Understand Azure Key Vault
Azure Key Vault is a tool used for storing and accessing secrets. Whether they be passwords, certificates or keys, Key Vault acts as a secure area for those secrets to be accessed in a secure fashion, typically programmatically. Key Vault data has its own RBAC policies, separate from the Azure subscription. This means someone who is in the role of subscription admin won't have access to the Key Vault unless explicitly granted.
SQL Server, either within an Azure Virtual Machine or on-premises, supports using Azure Key Vault to store certificates for features such as Transparent Data Encryption, Backup Encryption, or Always Encrypted. While this configuration is complex in an on-premises environment, it's easily managed when using SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machine, as shown in the following image.
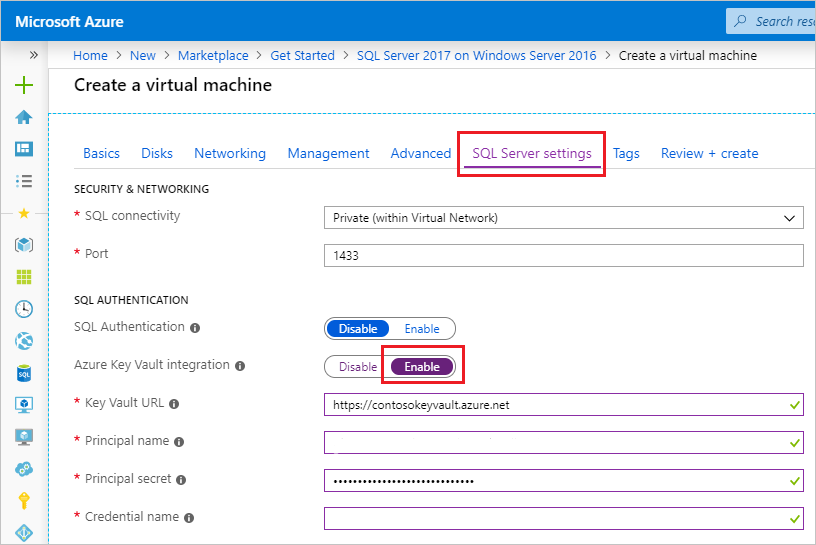
In order to configure the Azure Key Vault integration, you need to set the Key Vault URL, the Principal name, the Principal secret, and the name of the credential. This task can be done at the virtual machine creation or to an existing VM.
Configuring SQL Server to connect to Azure Key Vault first requires creating a normal SQL Server login within the instance. Next a Credential needs to be created and mapped to the login. For the identity of the credential, the name of the key vault should be used. For the secret of the credential, use the application ID from Azure Key Vault.
Once the credential is created, an asymmetric key can be created within the Azure Key Vault. An asymmetric key can then be created within the SQL Server database. The key in database can be mapped to the Azure Key Vault asymmetric key using the CREATE ASYMMETRIC KEY command with the FROM PROVIDER syntax. Once an asymmetric key is created within the database, that key can be used for TDE, or Backup Encryption or Always Encrypted.