Explore microservices architecture
Microservices architecture represents modern distributed system design patterns emphasizing autonomous, independently deployable, and horizontally scalable software components.
Service-oriented design principles focus on single-responsibility implementations that enable independent operation and autonomous lifecycle management. Service isolation ensures change propagation constraints limit cross-service impacts within distributed system landscapes.
Microservices architectural adoption creates distributed service ecosystems supporting parallel development, independent testing workflows, and decoupled deployment cycles. This architectural paradigm introduces complexity tradeoffs including interface contract management, service interaction orchestration, and multiple independent application lifecycle coordination requirements.
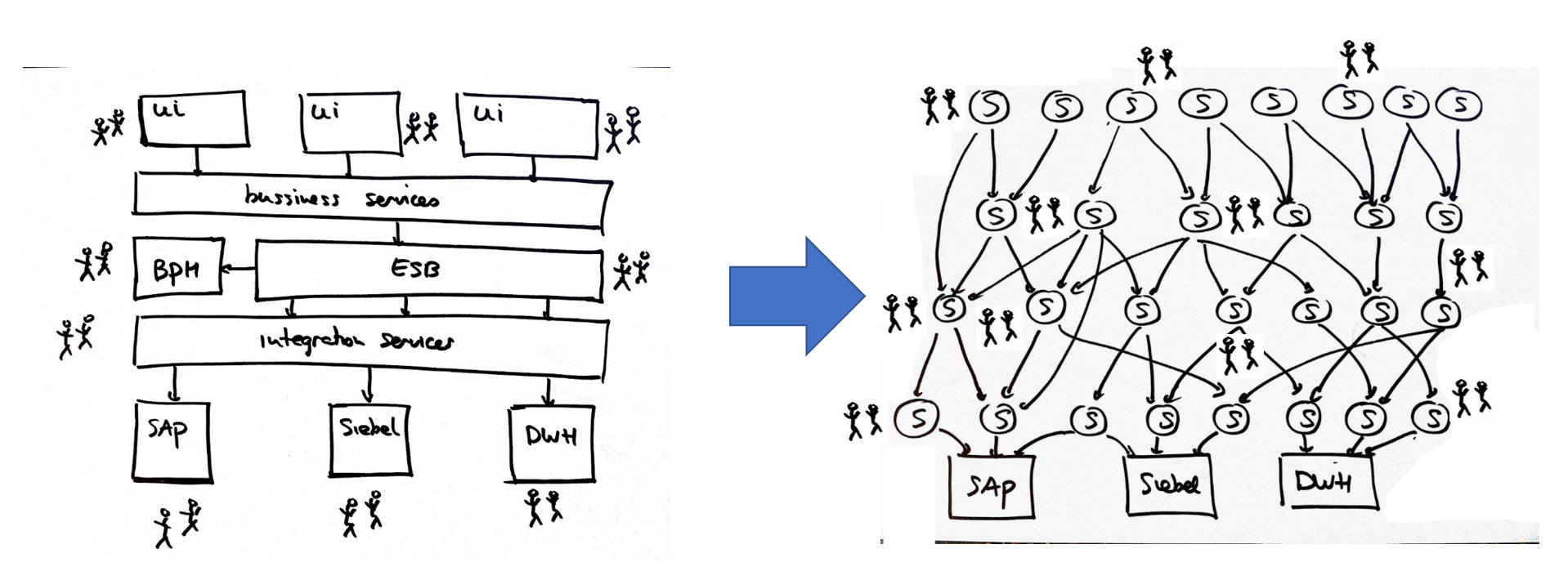
Traditional monolithic applications implement multi-layered architectures with distinct presentation, business logic, and data service tiers.
Organizational structures often reflect architectural boundaries through specialized UI and backend development teams. Cross-layer modifications require coordinated changes propagating through multiple architectural tiers, creating complexity and coordination overhead.
Microservices architecture consolidates all architectural layers within autonomous service boundaries, enabling full-stack ownership and independent evolution.
Each microservice encapsulates singular business capabilities through cohesive functional boundaries that enable focused development and targeted optimization.
Inter-service communication leverages asynchronous messaging patterns through message queues, event streams, and publish-subscribe architectures that decouple service dependencies and enable resilient distributed system operation.
Independent service lifecycles with dedicated Continuous Delivery pipelines enable isolated deployment workflows that minimize cross-service impact when properly architected, supporting parallel version releases without system-wide coordination requirements.
While microservices architecture doesn't constitute a Continuous Delivery prerequisite, service decomposition significantly simplifies pipeline automation implementation through reduced scope and isolated change management.