Understand the data science process
A common way to extract insights from data is to visualize the data. Whenever you have complex datasets, you may want to dive deeper and try to find intricate patterns in the data.
As a data scientist, you can train machine learning models to find patterns in your data. You can use those patterns to generate new insights, or predictions. For example, you can predict the expected number of products you expect to sell in the coming week.
Though training the model is important, it's not the only task in a data science project. Before exploring a typical data science process, let's explore common machine learning models you can train.
Explore common machine learning models
The purpose of machine learning is to train models that can identify patterns in large amounts of data. You can then use the patterns to make predictions that provide you with new insights on which you can take actions.
The possibilities with machine learning may appear endless, so let's begin by understanding the four common types of machine learning models:
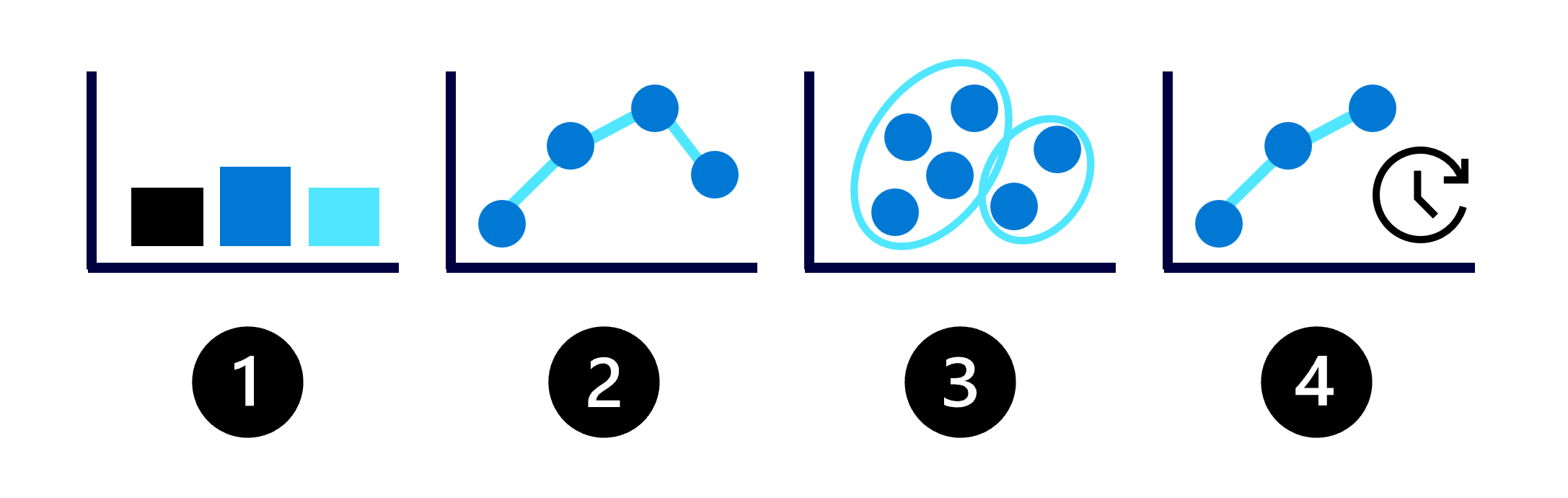
- Classification: Predict a categorical value like whether a customer may churn.
- Regression: Predict a numerical value like the price of a product.
- Clustering: Group similar data points into clusters or groups.
- Forecasting: Predict future numerical values based on time-series data like the expected sales for the coming month.
To decide which type of machine learning model you need to train, you first need to understand the business problem and the data available to you.
Understand the data science process
To train a machine learning model, the process commonly involves the following steps:
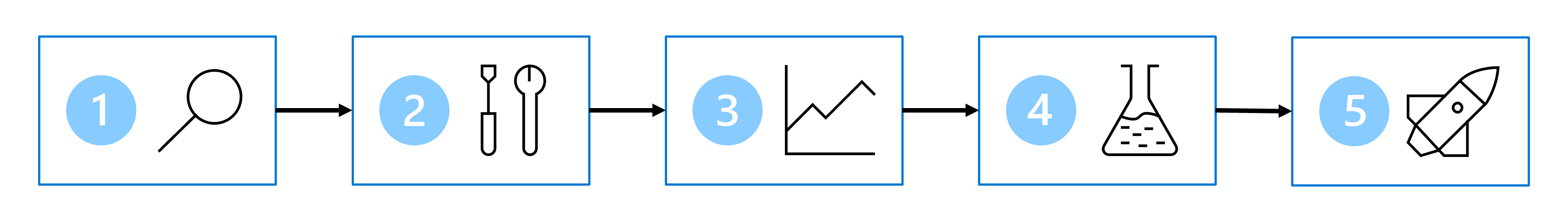
- Define the problem: Together with business users and analysts, decide on what the model should predict and when it's successful.
- Get the data: Find data sources and get access by storing your data in a Lakehouse.
- Prepare the data: Explore the data by reading it from a Lakehouse into a notebook. Clean and transform the data based on the model's requirements.
- Train the model: Choose an algorithm and hyperparameter values based on trial and error by tracking your experiments with MLflow.
- Generate insights: Use model batch scoring to generate the requested predictions.
As a data scientist, most of your time is spent on preparing the data and training the model. How you prepare the data and which algorithm you choose to train a model can influence your model's success.
You can prepare and train a model by using open-source libraries available for the language of your choice. For example, if you work with Python, you can prepare the data with Pandas and Numpy, and train a model with libraries like Scikit-Learn, PyTorch, or SynapseML.
When experimenting, you want to keep an overview of all the different models you've trained. You want to understand how your choices influence the model's success. By tracking your experiments with MLflow in Microsoft Fabric, you're able to easily manage and deploy the models you've trained.