Enable encrypted connections
It's possible to encrypt data that is transmitted across a network between an instance of SQL Server and a client application with Transport Layer Security (TLS). The TLS encryption is performed within the protocol layer and is available to all supported SQL Server and Azure SQL database services.
Certificates
You must run SQL Server Configuration Manager with a local administrator account in order to install certificates for use by SQL Server.
Furthermore, the certificate must satisfy the following conditions:
The certificate must be located in the local computer certificate store or the current user certificate store.
The SQL Server service account must have permission to access the certificate.
The certificate must be within a valid period.
Note
If the correct access isn't provided, restarting SQL Server service fails.
For a complete list of requirements when installing a TLS certificate, see Enable encrypted connections to the Database Engine.
Configure SQL Server instance
You can configure a SQL Server instance to use encrypted connections by following these steps:
On the SQL Server Configuration Manager, expand SQL Server Network Configuration, right-click Protocols for <server instance>, and then select Properties.
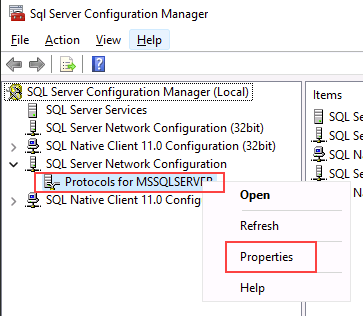
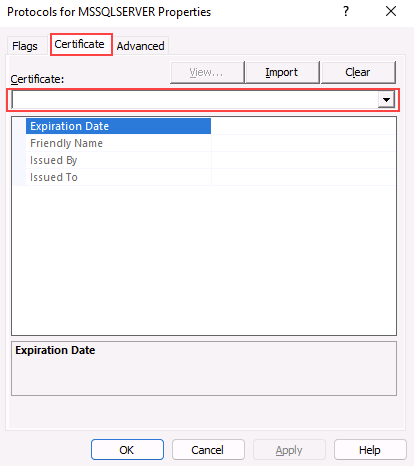
From the Protocols for <server instance> Properties dialog box, select the Certificate tab, then select the certificate from the Certificate drop-down.
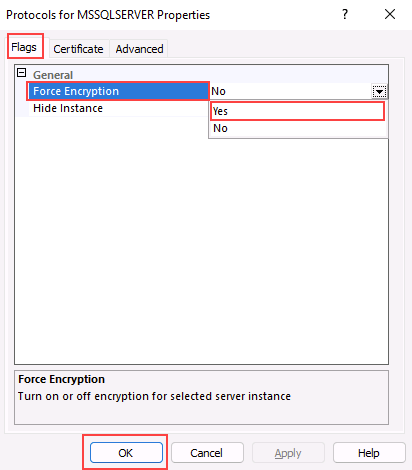
On the Flags tab, in the ForceEncryption property, select Yes, and then select OK.
Restart the SQL Server service.
Once the necessary configuration is in place, you can test the connection through SQL Server Management Studio:
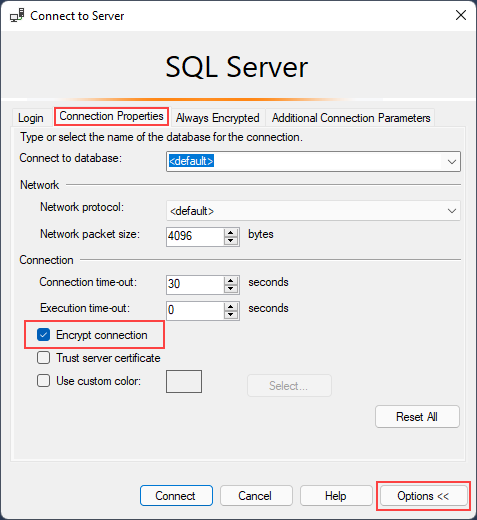
In the Connect to Server dialog box, complete the connection information, and then select Options.
On the Connection Properties tab, select Encrypt connection, and then Connect.
All steps must have been executed correctly for you to be able to authenticate through SQL Server Management Studio using TLS.