Overview
Two objectives of a typical financial management system in any company are:
Maximize profit - Trying to earn maximum profits for the company in the short term and the long term. Finance keeps all financial transactions in a ledger, and also offers tools and features to provide insight into incurring costs and projected revenue so that financial leaders can make proper decisions.
The General ledger module is the core of Finance and is integrated with other sub ledgers in Finance.
The Cash and bank management module allows companies to manage their banks and balances, and reconcile the bank statements with the General ledger module.
Maximize wealth - Earning maximum wealth for the shareholders of the company by increasing the market value of the shares, which is directly related to the performance of the company. A company must have a good cash flow to pay the daily expenses such as purchase of raw materials, wages, rent, electricity bills, and more. If the company has good cash flow, it can take advantage of many opportunities such as getting cash discounts on purchases, making large-scale purchases, giving credit to customers, and more. A healthy cash flow improves a company's chances of survival and success.
Finance offers tools and features, with built-in intelligent controls such as charts, KPIs (key performance indicators), and workspaces, to give insight into a company's cash flow, project supply, and demand. It can analyze customer demographics and costs of goods so that a company can better negotiate more advantageous agreements with their vendors and customers.
The Accounts payable and Accounts receivable modules offer what a company needs to manage vendor and customer daily processes such as invoicing and generating or collecting payments.
The Budgeting module lets a company properly estimate the total financial requirements by determining how much finance is necessary to operate and what the requirements are for fixed and working capital.
The Sales and marketing, Inventory management, Procurement and sourcing, Cost management, and Cost control modules in Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management all contribute to making proper decisions to maximize the wealth in a company.
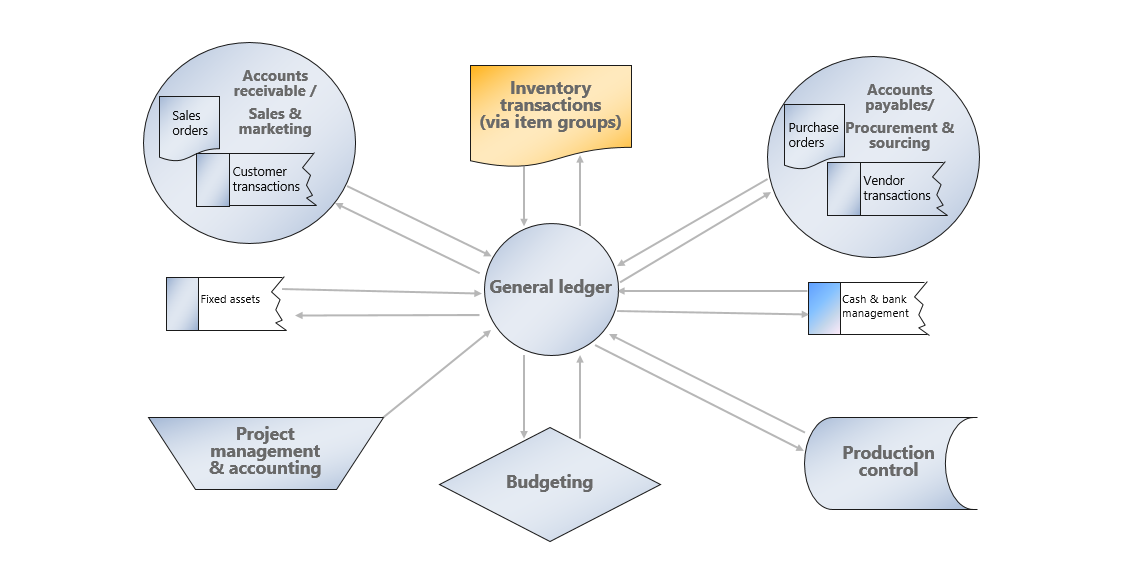
As the figure illustrates, the General ledger module interacts with other modules in the following scenarios:
Cash and bank management - All incoming and outgoing funds will be recorded in the general ledger, and each bank has a corresponding account in the general ledger chart of accounts. Therefore, this module simplifies your ability to reconcile bank statements with financial management transactions in periodic processing.
Accounts payable - All invoices and payment transactions are recorded in the general ledger. The Accounts payable clerk matches the purchase order with the recorded invoice to determine if the vendor invoice is qualified to be paid and, upon the due date, generates payments, which through the general ledger will impact cash and bank management.
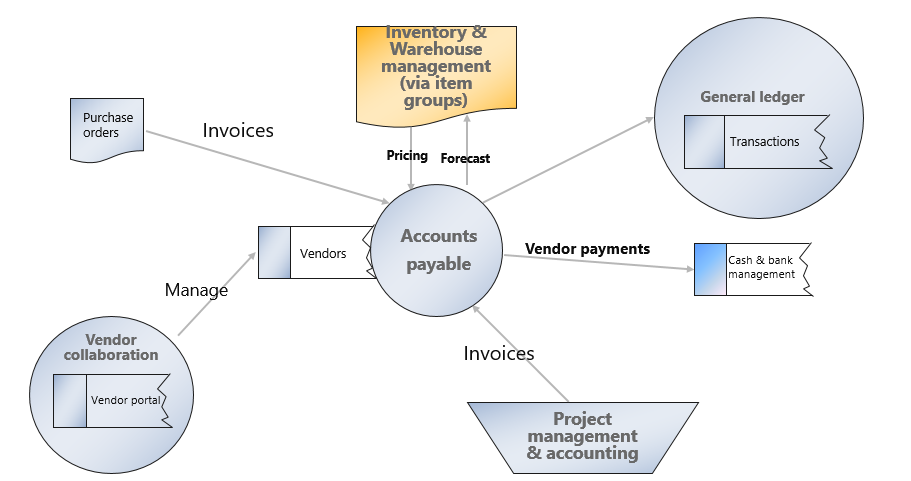
Project management and accounting - Based on time and materials or a fixed price project, purchases often need to be made. In this case, the Project management and accounting module can interact with the Procurement and sourcing module in Supply Chain Management to generate purchase orders, which will then be settled in the Accounts payable module in Finance.
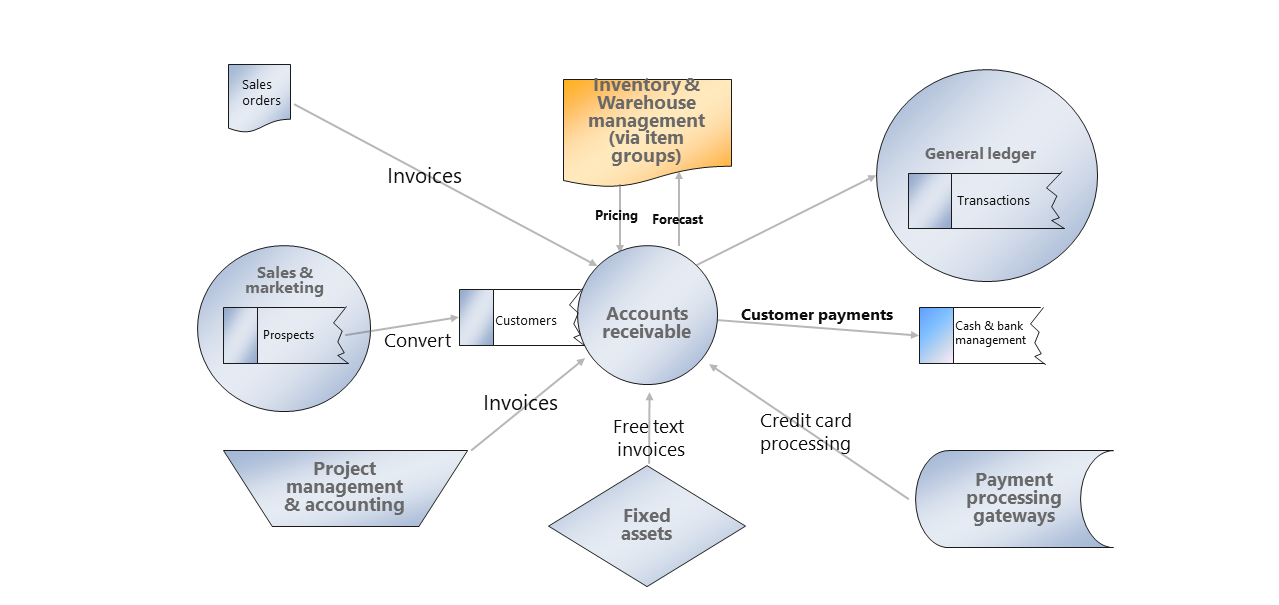
During project implementation, you can create invoices for customers, and then a Sales and marketing department will continue managing the quotations and converting them to invoices for ongoing projects, alongside their typical role of marketing goods and managing sales. Then, the Accounts receivable module will manage the customer payments and, perhaps, refunds.
The next units will cover each module in Finance.