Manage which updates are offered from Windows Update
Windows Update offers different types of updates, including feature updates and quality updates. As the admin for your organization, you want to control how these updates are provided to your devices.
In this unit, you'll learn about how to manage which updates are offered from Windows Update.
Understand feature updates
Microsoft releases a new feature update annually. By default, a device is not offered a feature update until the user looks for it (using the Check for updates option) on the Windows Update Settings page.
Additionally, if the feature update version the device is on is close to its end of service (EOS), the device will be offered a new feature update. Commercial customers, however, can specify which feature update they want and when they want it to be offered to the device. In fact, you have a few different ways of doing so. First let's discuss how to use Microsoft Intune to select a feature release for deployment.
Select a feature release version
Open Microsoft Endpoint Manager, and select Devices.
Select a Windows version from the Feature update to deploy drop-down list box. For this scenario, you select Windows 10 20H2.
Note
Once you configure this setting, the Windows Update service receives and applies the setting within 10 hours. The next time the devices in the selected group(s) check for updates, they will begin receiving the specified Windows 10 feature update version.
Get access to pre-release feature updates
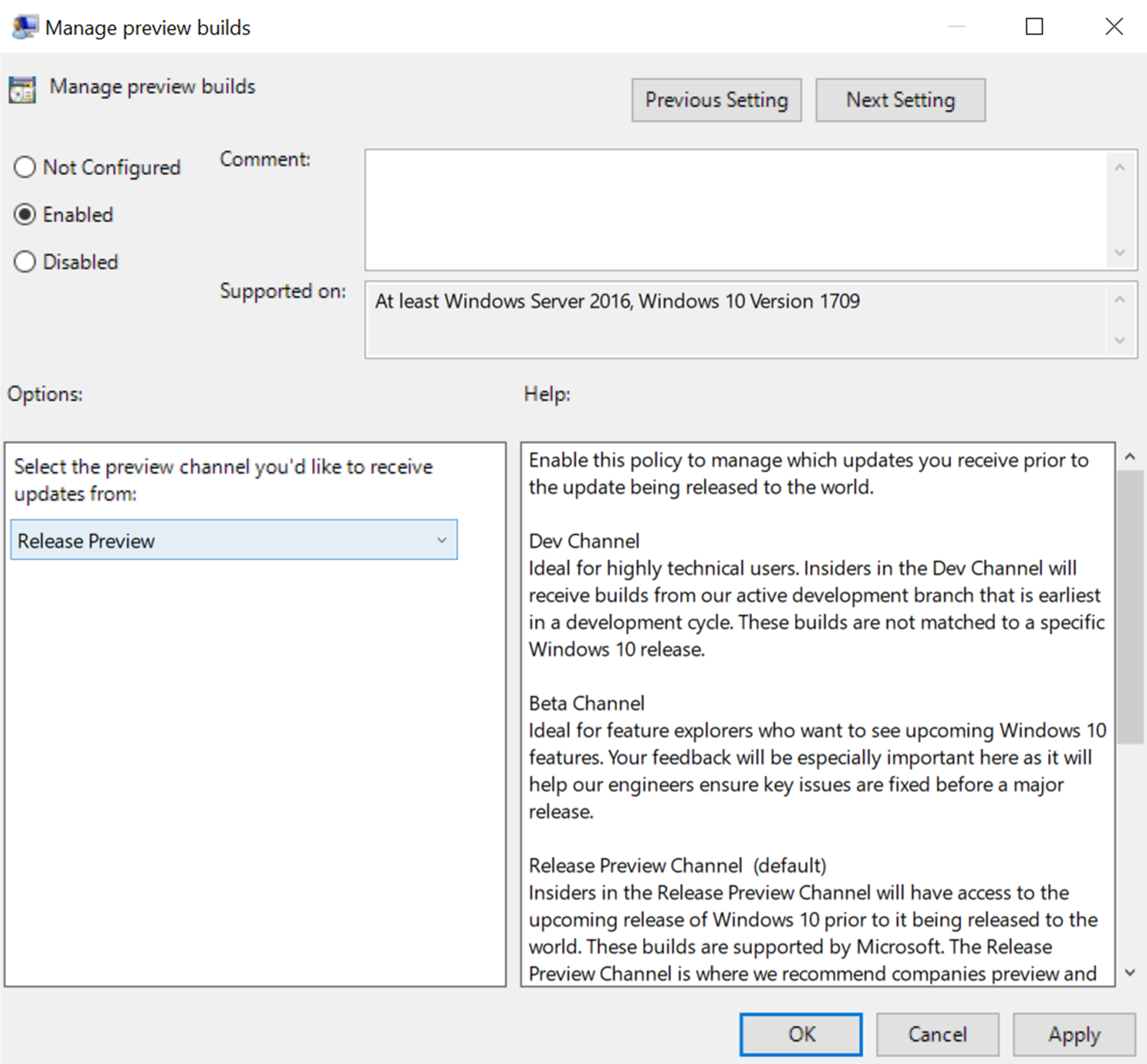
In addition to deploying a specific feature update, you can validate upcoming feature updates by enrolling some devices for Release Preview. To do this, you must first join the Windows Insider Program for Business; also see Get started with the Windows Insider Program. This will give you early access to the addressed issues and features that will be released soon. To receive the latest feature update before it's generally available, configure the following: For Group Policy, enable the Manage preview builds policy and specify when to receive preview builds and feature updates.
For configuration service provider (CSP), use the following policies:
Validating the preview release on at least 1% of the devices in your organization will help to increase your confidence about the upcoming feature update. You can report any problems you find for free to Microsoft's customer service representatives or the Feedback Hub so that they fixed before release.
Defer a feature update deployment
The final control you have over feature updates is a deferral. After Microsoft releases a new feature update, a deferral setting specifies how long to wait before the feature update is offered to a group of devices. The deferral days can range from zero to 365. You can also pause a feature update deployment if one of the groups encounters an issue during the deployment. A pause can last for up to 35 days from the specified start date or until you remove the policy. By using deferrals (and pausing), administrators can build an update process that gives them the necessary control and risk management without the overhead of managing updates individually. To configure deferrals:
- Open Microsoft Endpoint Manager, and select Devices.
- In the Feature update deferral period (days) box, type the numbers of days (0-365 days).
Warning
Ensure that you are not configuring Target Release Version (Feature Update Preview) and Feature Update Deferrals. If you do, you will not deploy the version you specified until you reach the number of deferral days.
Control driver updates
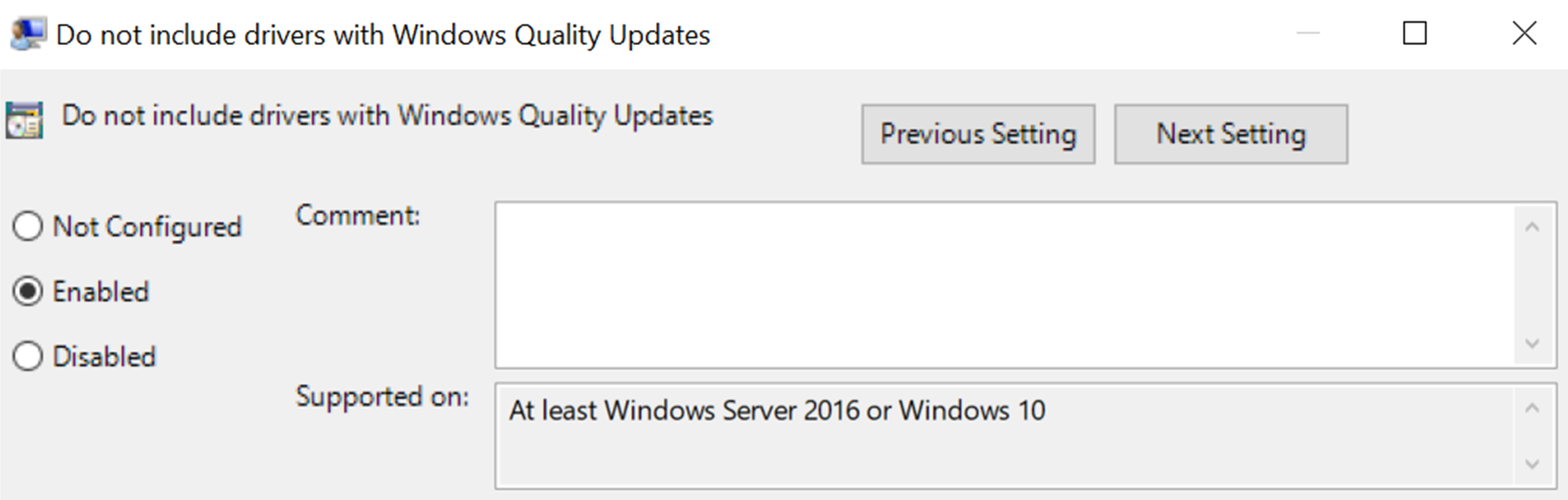
By default, driver updates automatically deploy to devices; we recommend that you leave automatic driver update deployment turned on. However, you can turn them off in one of the following ways:
Group Policy: Enable the Do not include drivers with Windows quality updates policy.
CSP: Configure the Update/ExcludeWUDriversInQualityUpdate policy.
Manage other Microsoft product updates
Windows Update for Business only offers Windows updates to devices. Updates for other Microsoft products do not deploy automatically. These products include applications like Visual Studio and Microsoft Edge. To manage updates for these kinds of products, do one of the following:
- On the Configure Automatic Update Group Policy template page, check the Install updates for other Microsoft products box.
- Configure the Update/AllowMUUpdateService CSP policy to 1 (Allow).
Use update rings
The number of groups you have and who is in the various groups will vary by size and type of organization, but there are some best practices you can keep in mind as you think about how to group and rollout to various devices within your organization. There are two key factors to grouping devices:
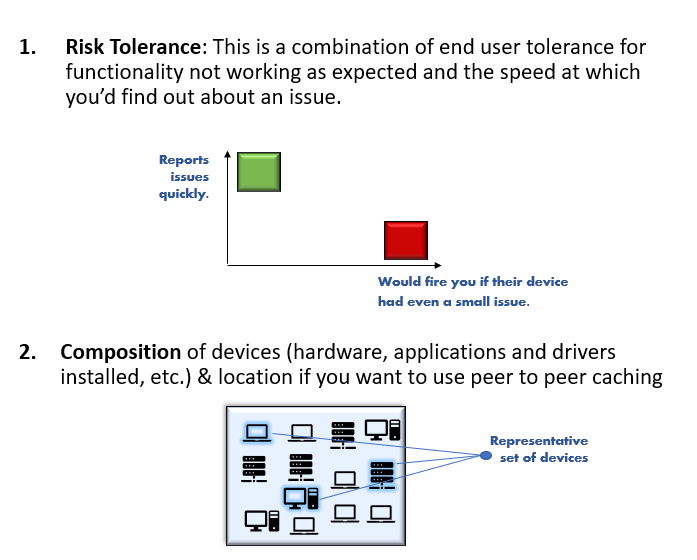
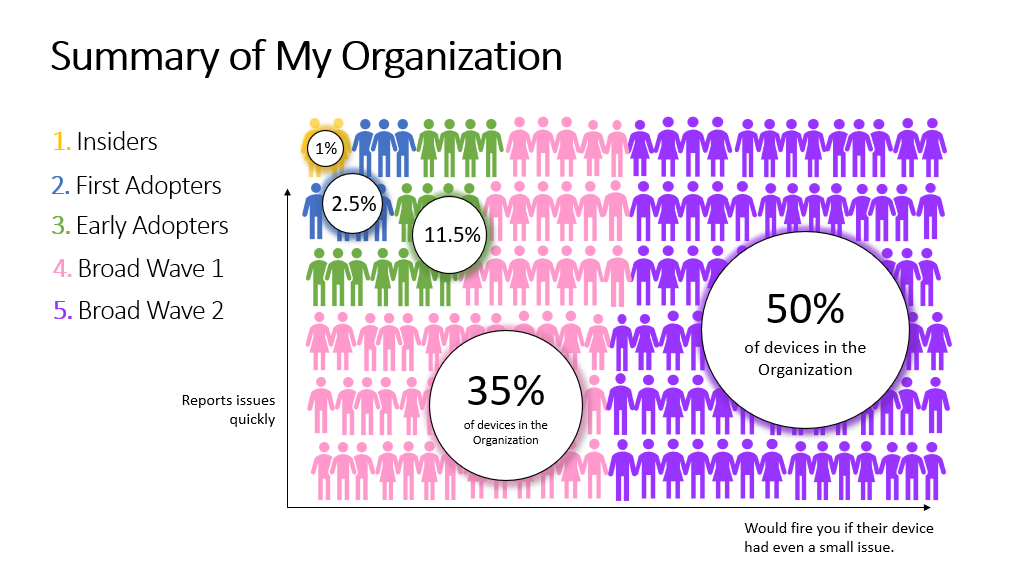
Risk tolerance can also be based upon device type such as airplanes, ATMs, or other machines that cannot be taken offline due to the critical nature of the job they perform. Let's take a look at an example organization with 54,000 employees running a variety of hardware, apps, etc. in various buildings.
- Yellow: There is an insider group of IT Admins and a representative set of devices used by tech friendly folks.
- Blue: A representative set of devices used by tech friendly folks across the organization in multiple locations with a high risk tolerance.
- Green: People with a medium risk tolerance.
- Pink, Purple: The broad deployment waves.
Note
For quality updates you may need fewer groups. For example, you may want to combine the early adopters and broad wave.