Explore Transparent Data Encryption
Microsoft SQL Server’s Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) encrypts all data within a target database at the page level. Data is encrypted as it's written to the data page on disk and decrypted when read into memory, resulting in all data pages on disk being encrypted.
TDE doesn't encrypt data at the table or column level. Anyone with the appropriate permissions can read, copy, and share the data. Encryption at rest protects against restoring a backup to an unsecured server or copying database and transaction log files to another unsecured server. No decryption occurs during the backup operation.
TDE protects data at rest and complies with various industry laws, regulations, and guidelines. It allows software developers to encrypt data using AES and 3DES encryption algorithms without changing existing applications.
Databases created in Azure SQL Database after May 2017 have TDE enabled automatically. Databases created before May 2017 need TDE to be manually enabled. For Azure SQL Managed Instance, TDE is enabled by default for databases created after February 2019. Databases created before February 2019 need TDE to be manually enabled.
To enable TDE in an Azure SQL Database, edit the database in the Azure portal. From the Transparent data encryption pane, select to enable data encryption.
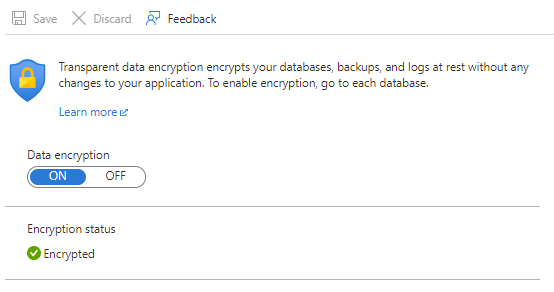
By default, databases in Azure SQL Database are encrypted using a Microsoft-provided certificate (service-managed key). Azure also offers a Bring Your Own Key (BYOK) option, allowing you to use a customer-managed key created by your company and uploaded to Azure Key Vault. If the customer-managed key is removed from Azure, database connections are closed, and access to the database are denied.
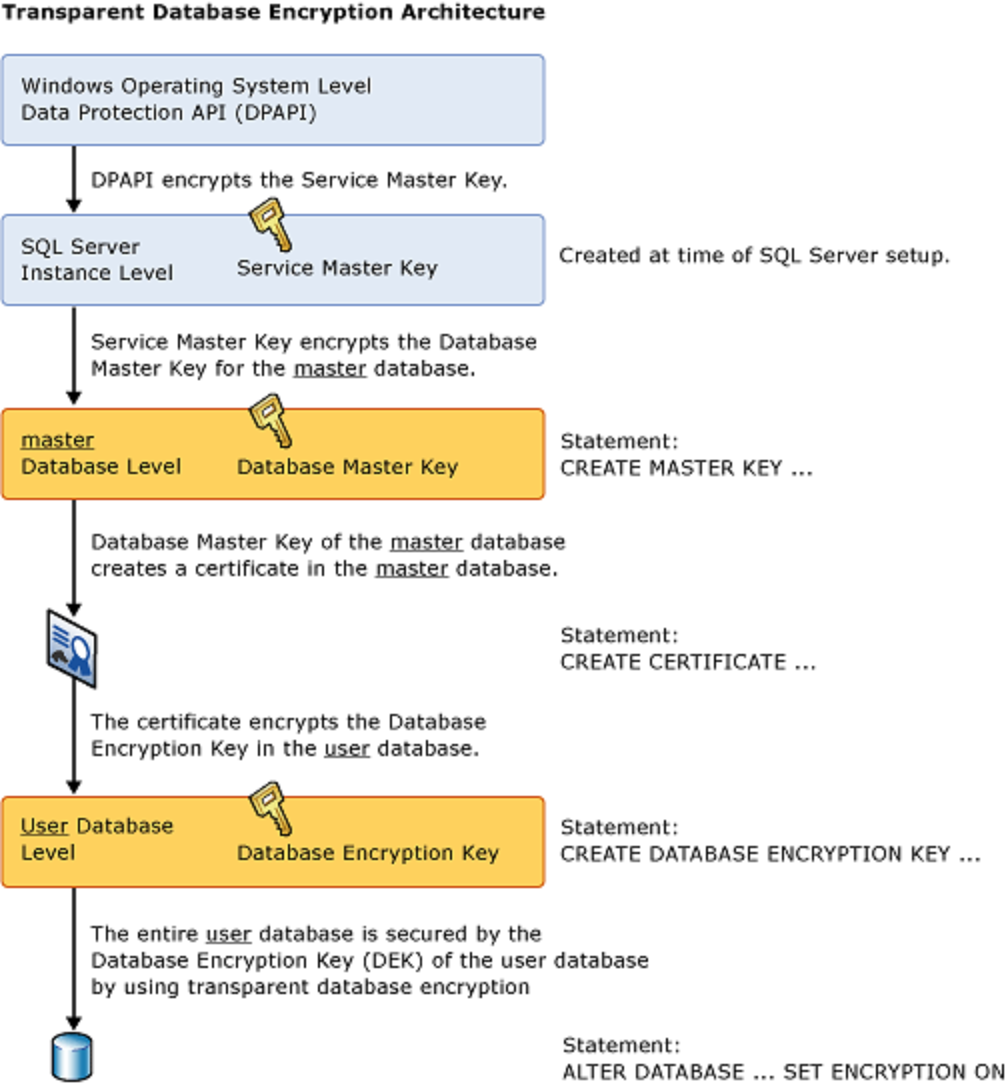
Enabling TDE within a Microsoft SQL Server database is an easy process as only a few T-SQL commands are required. This process involves the following steps:
- Set a master key within the master database using the
CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTIONcommand. - Create a certificate in the master database using the
CREATE CERTIFICATEcommand. - Create a database encryption key within the database using the
CREATE DATABASE ENCRYPTION KEYcommand. - Enable the encryption key using the
ALTER DATABASEcommand.
USE master;
GO
CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = '<your-pwd>';
GO
CREATE CERTIFICATE MyServerCert
WITH SUBJECT = 'TDEDemo_Certificate';
GO
USE [TDE_Demo];
GO
CREATE DATABASE ENCRYPTION KEY
WITH ALGORITHM = AES_256 ENCRYPTION BY SERVER CERTIFICATE MyServerCert;
GO
ALTER DATABASE TDE_Demo SET ENCRYPTION ON;
GO
Once TDE is enabled, it takes time to encrypt the database as each page must be read, encrypted, and written back to disk. The larger the database, the longer this process takes. This background process runs at a low priority to avoid overloading the system's I/O or CPU.
The certificate used by TDE must be manually backed up and stored securely. SQL Server integrates with Enterprise Key Managers (EKMs) like Azure Key Vault to manage encryption keys. Managing the certificate is crucial because if it's lost and the database needs to be restored from a backup, the restore fails as the database can't be read.
Note
To use TDE with databases in an Always On Availability Group, the certificate used to encrypt the database must be backed up and restored to the other servers within the Availability Group that will be hosting copies of the database.
Customer-managed keys
You can alternately use BYOK and take advantage of an Azure key vault. The advantages of using customer-managed keys are:
- Full and granular control over usage and management of the TDE protector
- Transparency of the TDE protector usage
- Ability to implement separation of duties in the management of keys and data within the organization
- The key vault administrator can revoke key access permissions to make encrypted database inaccessible
- Central management of keys in AKV
- Greater trust from your end customers because AKV is designed so that Microsoft can't see or extract encryption keys
You can also take advantage of using a user-assigned managed identity (UMI) with customer-managed keys for TDE, which:
- Enables the ability to preauthorize key vault access for Azure SQL logical servers by creating a user-assigned managed identity and granting it access to key vault, even before the server or database are created.
- Allows creation of an Azure SQL logical server with TDE and CMK enabled.
- Enables the same user-assigned managed identity to be assigned to multiple servers, eliminating the need to individually turn on system-assigned managed identity for each Azure SQL logical server and providing it access to key vault.
- Provides the capability to enforce CMK at server creation time with an available built-in Azure policy.
Automatic key rotation are introduced for customer-managed keys using TDE. When enabled, the server continuously checks the key vault for any new versions of the key being used as the TDE protector. If a new version of the key is detected, the TDE protector on the server is automatically rotated to the latest key version within 60 minutes.
Azure disk encryption
In addition to these SQL Server security features, Azure VMs include an extra layer of security, Azure Disk Encryption—a feature that helps protect and safeguard data and meet organization and compliance commitments. If you're using TDE, your data is protected by multiple layers of encryption with Azure Disk Encryption.