Azure DevOps
Because development is done in individual developer environments, source control is required to have a collaborative development life cycle and a set of processes that bring together developers, project managers, and contributors who are involved with developing and implementing finance and operations apps. We recommend that you use Azure DevOps as your source control tool.
Azure DevOps provides integrated features that you can access through your web browser or Microsoft Visual Studio.
Azure DevOps Services supports integration with GitHub.com and GitHub Enterprise Server repositories. Choose Azure DevOps Services when you want the following outcomes:
- Quick setup
- Maintenance-free operations
- Collaboration across domains
- Elastic scale
- Dependable security
For more information, see the Azure DevOps and GitHub integration overview.
Before you can begin developing with source control, you need to create and configure an Azure DevOps project for your organization.
To set up a new project, follow these steps.
Note
Before you begin, go to https://www.visualstudio.com/ to sign up for Azure DevOps.
Sign in with your Microsoft account.
Create an Azure DevOps organization and then select a URL for your account. You use this URL to connect from your development computer when you configure source control in Visual Studio. After you create the account, the system directs you to your account main page where you can create your first project.
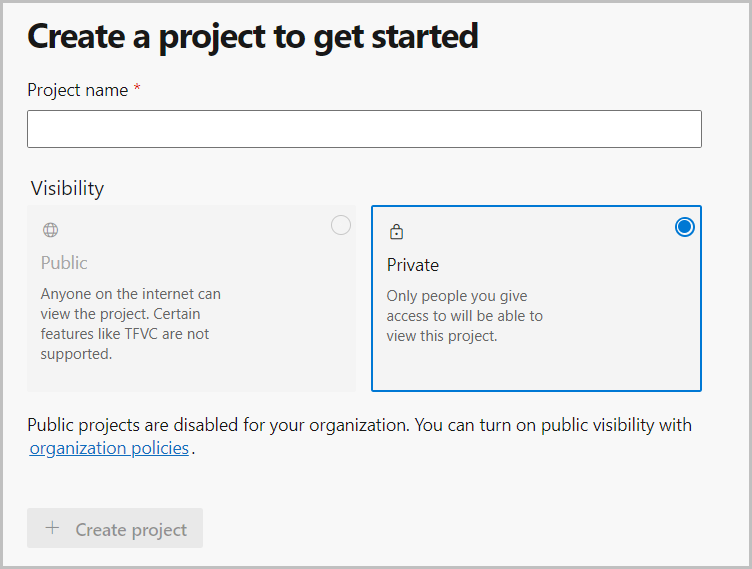
Name your project.
Change the visibility to Public or Private.
Select Create project.
Now, a dashboard should display for the new project that you created.
Branching and merging strategies
As part of the Azure DevOps project setup, you need to configure branching folders for moving code through a promotion life cycle. You can use Azure Pipelines to automate the build process and deploy code to environments.
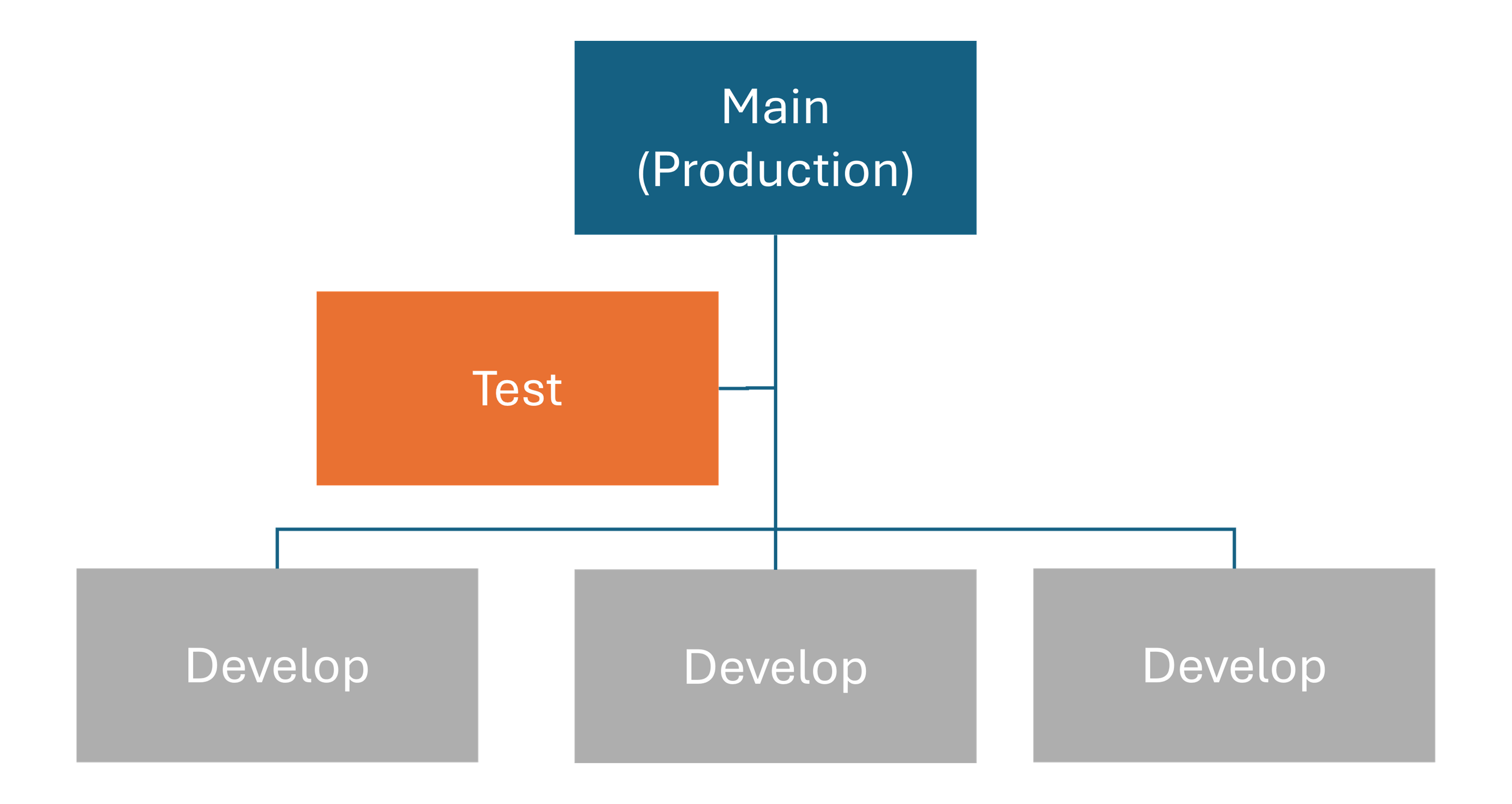
Effective branching strategies help teams organize their work. Common branch setups include:
- Development branch - For code under active development, shared among developers. Large teams can use individual branches for each developer.
- Test branch - For code changes that are ready for user testing.
- Production branch - For the source code that’s deployed to the production environment.
Deploy code changes
To move code changes between environments, you must create a deployable package. We recommend that you use a build environment to generate these packages. You can create deployable packages in Visual Studio and then deploy them by using Microsoft Dynamics 365 Lifecycle Services.
Deployment steps vary for non-production and production environments. Notably, deploying to production requires that the package successfully deploys to at least one sandbox environment in the same project.
By using Azure DevOps and following these structured processes, you can manage source control, streamline development workflows, and maintain code integrity across environments.