How Azure Database for MySQL works
In this unit, you explore how Azure Database for MySQL works, beginning with its architecture. You also learn how the service provides high availability, backup functionality, and scaling to meet your workload's needs.
Azure Database for MySQL architecture
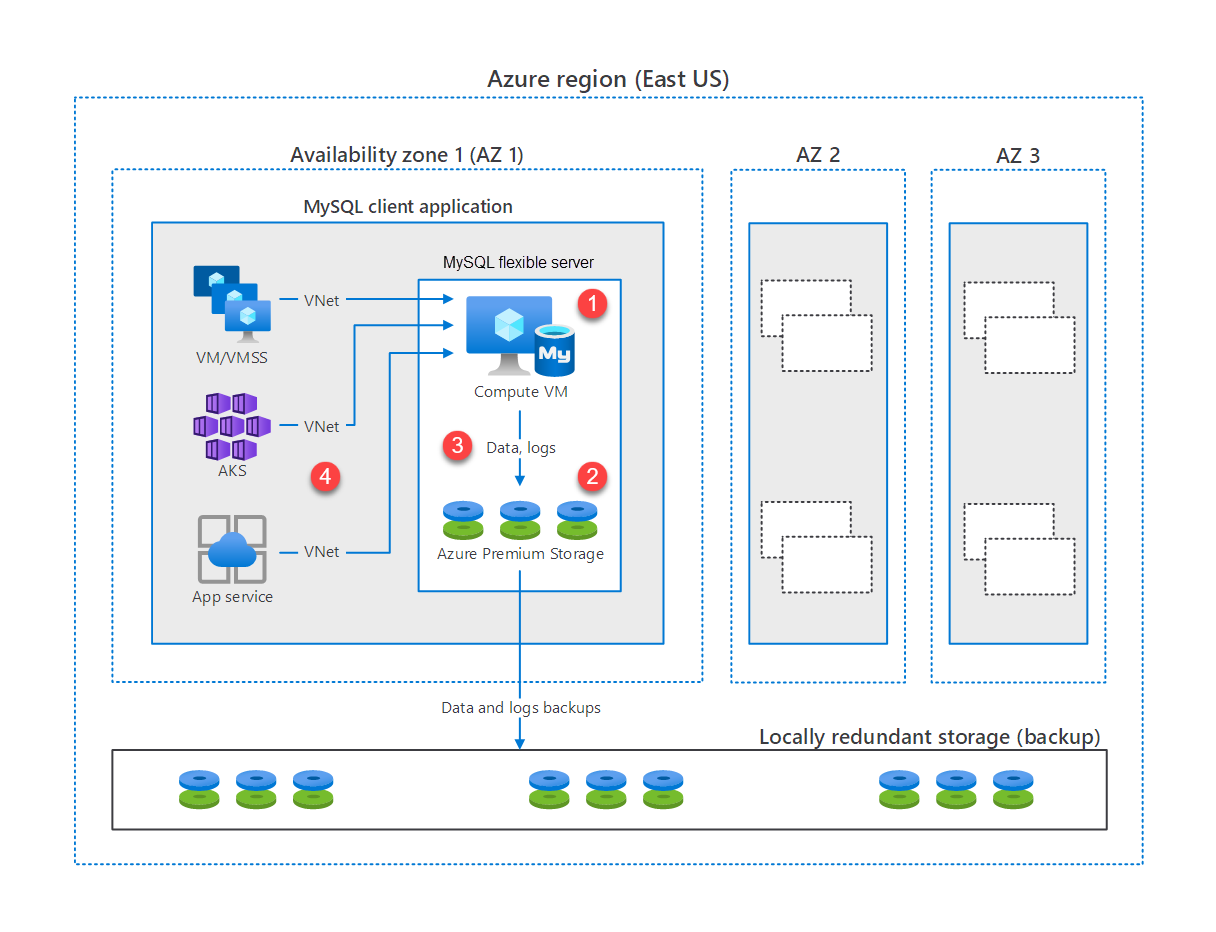
The following diagram describes the architecture of an instance of Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server.
- The MySQL instance runs on an Azure VM.
- Data and logs are stored in Azure Premium Storage.
- The data is replicated three times across locally redundant storage for backup and resiliency. The service also provides options to configure zone-redundant or geo-redundant storage backups.
- In addition, you have the option to co-locate your various client apps connected to the MySQL flexible server, within the same availability zone.
You can further opt in for same-zone or zone-redundant high availability, which automatically provisions and maintain a standby replica.
How high availability works
For Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server, within the single availability zone, the following process occurs after a hosting server failure:
- Azure provisions a new virtual machine (VM).
- Azure maps the storage and data files to the newly provisioned VM.
- The MySQL database engine is brought online.
- Client applications reconnect to the new MySQL instance.
Note
If you have provisioned high availability across zones, a hot standby server is maintained in another availability zone in the same Azure region. This server is a fully synchronized replica of the primary server. In the event of a primary server failure, the hot standby server can quickly take over with minimal disruption, thereby maintaining service availability.
How backups work
You can use backups to restore your server to any point in time within the retention period (35 days, or up to 10 years with long-term retention, in preview).
How scaling works
Scaling in Azure Database for MySQL involves adjusting the computing resources according to the application's needs, which can fluctuate based on user demand, the complexity of the operations processed, or other factors like business growth. This flexibility is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and cost efficiency.
Types of scaling
- Vertical scaling (Scaling Up/Down)
- Compute scaling: This refers to changing the compute tier of your MySQL flexible server. Azure offers several compute tiers, each designed to cater to different types of workloads:
- Burstable: Suitable for environments with intermittent bursts of CPU usage that don't require continuous full CPU performance.
- General Purpose: Designed for a wide range of applications, providing a balance of compute, memory, and I/O resources.
- Business Critical: Offers the highest performance for databases, with more powerful CPUs and faster I/O, suitable for high-transaction, low-latency workloads.
- Memory and CPU allocation: Depending on your selected tier, you can scale the number of vCores and the amount of RAM available to your database, which directly impacts the ability to handle larger or more complex queries and allows for a greater number of concurrent connections.
- Compute scaling: This refers to changing the compute tier of your MySQL flexible server. Azure offers several compute tiers, each designed to cater to different types of workloads:
- Horizontal scaling
- Azure Database for MySQL can scale horizontally by adding read replicas to distribute read traffic across multiple servers, improving read performance while keeping the primary server available for writes. Horizontal scaling allows your database to handle more query load, increasing application responsiveness.
- Storage scaling
- Dynamic storage scaling: With Azure Database for MySQL, you can increase storage capacity without downtime. You can start with a smaller allocation and scale up as your data grows.
- Autogrow feature: This feature automatically increases storage size before reaching the capacity limit, thus preventing any disruptions related to storage constraints.
Autoscale IOPS
Autoscale IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) is a feature that dynamically adjusts the I/O throughput based on the current workload. This is particularly useful for unpredictable or spike-prone workload patterns, as it ensures that the database can handle sudden increases in load without manual intervention.
- IOPS scaling based on load: When the workload increases and more I/O throughput is required, the Autoscale feature automatically increases the IOPS limit up to the maximum allowed in the chosen compute tier. Conversely, IOPS are reduced during periods of low activity to minimize costs.
- Cost-effectiveness: By automatically adjusting IOPS based on actual usage, you only pay for the IOPS you use rather than over-provision resources to handle peak loads, which might only occur sporadically.
Best practices for scaling
To effectively scale Azure Database for MySQL, monitor performance metrics using Azure Monitor, set up critical alerts, plan for future growth by reviewing usage patterns, and test scalability during off-peak hours to ensure smooth performance under increased load.
By understanding and using these scaling mechanisms, you can ensure that your Azure Database for MySQL flexible server always runs efficiently, adapting to both the current and future needs of your business.
Configure and tune engine behavior
To easily configure and customize server variables and parameters in Azure Database for MySQL, you can use the Azure portal, the Azure CLI, or the REST API to adjust settings such as query cache size, connection timeouts, and storage engine preferences, ensuring optimal performance and behavior for your specific workload.
Next, consider whether Azure Database for MySQL meets the needs of your organization, its apps, and database workloads.