Describe task status notifications
A crucial part of automation is providing notifications for job failures or specific system errors. SQL Server Agent facilitates this through a set of objects, with alerting commonly done via email using SQL Server's Database Mail functionality. The key objects in this workflow are:
- Operators: Aliases for individuals or groups who receive notifications.
- Notifications: Inform an operator about the completion, success, or failure of a job.
- Alerts: Assigned to an operator for either a notification or a defined error condition.
Operators
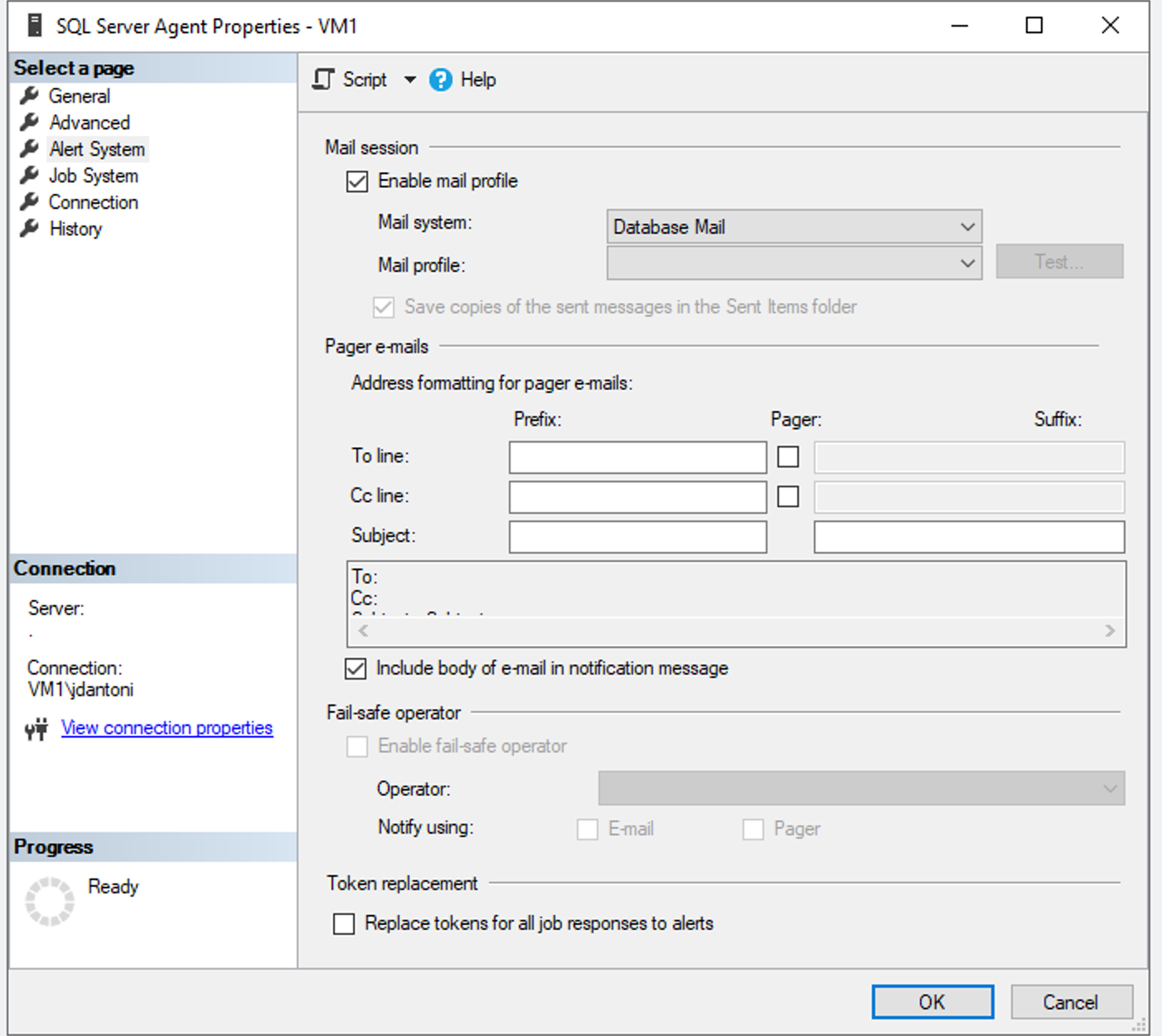
Operators act as aliases for users or groups configured to receive notifications of job completions or alerts from the error log. An operator is defined by a name and contact information, typically mapping to an email group. Using email groups provides redundancy, ensuring notifications aren't missed if someone is unavailable. It also simplifies updates when employees leave the organization. To send emails to an operator, you need to enable the SQL Server Agent's email profile, as shown below:
Notifications
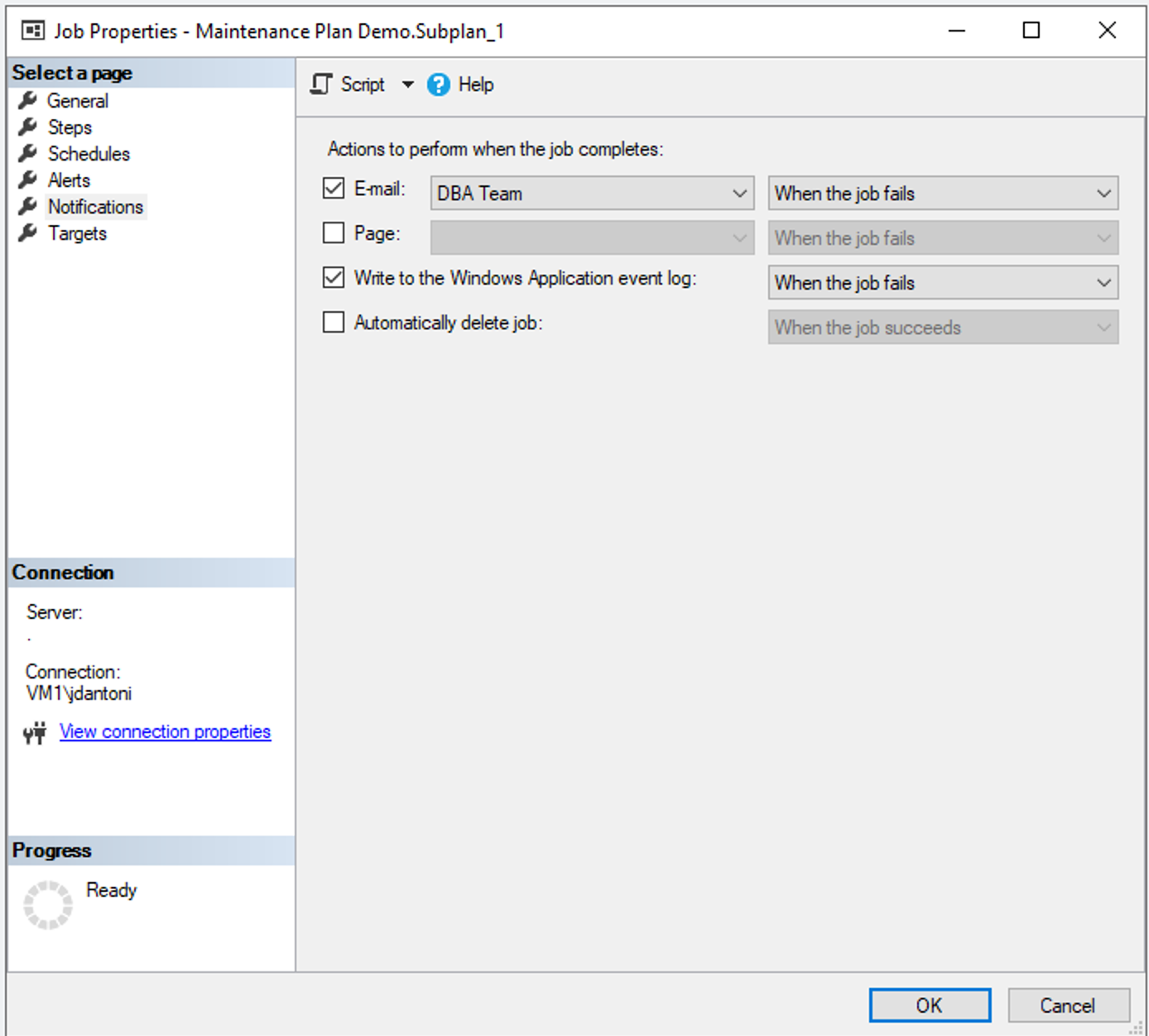
Notifications are part of each SQL Server Agent job. You can choose to send a notification on job completion, failure, or success. Most DBAs notify only on failure to avoid an influx of notifications for successful jobs. Notifications depend on an existing operator to send the alert.
Alerts
SQL Server Agent alerts enable proactive monitoring of your SQL Server. The agent reads the SQL Server error log and notifies an operator when it finds an error number for which an alert is defined. Besides monitoring the error log, you can set up alerts for SQL Server performance conditions and Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) events. You can specify alerts for one or more events. A common practice is to raise alerts for all SQL Server errors of level 16 and higher and add alerts for specific critical storage errors or Availability Group failovers. Another example is to alert on performance conditions like high CPU utilization or low Page Life Expectancy.
DBAs may also want to be notified of certain server conditions, such as CPU utilization over 90% for five minutes or low Page Life Expectancy. This is done by creating performance condition alerts based on Windows Performance Monitor (perfmon) metrics tracked within the SQL Server database engine. You can access the alert configuration screen by right-clicking SQL Server Agent (if it is running) and choosing New | Alert.
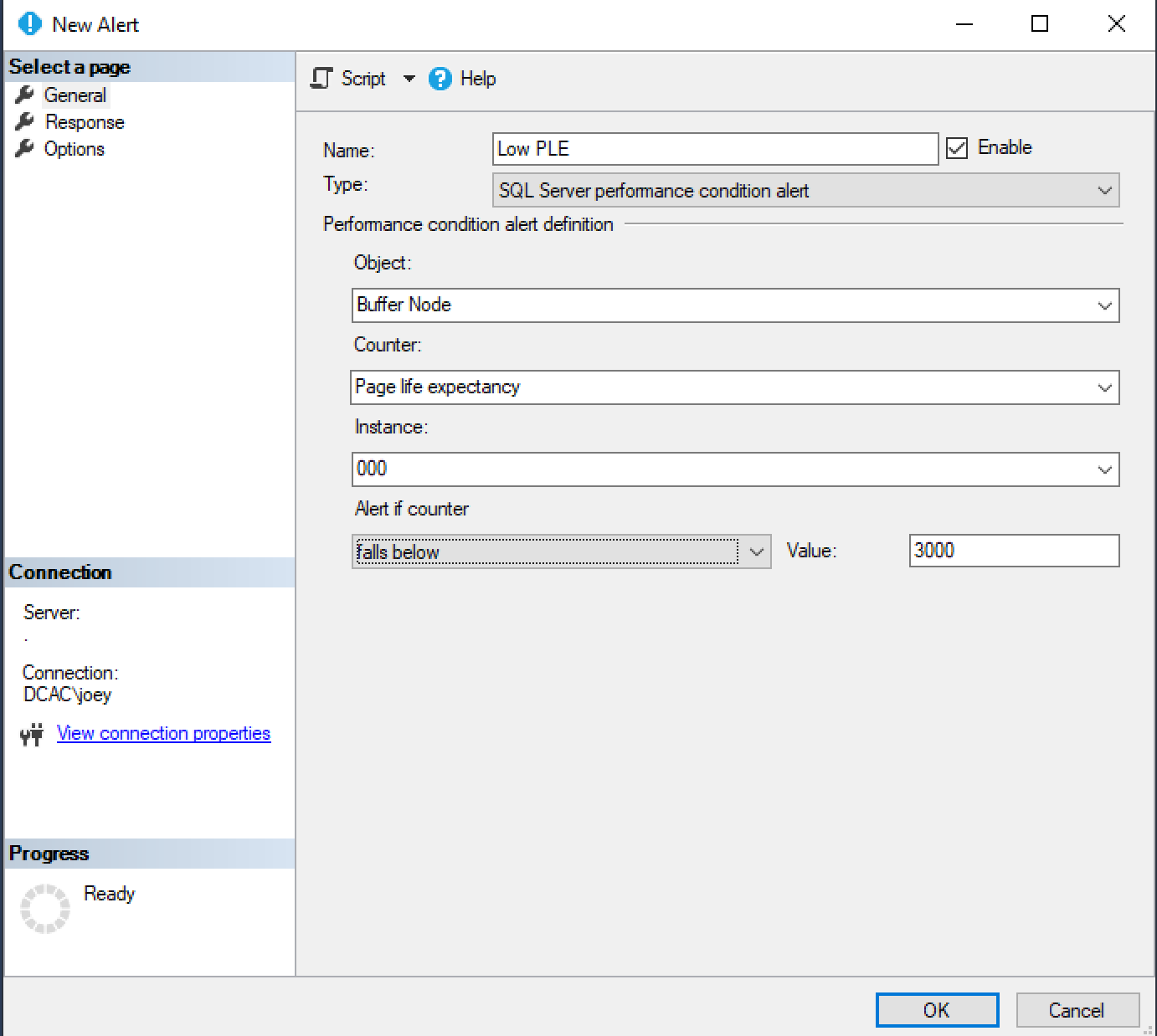
You have options for responding to performance conditions: notify an operator via email, which is the most common approach, or execute another SQL Server Agent job to resolve the issue. Executing another job is useful for well-known conditions that can be handled without manual intervention. For example, you could create an alert for SQL Server storage error conditions (errors 823, 824, 825) and execute a job to perform a database consistency check. Notifications for these alerts use the same SQL Server Agent subsystem.