Exercise - Retrieve an existing Docker image and deploy it locally
A good starting point for building and running your own Docker images is to take an existing image from Docker Hub and run it locally on your computer.
As a proof of concept for the company's applications, you decide to try running a sample image from Docker Hub. The image you selected implements a basic .NET Core ASP.NET web app. Once you establish a process for deploying a Docker image, you're able to run one of your company's own web apps using Docker.
In this exercise, you pull an image from Docker Hub and run it. You examine the local state of Docker to help understand the elements that are deployed. Finally, you remove the container and image from your computer.
Important
This exercise takes place on your computer, not in Azure. You need a local installation of Docker to proceed with the exercise. Download: https://docs.docker.com/desktop/install/windows-install/
Pull and run a sample application from Docker Hub
Start Docker on your computer.
Open a command prompt window on your local computer.
Enter the following code to pull the ASP.NET Sample app image from the Docker Hub registry. This image contains a sample web app developed by Microsoft, and is based on the default ASP.NET template available in Visual Studio.
docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/samples:aspnetappEnter the following code to verify that the image was stored locally.
docker image lsYou should see a repository named mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/samples with a tag of aspnetapp.
Enter the following code to start the sample app. The
-dflag is to run it as a background, non-interactive app. Thepflag is to map port 8080 in the container that's created to port 8080 locally. This setting is intended to avoid conflicts with any web apps already running on your computer. The command responds with a lengthy hexadecimal identifier for the instance.docker run -d -p 8080:8080 mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/samples:aspnetappOpen a web browser and go to the URL for the sample web app:
http://localhost:8080. You should get a page that looks like the following screenshot: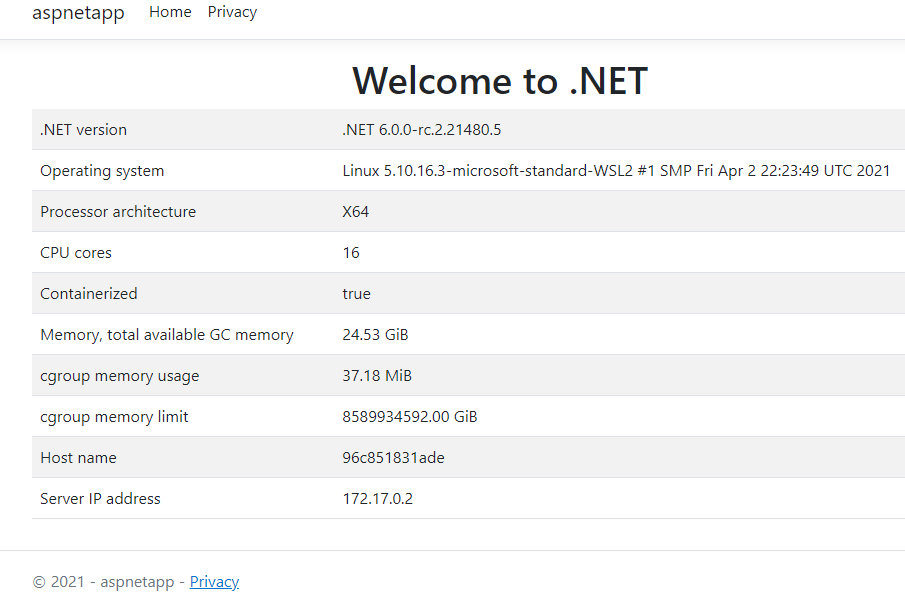
Examine the container in the local Docker registry
At the command prompt, run the following command to view the running containers in the local registry.
docker psThe output should look similar to the following example:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 96c851831ade mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/samples:aspnetapp "dotnet aspnetapp.dll" 22 minutes ago Up 22 minutes 0.0.0.0:8080->80/tcp eager_montalciniThe COMMAND field shows the container started by running the command dotnet aspnetapp.dll. This command invokes the .NET Core runtime to start the code in the aspnetapp.dll (the code for the sample web app). The PORTS field indicates that port 8080 in the image was mapped to port 80 on your computer. The STATUS field shows the application is still running. Make a note of the container's NAME.
Run the following command to stop the Docker container, replacing the placeholder
<NAME>with the output name from the previous command.docker container stop <NAME>Run the following command to verify that the container is no longer running. The -a flag indicates that the command shows the status of all containers, not just the containers that are running. The output should show the STATUS of the container as Exited.
docker ps -aIn your web browser, refresh the page for the sample web app (http://localhost:8080/). It should fail with a Connection Refused error.
Remove the container and image from the local registry
Although the container has stopped, it's still loaded and can be restarted. Run the following command in the command prompt window to remove it, replacing
<NAME>placeholder with the name of your container.docker container rm <NAME>Verify that the container was removed by running the following command. The command should no longer list the container.
docker ps -aList the images currently available on your computer. The output should show the samples repository.
docker image lsRemove the image from the registry.
docker image rm mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/samples:aspnetappThe output should list numerous items that were untagged and deleted. Run the following command to list the images again and verify that the image for the microsoft/dotnet-samples web app has disappeared.
docker image ls