Azure Remote Rendering overview
Three-dimensional visualization is important in scenarios where every detail matters, such as:
- Industrial plant management.
- Design review for complex assemblies like truck engines.
- Preoperative surgery planning.
Bringing detail to life with 3D visualization can help designers, engineers, doctors, and students better understand complex information and make the right calls.
Decimation
Untethered virtual and mixed reality devices have limited computational power for rendering complex models. A traditional approach to viewing 3D content on untethered devices is decimation, which compresses the models and removes some polygons. Decimation simplifies the model enough so it can run on slower GPU hardware.
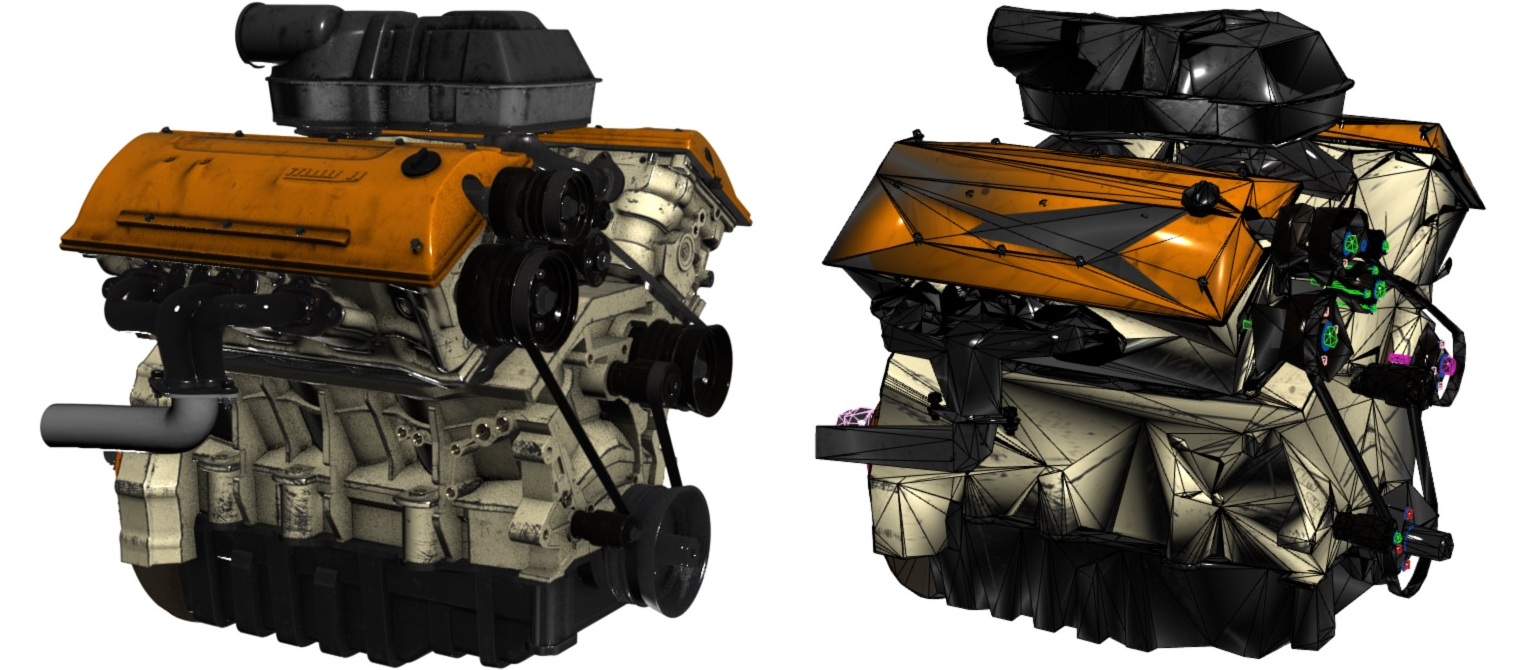
The preceding illustration shows a side-by-side comparison of an engine model at full detail and a decimated model. The reduced model consists of approximately 200,000 triangles, including the detailed inner parts, compared to more than 18 million triangles in the original model.
Azure Remote Rendering
Although reducing the quality or complexity of a model can help it render, this simplification can result in a loss of important detail that's needed to make key decisions. Azure Remote Rendering solves this problem by moving the rendering workload to high-end graphics processing units (GPUs) in the Azure cloud. A cloud-hosted graphics engine renders the image, encodes it as a video stream, and streams the image in real time to devices such as HoloLens 2. Users can both view and interact with the model.
Remote Rendering can render hundreds of millions of polygons and stream to mixed reality devices with low latency, reducing the need for decimation. When models are too complex for even high-end GPUs to render at interactive frame rates, Remote Rendering can distribute the workloads to multiple GPUs. The results are merged into a single image, making the process transparent to the user.
Remote Rendering sessions
To use Remote Rendering, you create a session, which allocates a server in Azure to render the model. When a client device connects, the server renders the requested data and serves the result as a video stream. The session shuts down automatically when its lease time expires, or you can stop it manually.
You choose the kind of server to run on, which determines pricing. Once a session is stopped, you aren't billed further. To learn more about pricing, see Remote Rendering pricing.