Explore actions flow
Understanding how GitHub Actions workflows execute from start to finish helps you design efficient automation pipelines and troubleshoot issues effectively.
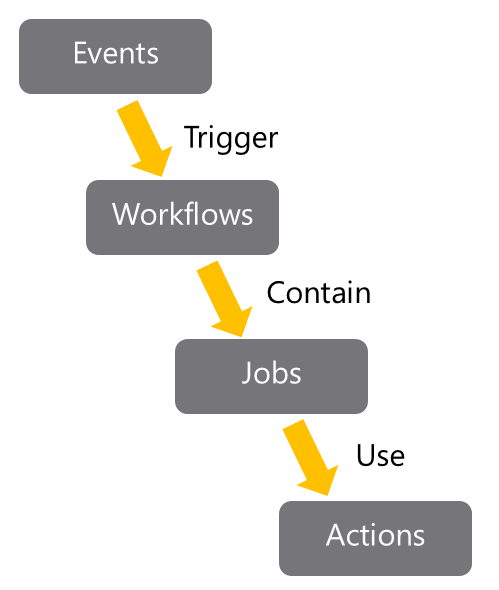
The GitHub Actions execution flow
Event detection and triggering
GitHub continuously monitors your repository for specific events that can initiate workflows:
Repository events:
- Code pushes to branches
- Pull request creation, updates, or merging
- Issue creation or modification
- Release publishing
Scheduled events:
- Cron-based time schedules
- Recurring maintenance tasks
External events:
- Manual workflow triggers via GitHub UI or API
- Webhook calls from external systems
- Repository dispatch events from third-party integrations
Workflow orchestration
Once triggered, GitHub Actions processes your workflow:
Workflow parsing:
- Reads the YAML workflow file from
.github/workflows/ - Validates syntax and configuration
- Determines job dependencies and execution order
Runner allocation:
- Assigns appropriate runners (GitHub-hosted or self-hosted)
- Provisions clean virtual environments for each job
- Sets up required operating systems and software
Job execution and coordination
Parallel execution (default):
jobs:
lint: # Runs simultaneously
test: # Runs simultaneously
security-scan: # Runs simultaneously
Sequential execution (with dependencies):
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
test:
needs: build # Waits for build to complete
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
deploy:
needs: [build, test] # Waits for both jobs
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
Action execution within jobs
Each job executes its steps sequentially:
- Environment preparation: Runner setup and checkout
- Action resolution: Download and cache required actions
- Step execution: Run commands and actions in order
- Artifact handling: Save and share files between jobs
- Cleanup: Tear down environment and release resources
Results and feedback
Upon completion, GitHub Actions provides comprehensive feedback:
Status reporting:
- Individual step success/failure indicators
- Job-level status and duration metrics
- Overall workflow status and summary
Notification integration:
- Email notifications for workflow failures
- Slack, Teams, or custom webhook integration
- Status checks on pull requests
Flow optimization strategies
Efficient job design
jobs:
# Fast feedback loop - run linting first
lint:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Lint code
run: npm run lint
# Resource-intensive jobs run in parallel
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
strategy:
matrix:
node-version: [18, 20, 22]
# Deploy only after all checks pass
deploy:
needs: [lint, test]
if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/main'
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
Conditional execution
Control workflow behavior based on context:
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
deploy-staging:
needs: build
if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/develop'
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
deploy-production:
needs: build
if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/main' && github.event_name == 'push'
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
This flow design ensures workflows are efficient, predictable, and provide clear feedback throughout the automation process.