Use role-based access control (RBAC)
Azure role-based access control (RBAC) is provided in Azure Cosmos DB to do common management operations. Role-based access control will grant or deny access to resources and operation on Azure Cosmos DB resources. These roles can be assigned with a Microsoft Entra account to users, groups, service principals, or managed instances. Role assignments aren't used for data plane operations, they're scoped to control plane access only, such as the Azure Cosmos DB account, databases, containers, and offers (throughput). Let's take a look at these built-in roles supported by Azure Cosmos DB.
Built-in roles
| Built-in role | Description |
|---|---|
| DocumentDB Account Contributor | Can manage Azure Cosmos DB accounts. |
| Cosmos DB Account Reader | Can read Azure Cosmos DB account data. |
| Cosmos Backup Operator | Can submit a restore request from the Azure portal for a periodic backup-enabled database or a container. Can modify the backup interval and retention on the Azure portal. Can't access any data or use Data Explorer. |
| CosmosRestoreOperator | Can perform a restore action for an Azure Cosmos DB account with continuous backup mode. |
| Cosmos DB Operator | Can provision Azure Cosmos accounts, databases, and containers. Can't access any data or use Data Explorer. |
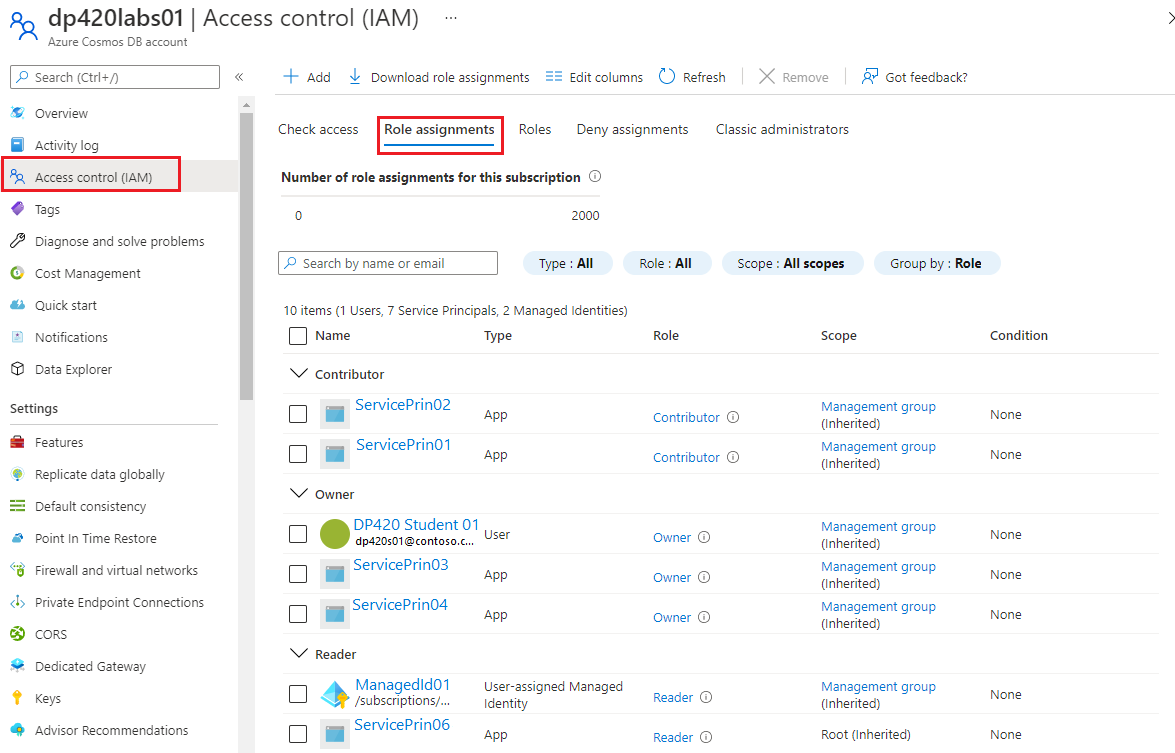
Identity and access management (IAM)
Azure RBAC on Azure Cosmos DB is set up using the Access Control (IAM) pane in the Azure portal. Individuals or groups can be assigned built-in roles or custom roles.
Custom Controls
Custom roles provide users a way to create Azure role definitions with a custom set of resource provider operations. Custom roles can be applied to Active Directory service principal and used to define RBACs just like the built-in roles.
Preventing changes from the Azure Cosmos DB SDKs
Clients connecting from the Azure Cosmos DB SDK can be locked down to prevent them from changing any property for the Azure Cosmos accounts, databases, containers, and throughput. The operations involving reading and writing data to Cosmos containers themselves would not affected. This lock down could be desirable to have a higher degree of control and governance for production environments. Only users with the right Azure role and Active Directory credentials, including Managed Service Identities, can change resource properties when this feature is enabled.
If your applications do any of the following actions, they'll no longer be able to do these actions through the Cosmos DB SDK, tools that connect via account keys or from the Azure portal. These actions will need to be executed from Azure Resource Manager Templates, PowerShell, Azure CLI, REST, or Azure Management Library.
- Any change to the Cosmos account including any properties or adding or removing regions.
- Creating, deleting child resources such as databases and containers.
- Updating throughput on database or container level resources.
- Modifying container properties including index policy, TTL and unique keys.
- Modifying stored procedures, triggers or user-defined functions.