List the functionalities, components, benefits, and use cases of Storage Spaces Direct
Storage Spaces simplify storage provisioning and management. However, when using shared storage, they're subject to scalability and performance limits that might not be acceptable in business critical. To accommodate more performance- and scale-demanding scenarios, you can leverage Storage Spaces Direct.
What is Storage Spaces Direct?
Storage Spaces Direct is the evolution of Storage Spaces, first introduced in Windows Server 2012. It leverages Storage Spaces, Failover Clustering, Cluster Shared Volumes (CSVs), Software Storage Bus, and SMB 3.x to implement virtualized, highly-available shared storage by using local disks on each of the Storage Spaces Direct cluster nodes. It's suitable for hosting highly-available workloads, including virtual machines and SQL Server databases. Storage Spaces Direct supports both direct-attached storage (DAS) and JBODs. This eliminates the need for a shared storage fabric and enables you to use a mix of SATA disks to lower costs and NVMe devices to improve performance.
Note
CSV is a clustered file system that enables cluster nodes to simultaneously read from and write to the same set of NTFS or ReFS volumes. This provides a balanced load distribution and increases failover speed by eliminating the need for drive ownership changes or dismounting and remounting volumes.
Note
Software Storage Bus forms a software-defined storage fabric consisting of local drives on cluster nodes. It also dynamically binds the fastest drives to slower drives to provide server-side read/write caching that accelerates I/O operations and increases throughput.
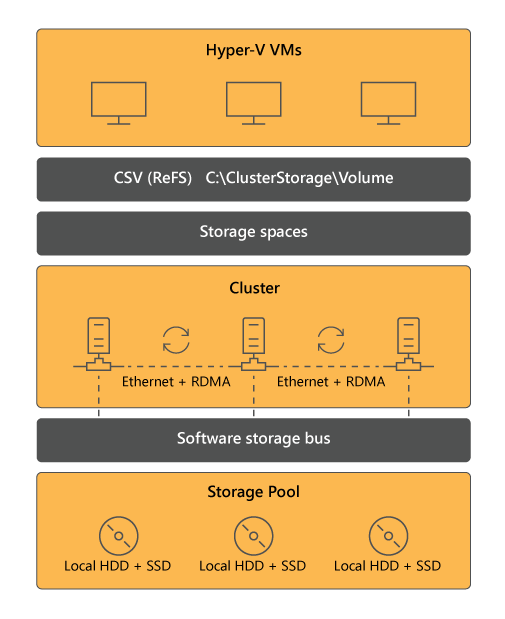
Storage Spaces Direct architecture
The architecture of Storage Spaces Direct consists of the following components:
- Storage Spaces Direct workloads. Common workloads include VMs and SQL Server databases.
- CSV. CSVs consolidate multiple volumes into a single namespace that's accessible through the file system on any cluster node.
- ReFS or NTFS-formatted volumes. ReFS is the recommended option because it accelerates virtual hard disk (VHD/VHDX) operations, providing superior performance in comparison with NTFS. ReFS also offers resiliency benefits such as error detection and automatic correction.
- Storage Spaces and the underlying virtual disks. With Storage Spaces, you create virtual disks by using available storage in the storage pool. Virtual disks provide resiliency against disk and server failure because data is distributed across disks on different servers.
Note
In the context of Storage Spaces Direct, the term volume typically refers to the volume and the underlying virtual disk.
- Software Storage Bus. Storage Spaces Direct uses Server Message Block (SMB) for intranode communication by using Software Storage Bus. Software Storage Bus exposes the storage on each node, making it part of the Storage Spaces layer.
- Failover clustering. Failover clustering is the Windows Server feature that allows you to implement highly available workloads, including Storage Spaces Direct.
- Windows Server instances. Storage Spaces Direct cluster can include between 2 and 16 servers.
- SMB Networking. SMB networking includes support for SMB Direct and SMB Multichannel.
- Network. Storage Spaces Direct requires network connectivity between cluster nodes. You should use multiple, RDMA-capable network adapters per node.
- Storage pool. The storage pool uses local disks from all cluster nodes.
- Local disks. Each server must have locally-attached storage, such as HDD, SSD, NVMe, or PMem disks.
Storage Spaces Direct benefits
Windows Server offers a range of Storage Spaces Direct-related benefits, including:
- Deduplication and compression for ReFS volumes. Deduplication supports volumes up to 64 terabytes (TB) and will deduplicate the first 4 TB of each file.
- Native support for persistent memory modules in Storage Spaces Direct clusters. You can use persistent memory as cache to accelerate the active working set, or as capacity to guarantee consistent, low latency on the order of microseconds.
- Nested resiliency for two-node hyper-converged infrastructure. With nested resiliency, a two-node Storage Spaces Direct cluster can provide continuously accessible storage for apps and VMs even if one server node stops working and a drive fails in the other server node.
- USB flash drive as a witness. You can use a low-cost USB flash drive that's plugged into your router to function as a witness in two-node Storage Spaces Direct clusters.
- Performance history for visibility into resource utilization and performance. This built-in functionality automatically collects over 50 essential counters spanning compute, memory, network, and storage and stores them for up to one year.
- Scaling for up to 4 petabytes (PB) per cluster. Starting with Windows Server 2019, Storage Spaces Direct supports up to 4 PB (or 4,000 TB) of raw capacity per storage pool.
- Mirror-accelerated parity. With mirror-accelerated parity you can create Storage Spaces Direct volumes that are part mirror and part parity, similar to mixing RAID-1 and RAID-5/6 to combine their benefits. In Windows Server 2019, mirror-accelerated parity performance more than doubled compared to Windows Server 2016.
- Drive latency outlier detection. Storage Spaces Direct automatically detects anomalous changes in drive performance and labels them in Windows PowerShell and Windows Admin Center with the Abnormal Latency status.
- Storage-class memory support for VMs. This enables NTFS-formatted direct access volumes to be created on non-volatile dual inline memory modules (DIMMs) and exposed to Microsoft Hyper-V VMs. This enables Hyper-V VMs to take advantage of the low-latency performance benefits of storage-class memory devices.
- Windows Admin Center extensions. You can manage and monitor Storage Spaces Direct with purpose-built dashboards in Windows Admin Center.
Storage Spaces Direct use cases
When planning for Storage Spaces Direct, you need to determine whether you want to separate the virtualization and storage layers. This separation determines whether you'll implement hyper-converged or disaggregated architecture.
In the hyper-converged architecture, you configure a Hyper-V cluster with local storage on each Hyper-V server, and scale this solution by adding extra Hyper-V servers with extra storage. This is the optimal solution for small and medium-sized businesses.
If you need to be able to scale the virtualization layer and the storage layer independently of each other, you should choose the disaggregated architecture. This approach consists of two separate clusters, with one hosting Hyper-V VMs and the other a Scale-Out File Server (SOFS) where the VM disks reside. This solution lets you scale processing power for the virtualization layer separately from storage capacity for the storage layer. This is typically optimal for large-scale deployments.
Note
SOFS provides access to the storage system by using SMB 3.x. SOFS provides SMB-based storage in disaggregated configurations. However, it's not suitable for hyper-converged configurations.
Other use cases for Storage Spaces Direct include storage of Hyper-V Replica files and for backup or archival of VM files. You can also deploy Storage Spaces Direct to host Microsoft SQL Server system and user database files.