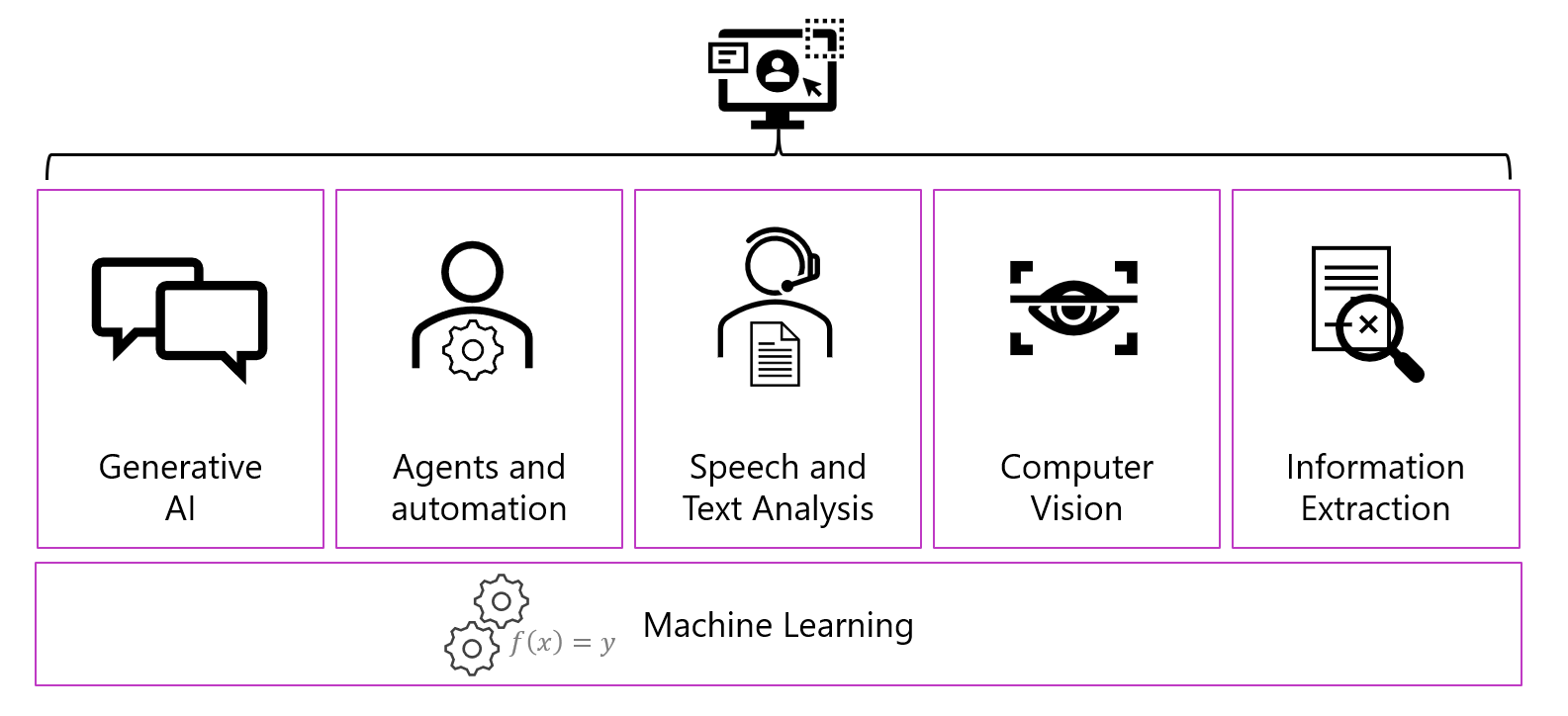
Key AI workloads:
- Generative AI
- Agents and automation
- Speech
- Text analysis
- Computer Vision
- Information Extraction
All these workloads are built on the foundation of machine learning.
AI is the broader goal—creating systems that mimic human intelligence. Machine learning (ML) is the primary method we use to reach AI and is made possible by data-driven algorithms. In general, ML enables machines to learn patterns from data and improve performance without explicit programming.
Types of ML:
- Supervised and Unsupervised Learning: such as regression (supervised) for predicting prices, classification (supervised) for spam detection, and clustering (unsupervised) for customer segmentation.
- Deep Learning: A specialized branch of ML using neural networks with multiple layers for tasks like image recognition and speech synthesis. Deep learning provides the foundation through neural networks that learn complex patterns from massive datasets.
- Generative AI: uses deep learning capabilities to create new content—text, images, audio, code—rather than just classify or predict outcomes.
AI Applications
An AI application is a software solution that uses AI techniques—such as computer vision, speech, and information extraction—to perform tasks that typically require human-like intelligence. These applications can understand, reason, learn, and respond to inputs in a way that feels more adaptive and intelligent than traditional software.
AI applications are:
- Model-powered: They use trained models to process inputs and generate outputs, such as text, images, or decisions.
- Dynamic: Unlike static programs, AI apps can improve over time through retraining or fine-tuning.
Some of the typical ways people interact with AI applications include:
- Conversational Interfaces: Users interact via chatbots or voice assistants (such as: asking questions, getting recommendations).
- Embedded Features: AI is integrated into apps for tasks like autocomplete, image recognition, or fraud detection.
- Decision Support: AI applications provide insights or predictions to help users make informed choices (such as: personalized shopping, medical diagnostics).
- Automation: They handle repetitive tasks, such as document processing or customer service, reducing manual effort.
Some examples of AI applications for different industries include:
- Healthcare: AI-powered diagnostic tools that analyze medical images (such as X-rays or MRIs) to help doctors detect diseases more accurately and quickly.
- Finance: Fraud detection systems that use AI to monitor transactions in real time and identify suspicious activity, helping prevent financial crimes.
- Retail: Personalized recommendation engines that analyze customer behavior and preferences to suggest products, improving the shopping experience.
- Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance solutions that use AI to monitor equipment and forecast when machines are likely to fail, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Education: Intelligent tutoring systems that adapt to each student’s learning style and pace, providing customized feedback and support to enhance learning outcomes.
Next, let's look at each component of an AI application as it relates to Microsoft technologies.