Introduction
To ensure that customers are satisfied with the service that they're being provided, many organizations will connect the incoming work items, such as cases, phone calls, or chat requests, to the most qualified representative to assist with each specific need. For example, when a customer has a billing question, they should be directed to someone who has knowledge of billing-related information. A customer who needs service on a specific product should be routed to someone who has knowledge of that product.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Service includes many features that work together to provide organizations with an end-to-end case management solution. One feature is the ability to route incoming work items to the most appropriate representative, team, or queue.
Routing options in Dynamics 365
Depending on your organization, how you handle the routing and distributing of work items to representatives can vary. A smaller organization might move a new case that's related to a billing question to a billing queue until a representative manually selects, or picks, the case and begins working on it. Conversely, a contact center might want to route billing-related items to a billing queue, and they might also want to automatically assign, or push, the item to a member of that queue who has availability to work on it. This approach would ensure that all items are assigned, avoiding the potentiality of something being missed.
Dynamics 365 Customer Service provides organizations with two different routing options that organizations can apply to meet their routing needs, regardless of whether it's a small organization or a large enterprise.
Unified routing
Unified routing is an intelligent, scalable, and enterprise-grade routing and assignment capability. It can direct the incoming work item to the best-suited queue and representative by adhering to work item requirements and matching them with the representative's capabilities.
Unlike basic routing, where you're typically working with records such as cases or emails, you can use the unified routing infrastructure to route service requests across all channels that your organization uses, such as chat, voice, text, and more. This feature creates a unified view of workforce use across multiple channels, thus helping to optimize distribution of work across the workforce. It works in an omnichannel way by ensuring that work items on all channels are routed in a consistent and similar manner. Unified routing considers representative engagement on different channels before it assigns new work to them.
Unified routing consists of two main stages:
Classification - In this stage, unified routing will use rules and machine learning models to add information on the work item, which the feature will use to find the best-suited representative.
Assignment - During this stage, unified routing prioritizes the service requests and then assigns them to the representatives based on the nature of the work, related entities, representative skills, and the current state of the representative workforce in terms of availability and workload.
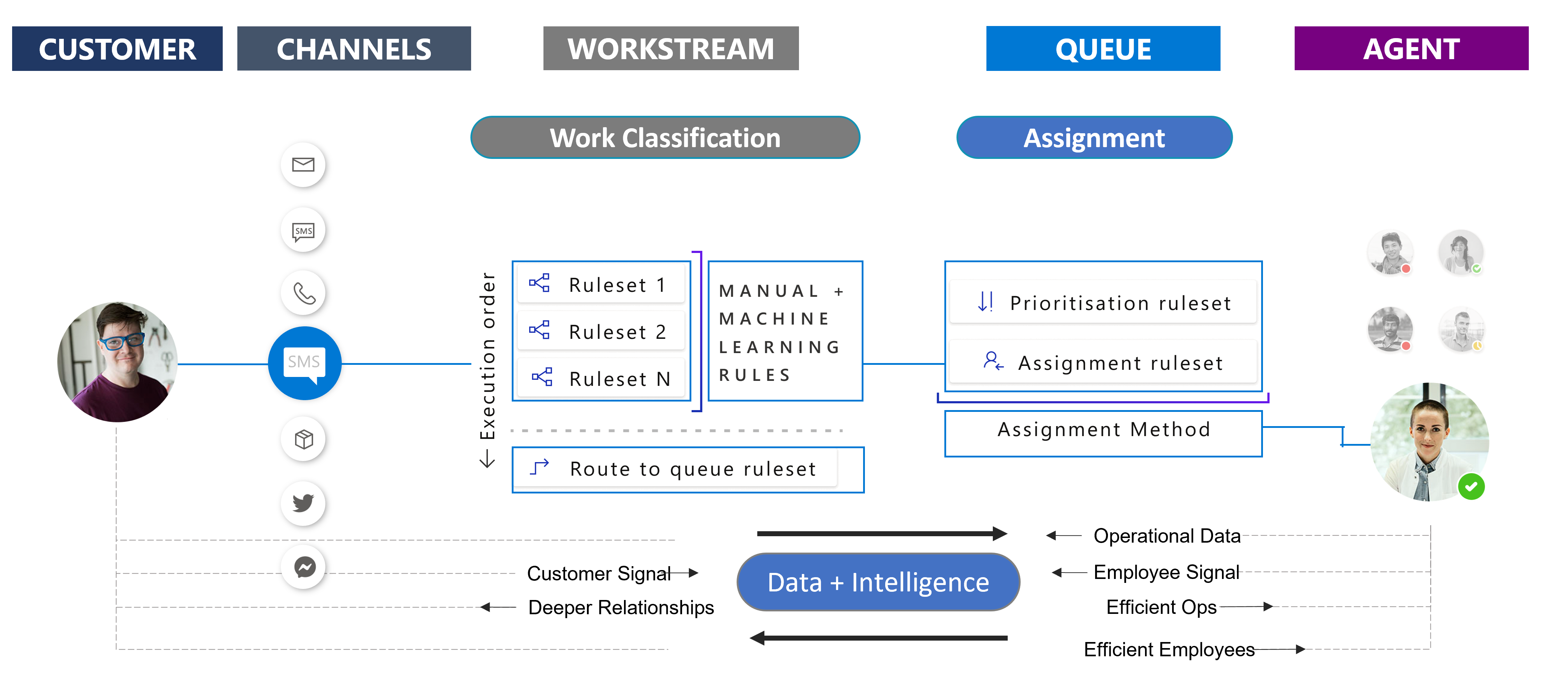
The following image shows this process in action:
As an incoming chat comes in, it will go through the work classification stage.
During this stage, information such as skills that are required by the representative, the urgency level of the item, category of customer, and importance level, can be added to the item.
After the work is classified, route-to-queue rules are used to send the item to the most appropriate queue.
After the item has been added to the correct queue, it will enter the assignment stage.
The organization might want to prioritize the chat based on the highest urgency level and importance.
After the chat has been prioritized, unified routing will assign the chat to a representative by matching the skills required, current workload status, and availability.
The remainder of this module will examine what's needed for you to get started using unified routing in your organization.