Use Azure Arc to manage Windows Server instances
After you have onboarded a Windows Server to Azure Arc, you can use Azure to manage and configure the machine. Some of the available functions are described in the following table.
Option
Explanation
Overview
Enables you to review basic information about the VM, including status, location, subscription, computer name, operating system, and tags.
Activity log
Enables you to review a list of activities performed against the VM, and by whom the event was performed.
Access control
Enables you to review and manage access to Azure resources for users, groups, service principals. and managed identities at this scope by creating role assignments.
Tags
Name/value pairs that enable you to categorize resources.
Extensions
Enables you to add and remove extensions for the VM.
Policies
Enables you to add, configure, and remove policies for the VM.
Update management
Enables you to maintain consistent control and compliance of the VM with Update Management.
Change Tracking and Inventory
Enables you to review change tracking and inventory configuration for the VM. Change Tracking and Inventory help to enable consistent control and compliance of your resources.
Insights
Enables you to use Azure Monitor to review host CPU, disk, and up/down state of your Azure Arc VMs.
Logs
Enables you to run queries against logs to gather information about the VM.
Manage extensions
.VM extensions are small apps that provide post-deployment configuration and automation tasks on Azure VMs. For example, if Contoso required that a VM needed some new software to be installed, or wanted to enable antivirus protection, or IT staff needed to run a script inside of the VM, they could use a VM extension. Azure Arc for servers enables you to deploy Azure VM extensions to both non-Azure Windows and Linux VMs; this can help to simplify management of those computers.
VM extensions can be managed from the Azure portal or using Azure CLI, Azure PowerShell, and Azure Resource Manager templates. You can add the extensions listed and described in the following table, to an Azure Arc VM.
Extension
Additional information
Microsoft Defender for Cloud integrated vulnerability scanner
.Qualys
Microsoft Antimalware extension
Microsoft.Azure.Security
Custom Script extension
Microsoft.Compute.
Log Analytics agent
Microsoft.EnterpriseCloud.Monitoring
Azure Monitor for VMs
Microsoft.Azure.Monitoring.DependencyAgent
Azure Key Vault Certificate Sync
Microsoft.Azure.Key.Vault
Azure Monitor Agent
Microsoft.Azure.Monitor
Azure Automation Hybrid Runbook Worker extension
Microsoft.Compute
Govern with Azure Policy
Azure Policy is a service that can help organizations to manage and evaluate compliance for their Microsoft Azure environment's organizational standards. Azure Policy uses declarative rules based on properties of target Azure resource types. These rules form policy definitions, which administrators can apply through policy assignment to a scope such as an individual Azure resource, resource group, subscription, or management group.
For example, to simplify management of policy definitions, Contoso could consider combining multiple policies into initiatives, and then create a few initiative assignments in lieu of multiple policy assignments.
Azure Policy functionality can be grouped into four main categories:
- Enforcing compliance when provisioning new Azure resources
- Auditing compliance of existing Azure resources
- Remediating non-compliance of existing Azure resources
- Auditing compliance of the OS, application configuration, and environment settings within Azure VMs
Tip
The last of these categories is implemented by using the Azure Policy Guest Configuration client, which is available as an Azure VM extension. Azure Arc for servers leverages the same client to provide the auditing functionality in hybrid scenarios.
Specifically, Contoso could use Azure Policy with Arc-enabled servers to implement the following rules:
- Assigning tags to machines during their deployment to Azure Arc
- Deploying the Log Analytics extension to non-Azure machines
- Identifying Arc-enabled servers without Microsoft Defender enabled
Azure Arc allows you to extend Azure Policy’s governance to servers and clusters running in on-premises datacenters or hosted by third-party cloud providers. This functionality applies to auditing compliance of settings for the OS, applications, and environment.
Note
Enabling this functionality requires that the Azure Connected Machine agent be installed on each computer in the scope of management.
After you install the agent, it requires outbound connectivity to Azure Arc over Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port 443. At that point, any Azure Policy Guest Configuration client-based configuration included in the assigned policy or initiative definition will automatically take effect.
In particular, Contoso could use the [Preview] Audit Windows VMs that do not match Azure security baseline settings policy initiative to audit compliance against Azure Security Center baselines. They also have the ability to set the time zone on target servers by assigning the policy definition [Preview] Configure time zone on Windows machines. When auditing target computers, Contoso would have the option of reviewing the logs either locally or remotely via the Azure VM Run command, which is available from the Azure portal.
Note
To identify whether a particular policy definition supports Azure Policy Guest Configuration client, you must determine whether it includes a reference to the Microsoft.HybridCompute/machines resource type.
Assign Azure Arc policies
To manage and assign Azure Arc policies for a computer:
From the Azure portal, navigate to Azure Arc, and then select Manage servers.
From the returned list of managed servers, select the appropriate server, and then in the navigation pane, under Operations, select Policies.
To assign a policy, on the toolbar, select Assign policy.
On the Assign policy page, select the following information:
- Scope and any exclusions from the scope of the policy
- Policy definition.
- Assignment name.
- Description.
- Policy enforcement (Enabled or Disabled)
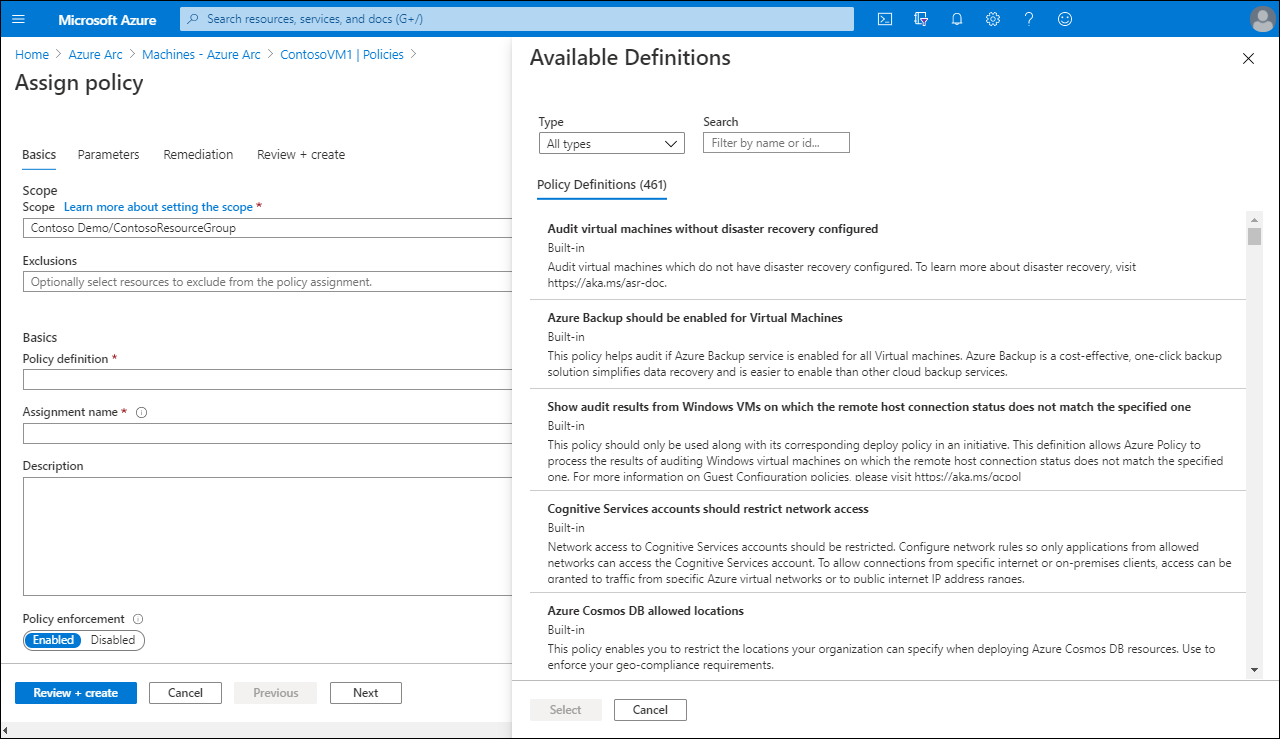
Select either Review + create, or the Parameters and Remediation tabs to configure additional behaviors.
After you have assigned policies, from the Azure Arc homepage, on the selected VM, you can review the policy settings.
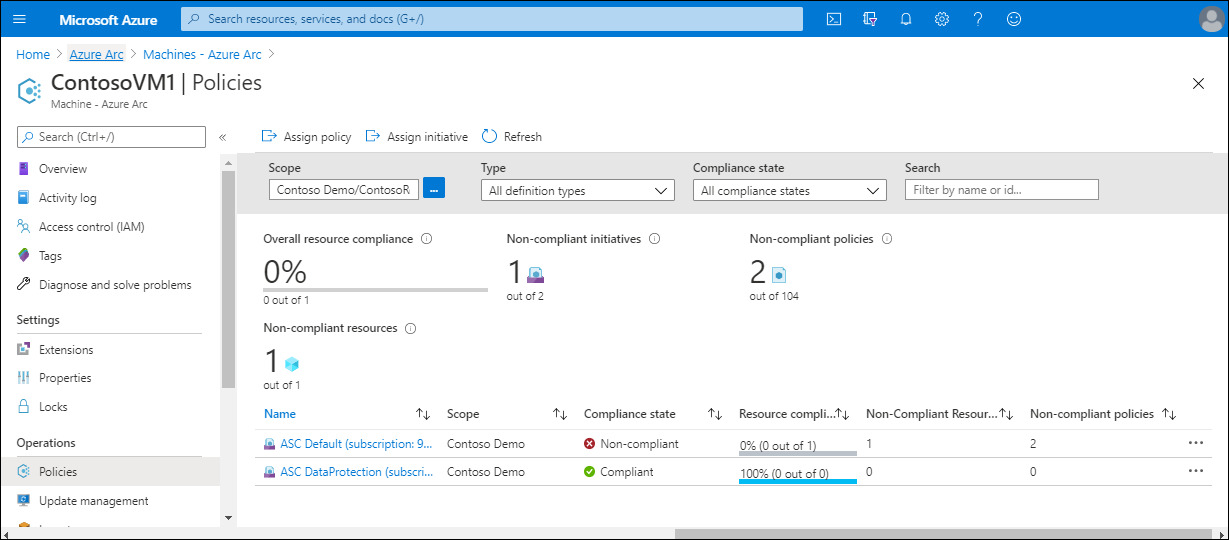
Additional reading
You can learn more by reviewing the following documents.