Create a datastore
In Azure Machine Learning, datastores are abstractions for cloud data sources. They encapsulate the information needed to connect to data sources, and securely store this connection information so that you don’t have to code it in your scripts.
The benefits of using datastores are:
- Provides easy-to-use URIs to your data storage.
- Facilitates data discovery within Azure Machine Learning.
- Securely stores connection information, without exposing secrets and keys to data scientists.
When you create a datastore with an existing storage account on Azure, you have the choice between two different authentication methods:
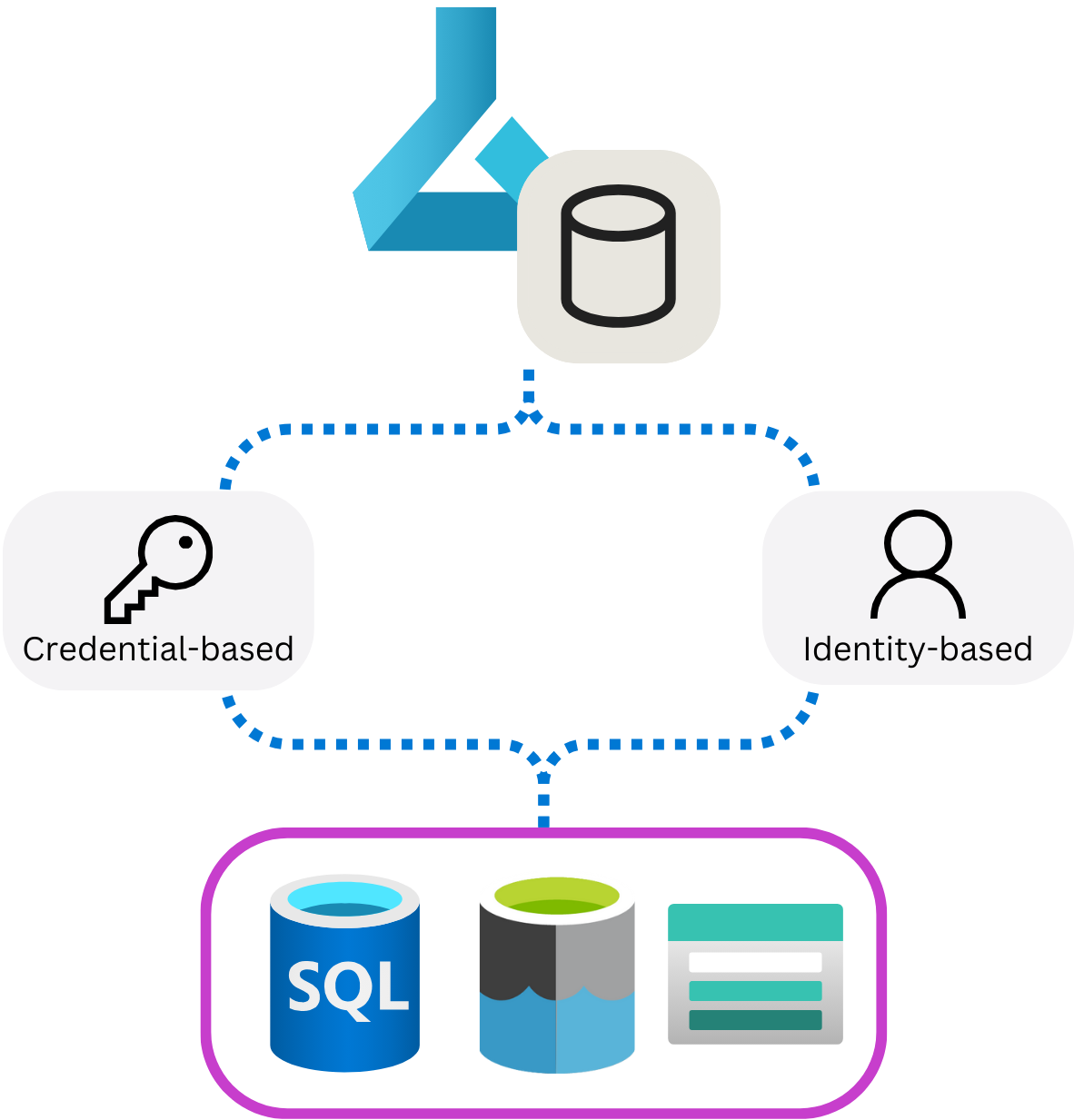
- Credential-based: Use a service principal, shared access signature (SAS) token or account key to authenticate access to your storage account.
- Identity-based: Use your Microsoft Entra identity or managed identity.
Understand types of datastores
Azure Machine Learning supports the creation of datastores for multiple kinds of Azure data source, including:
- Azure Blob Storage
- Azure File Share
- Azure Data Lake (Gen 2)
Use the built-in datastores
Every workspace has four built-in datastores (two connecting to Azure Storage blob containers, and two connecting to Azure Storage file shares), which are used as system storages by Azure Machine Learning.
In most machine learning projects, you need to work with data sources of your own. For example, you can integrate your machine learning solution with data from existing applications or data engineering pipelines.
Create a datastore
Datastores are attached to workspaces and are used to store connection information to storage services. When you create a datastore, you provide a name that can be used to retrieve the connection information.
Datastores allow you to easily connect to storage services without having to provide all necessary details every time you want to read or write data. It also creates a protective layer if you want users to use the data, but not connect to the underlying storage service directly.
Create a datastore for an Azure Blob Storage container
You can create a datastore through the graphical user interface, the Azure command-line interface (CLI), or the Python software development kit (SDK).
Depending on the storage service you want to connect to, there are different options for Azure Machine Learning to authenticate.
For example, when you want to create a datastore to connect to an Azure Blob Storage container, you can use an account key:
blob_datastore = AzureBlobDatastore(
name = "blob_example",
description = "Datastore pointing to a blob container",
account_name = "mytestblobstore",
container_name = "data-container",
credentials = AccountKeyConfiguration(
account_key="XXXxxxXXXxXXXXxxXXX"
),
)
ml_client.create_or_update(blob_datastore)
Alternatively, you can create a datastore to connect to an Azure Blob Storage container by using a SAS token to authenticate:
blob_datastore = AzureBlobDatastore(
name="blob_sas_example",
description="Datastore pointing to a blob container",
account_name="mytestblobstore",
container_name="data-container",
credentials=SasTokenConfiguration(
sas_token="?xx=XXXX-XX-XX&xx=xxxx&xxx=xxx&xx=xxxxxxxxxxx&xx=XXXX-XX-XXXXX:XX:XXX&xx=XXXX-XX-XXXXX:XX:XXX&xxx=xxxxx&xxx=XXxXXXxxxxxXXXXXXXxXxxxXXXXXxxXXXXXxXXXXxXXXxXXxXX"
),
)
ml_client.create_or_update(blob_datastore)
Tip
Learn more about how to create datastores to connect to other types of cloud storage solutions.